Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Notes
Uploaded by
Mischi Jeda ElumbaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Notes
Uploaded by
Mischi Jeda ElumbaCopyright:
Available Formats
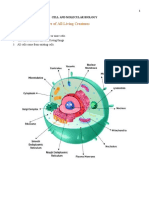
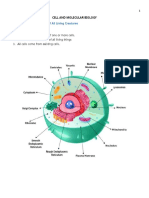
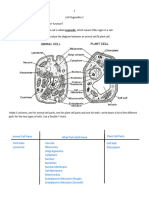
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
All cells are categorized between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Your common E.coli and other bacteria are prokaryotes — these organisms lack
nucleus in their cells.
Eukaryotes, on the other hand, are organisms with true nucleus like plants and
animals.
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, DNA,
ribosomes, and cytoskeletons
Prokaryotic Cells
Houses its genetic material in an
irregularly shaped region called
nucleoid.
Its ribosome (70S) is composed of
two subunits (50S and 30S) and 60%
RNA.
Found to have cytoskeletons
structural filaments that aids in cell
division and other cellular functions.
Reproduction occurs through binary
fission.
External Structures:
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells 1
Protection
Cell Wall: extra layer of protection usually made of peptidoglycan; also provides
shape and rigidity to prokaryotes.
Capsule: sticky layer composed of carbohydrates that aids the cell attach to
surfaces.
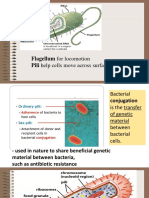
Locomotion
Flagella: whip-like structures responsible for bacterial motility by responding to
chemical gradients (protons) in the environment (chemotaxis).
Fimbriae: filamentous structures that are shorter than Pili helps the cell adhere
to surfaces.
Pili: fibrous proteins commonly found in bacteria; also used to transfer genetic
material during conjugation.
Eukaryotic Cells
Has true nucleus and membrane-
bounded organelles allowing
compartmentalization in the cell.
Its ribosome is larger than
prokaryotes and mostly made of
proteins (60%).
Cell division occurs in two major
steps: mitosis and cytokinesis.
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles (Common)
Mitochondria/Mitochondrion Lysosomes
Golgi Body/Apparatus/Complex Endoplasmic Reticulum
Vesicles
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells 2
Plants, Algae, and Fungi
Cell Wall: provides cell structure and prevents it from bursting due to pressure
plants: cellulose
algae: carrageenan
fungi: chitin
Vacuole: a membrane-bound sac present in most plant cells that maintains the
water pressure in the cell wall.
Chloroplast: the organelle responsible for photosynthesis.
granum
thylakoid
stroma
Animals
Centrioles: cylindrical paired organelles in the cytoplasm that aids the cell
during cell division by producing spindle fibres.
Flagella: whip-like extensions of the cell membrane that is primarily responsible
for cell movement and is driven by ATP
Cilia: numerous hair-like structures around the cell that helps in cell movement
(motile cilia) and acts as sensory organelles (nonmotile cilia).
Summary
Features Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell
Nucleus No nuclear membrane True nucleus
Membrane-bound Present: mitochondria, golgi body,
Absent
organelles lysosomes, vesicles, RER, SER
Flagella Simple; proton driven Complex; ATP driven
Complex; made of Simple; made of cellulose, chitin, or
Cell wall
peptidoglycan carrageenan
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells 3
Features Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell
Ribosomes Smaller; mostly made of RNA Larger; mostly made of proteins
Cell division Binary fission Mitosis and Cytokinesis
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells 4
You might also like
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureDocument31 pagesDokumen - Tips - Cell Structure Functions Introduction Eucaryotic Cell StructureJairra Jae LunaNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeDocument40 pagesMrs. Anamika Sahu GulbakeAnamika SahuNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- 2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsDocument37 pages2 Biology 1 - 2 - 07 Pro Vs Eu CellsJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Cell Organelles GuideDocument43 pagesCell Organelles GuideMariam Qais100% (1)
- Classification and evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsDocument7 pagesClassification and evolution of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cellsjodeoiraluis josonNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument21 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup Penyusun Mahluk HidupYunita RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology BasicsDocument17 pagesCell Biology BasicsHizzei Caballero100% (3)
- Acfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4Document8 pagesAcfrogahwtgjhymcdbhqd9juy0ihb5dgzqyobwgygm44pyrxkeh Dixuo Odyslryl Jpqgjhd4udt63zm6ot2mgudp GWKKKDFLLJD 4nxfp5i Pvcee 9pyuxltmliuwhn9qmanxfhy82jt1l4s20003No ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and Taxonomyporkypig100% (11)
- Cell Structure ComparisonDocument29 pagesCell Structure ComparisonChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument29 pagesCell TopicChynna PorneteNo ratings yet
- NeucleDocument25 pagesNeucleUjala SinghNo ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic CellDocument23 pagesProkaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic CellEleonor DistrajoNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument56 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupYahya RhamadanNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesCell (Biology) - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaapi-3714451100% (2)
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- The Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeDocument45 pagesThe Cell - The Basic Unit of LifeMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document14 pagesCell (Biology)gigiuobohoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument50 pagesCell Structure and TaxonomyCarl Elexer Cuyugan AnoNo ratings yet
- Introduction CellDocument48 pagesIntroduction CellabdNo ratings yet
- Understanding the Structures and Functions of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument21 pagesUnderstanding the Structures and Functions of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsrinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction and Pioneers in Microbiology and ParasitologyJasmin Pearl AndayaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Organelles ExplainedDocument48 pagesCell Structure and Organelles ExplainedNatalie GraceNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byDocument11 pagesRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byKamlesh RatnamNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument50 pagesThe Cellular Basis of LifeSteve EstebanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ActivityDocument4 pagesCell Structure ActivitysharksiedNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM Biotechnology (BT) Sample TheoryDocument55 pagesIIT-JAM Biotechnology (BT) Sample TheorysonamNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology)Document4 pagesCell (Biology)Marella SatorreNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document17 pagesLecture 1Zunaira IhsanNo ratings yet
- Flagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesDocument18 pagesFlagellum For Locomotion Pili Help Cells Move Across SurfacesEvangeline WongNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument92 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFAishaizl100% (1)
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TextDocument54 pagesBiochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TexttNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles and Their FunctionsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- General Biology: System Consists of TheDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology: System Consists of ThePhilipp MendozaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument6 pagesComparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesProkaryotes vs Eukaryotes Structures and FunctionsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Cells F05Document31 pagesCells F05Fetro Dola SyamsuNo ratings yet
- 2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelDocument56 pages2022-1-Tinjauan Umum Sel - Struktur SelVe LinNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument10 pagesCELLMAAYER MUHAMMADNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2Document8 pagesKami Export - Rishabh Roy - Cell Organelles 2bloomington369No ratings yet
- Prok A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsDocument31 pagesProk A Ryo Tic Eukaryotic CellsAMADO JR BANAWANo ratings yet
- 1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)Document46 pages1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells (Main)MeryemNo ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Hazards of Fire Residue RestorationDocument8 pagesUnderstanding The Hazards of Fire Residue RestorationKeeterjonesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Wool Spinning ProcessesDocument68 pagesPrinciples of Wool Spinning ProcessesCẩm Tú100% (1)
- Polymers 14 04269Document22 pagesPolymers 14 04269Athlur Sai KiranNo ratings yet
- Boax B PDFDocument20 pagesBoax B PDFSiapa PunNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question bp202tDocument5 pagesPrevious Year Question bp202tMONIKA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impacts of Oil Spills and Their Remediation by Magnetic NanomaterialsDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Impacts of Oil Spills and Their Remediation by Magnetic NanomaterialsrmvanginkelNo ratings yet
- Hvac Solid (Who)Document75 pagesHvac Solid (Who)KundzoNo ratings yet
- Redox Titration GuideDocument132 pagesRedox Titration GuideAnis SayyedNo ratings yet
- Y11A Cycle Test 9.2.23Document16 pagesY11A Cycle Test 9.2.23sharkeesha sharkeeshaNo ratings yet
- Q.1 The Major Product Formed in The Following Reaction IsDocument10 pagesQ.1 The Major Product Formed in The Following Reaction IsDoom RefugeNo ratings yet
- 17 Eh - PH - DiagramsDocument16 pages17 Eh - PH - DiagramsmercantjeduNo ratings yet
- Brunner-Emmett-Teller Theory: Presented By: Tehseen Zehra Uswa Zahra Muntaha Nasir Summayya ShafiqueDocument22 pagesBrunner-Emmett-Teller Theory: Presented By: Tehseen Zehra Uswa Zahra Muntaha Nasir Summayya ShafiqueSummayya ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Lab Report GCDocument18 pagesLab Report GCMohamad Saiful Mohd RaffiahNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Document9 pagesOrca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Mic Houston Mar T. ParroNo ratings yet
- Hnology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: CookeryDocument27 pagesHnology and Livelihood Education: Quarter 1 - Module 2: CookeryDomeng Karo100% (5)
- Simplifying Chemistry Volume OneDocument64 pagesSimplifying Chemistry Volume OneMoses MulengaNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Amino Acids: Function Follows FormDocument23 pagesProteins and Amino Acids: Function Follows FormbobNo ratings yet
- Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride: Safety Data Sheet 6162601Document7 pagesTrifluoromethanesulfonyl Chloride: Safety Data Sheet 6162601saravanaknNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18 - Isopropanol and Acetone From PropyleneDocument6 pagesLecture 18 - Isopropanol and Acetone From PropyleneRichardN55No ratings yet
- Data in BriefDocument10 pagesData in BriefeaeNo ratings yet
- OFFICE CONCEPT Milliken LVTStandard SDSDocument2 pagesOFFICE CONCEPT Milliken LVTStandard SDSKatyhuska NunezNo ratings yet
- Etulay Online Tutorial: Physical ScienceDocument39 pagesEtulay Online Tutorial: Physical ScienceTara SantosNo ratings yet
- Delhi Milk SchemeDocument12 pagesDelhi Milk Schemeank29jplease67% (3)
- Material Characterization of Sugarcane Bagasseepoxy Composites For - 2022Document5 pagesMaterial Characterization of Sugarcane Bagasseepoxy Composites For - 2022bakhrul ilmiNo ratings yet
- Gas Sweetening Simulation and Its Optimization by Two Typical AmineDocument8 pagesGas Sweetening Simulation and Its Optimization by Two Typical AmineYogesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Raman - Spectroscopy - Identification of Cocaine and Other Illegaldrugs of AbuseDocument11 pagesRaman - Spectroscopy - Identification of Cocaine and Other Illegaldrugs of AbuseGustavo SánchezNo ratings yet
- A Method For Iron Determination During Copper Electrometallurgy ADocument88 pagesA Method For Iron Determination During Copper Electrometallurgy Amaría joséNo ratings yet
- FAO DiuronDocument9 pagesFAO DiuronmercuriusNo ratings yet
- Rotron Regenerative Blowers Catalog PDFDocument196 pagesRotron Regenerative Blowers Catalog PDFSolikin PatiNo ratings yet
- SN2 RXDocument25 pagesSN2 RXGebby FebriliaNo ratings yet