Professional Documents
Culture Documents
List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Fayeann Vedor LoriegaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
List All The Structures of Both Cell Types and Their Functions
Uploaded by
Fayeann Vedor LoriegaCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:Loriega faye ann
Course/Year: BSN-2D
Seatwork#:3
Date:10-28-21
List all the structures of both cell types and their functions.
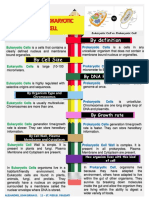
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes Prokaryotes
Structure Function
1. -no nucleus, circular
Nucleus -Contains DNA/genetic material
DNA/plasmid is contained in a
-coiled, singular strand
region inside the cell
2. DNA Form Circular Linear
3. Complexity Simpler More complex
4. Membrane-bound Eukaryotic cells contain many prokaryotic cells do not contain
organelles membrane-enclosed, large, these membrane-bound
complex organelles in the organelles.
cytoplasm
5. Sexual Sexual reproduction in eukaryotes prokaryote will reproduce clones
reproduction results in offspring with genetic of itself via binary fission and
material which is a mixture of the relies more on horizontal genetic
parents’ genome and during this transfer for variation.
process, genetic variation is
generated via sexual
recombination.
6. Cell division involves numerous stages - the undergo a simpler process of
nuclear membrane disintegrates binary fission. This is faster than
then the chromosomes are sorted mitosis and involves DNA
and separated to ensure that each replication, chromosomal
daughter cell receives two sets of segregation, and ultimately cell
chromosomes. separation into two daughter cells
genetically identical to the parent
cell.
7. Cell arrangement Eukaryotes are often multicellular prokaryotes are unicellular.
8. Cell size Eukaryotic cells are ordinarily prokaryotic cells (1 – 10um).
larger (10 – 100um)
9. Glycocalyx Some eukaryotic cells that don’t Glycocalyx acts as a capsule
have cell walls possess a glycocalyx
10. Cell Division Cell division takes place through Cell division occurs through
mitosis binary fission
11. Cytoplasm Eukaryotic cells have complex Prokaryotic cells are primitive
cytoskeleton with cytoplasmic cytoskeleton with no cytoplasmic
streaming streaming
12. Flagella Some cells without cell wall contain Flagella are made up of two
flagella. proteins
13. Plasma Carbohydrates and sterols serves Carbohydrates and sterols are not
Membrane as receptors on the plasma found in the plasma membrane
membrane
14. Cell Wall Eukaryotic Cell: Eukaryotic Prokaryotic cells are mostly made
cells are made up of up of peptidoglycans. They are
cellulose, chitin and pectin. chemically complex
Prokaryotic cells are
chemically
simple
Eukaryotic Cell: Eukaryotic
cells are made up of
cellulose, chitin and pectin.
Prokaryotic cells are
chemically
simple
Eukaryotic Cell: Eukaryotic
cells are made up of
cellulose, chitin and pectin.
Prokaryotic cells are
chemically
simple
Eukaryotic cells are made
up of cellulose, chitin and
pectin. Prokaryotic cells are
chemically
simple
Eukaryotic cells are made up of
cellulose, chitin and pectin.
Prokaryotic cells are chemically
simple
15.Ribosome Eukaryotic cells arelargein Prokaryotic cells are small in size,
size,
80S.70Sribosomesarepresent
inorganelleslikemitochondria
andchloroplast
Eukaryotic cells are large in size,
80S. 70S ribosomes are present in
organelles like mitochondria and
chloroplast
16. Genetic Meiosis and fusion of gametes Partial, undirectional
Recombination transfers DNA
17. DNA Eukaryotes wrap their DNA around Multiple proteins act together to
wrapping on proteins called histones. fold and condense prokaryotic
proteins. DNA. Folded DNA is then
organized into a variety of
conformations that are
supercoiled and wound around
tetramers of the HU protein.
Mitochondria PRESENT ABSENT
Golgi apparatus PRESENT ABSENT
Vacuoles PRESENT ABSENT
Endocytosis OCCURED ABSENT
exocytosis OCCURED ABSENT
Permeability of SELECTIVE ABSENT
Nuclear membrane
Endoplasmic PRESENT ABSENT
reticulum
Microtubules PRESENT ABSENT
Lysosomes PRESENT ABSENT
Peroxisomes PRESENT ABSENT
Genome nature Efficient and compact with little With large amounts of non-coding
repetitive DNA. repetitive DNA.
You might also like
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cell BiologyDocument9 pagesCell BiologyMick HardyNo ratings yet
- Struckture of ProkaryoticDocument5 pagesStruckture of ProkaryoticAuni NaemiNo ratings yet
- Farmasi 1Document50 pagesFarmasi 1Suci Umniyah RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsCrocky CookNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellDocument49 pagesProkaryotic & Eukaryotic CellArthe RajarajanNo ratings yet
- 2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1Document24 pages2.1 A. Cell Theory B. Prokaryote Eukaryote 1saidatulNo ratings yet
- Camposano, Chona PRE-TEST - May 22, 2021Document7 pagesCamposano, Chona PRE-TEST - May 22, 2021Chona Camposano - BorjaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument20 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesKerubin Mamaril67% (3)
- BTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Document55 pagesBTC 01: Life Science: Instructors: 1. Sudit S. Mukhopadhyay (SSM) 2. Surabhi Choudhuri (SC)Om JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Arindam Mondal: School of Bio ScienceDocument39 pagesArindam Mondal: School of Bio ScienceSohini RoyNo ratings yet
- Cell CompiledDocument7 pagesCell CompiledRizza Mae Telebrico CantereNo ratings yet
- Prokaryote Vs EukaryoteDocument48 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryotesunifeb128075No ratings yet
- Basic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsDocument28 pagesBasic Cell Types, Cell Structure and Function,& Cell ModificationsMary Ann Gonzales Abeñon100% (1)
- Your Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesYour Turn .: Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic CellsVisca El BarcaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TextDocument54 pagesBiochemistry & Genetics: II SHS 109: Resource Person: DR Tanveer Akbar Reference TexttNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument24 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatNo ratings yet
- Andaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2Document2 pagesAndaya, RJ Gen Bio Act No.2Rj AndayaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes Have A Much More Complex Cell Structure Than ProkaryotesDocument9 pagesEukaryotes Have A Much More Complex Cell Structure Than Prokaryotesnevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument21 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup Penyusun Mahluk HidupYunita RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument21 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HiduprinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument16 pagesLecture Differences Between Prokaryotes and EukaryotesAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic 1Document39 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic 1Luke kenneth MacalawaNo ratings yet
- Prokalytic Vs EurokalyticDocument1 pageProkalytic Vs EurokalyticJessielyn DangananNo ratings yet
- The Biological CellDocument23 pagesThe Biological CellVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument17 pagesCellAaliyah Quesha LadjamatliNo ratings yet
- BIOL107 - Different Cell TypesDocument4 pagesBIOL107 - Different Cell TypesJahsuah OrillanedaNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- Structural and Functional Manifestation of LifeDocument6 pagesStructural and Functional Manifestation of LifeKaila StefanieNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells NotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells NotesMischi Jeda ElumbaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsDocument18 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotics CellsClaire JosephNo ratings yet
- Genbio 1 2 3 4 5Document23 pagesGenbio 1 2 3 4 5John MarkNo ratings yet
- Agr122 Lab ReportDocument12 pagesAgr122 Lab ReportNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsDocument58 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsKurt DimacaliNo ratings yet
- Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument18 pagesCell and Molecular BiologyHizzei Caballero100% (1)
- Prokaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsDocument5 pagesProkaryotic VS Eukaryotic CellsAngelica FloraNo ratings yet
- Unit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupDocument56 pagesUnit Mahluk Hidup - Penyusun Mahluk HidupYahya RhamadanNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument10 pagesProkaryotes & EukaryotesJogie De GuiaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document3 pagesGeneral Biology 2Sean CaloyloyNo ratings yet
- 2nd Lec Cell Structure and FunctionDocument15 pages2nd Lec Cell Structure and FunctionArslan AliNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsDocument11 pagesProkaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell: Botany Lecture Reviewer A. CellsRosemarie OngNo ratings yet
- NMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDocument26 pagesNMAT Study Guide Updated PDFDax Arcega100% (1)
- NmatstudyguideupdatedpdfDocument26 pagesNmatstudyguideupdatedpdfRafael GoldbergNo ratings yet
- HDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesDocument43 pagesHDTD-B-4 - Cell OrganellesMariam Qais100% (1)
- General Principles of Cell OrganisationDocument3 pagesGeneral Principles of Cell Organisation22194No ratings yet
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMDocument27 pagesScreenshot 2023-10-27 at 1.09.50 AMcfhsmjmdqnNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsDocument11 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic Cells and Eukaryotic CellsMuhammed Sabdat100% (1)
- 1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument45 pages1.cell Theory and Cell OrganellesMaham AdnanNo ratings yet
- Tugas KLP 1 Biologi SelDocument25 pagesTugas KLP 1 Biologi SeldeweweweweweNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Biol 266 - Cell Biology Unit 1 "Cells and Organelles - I"Document78 pagesBiol 266 - Cell Biology Unit 1 "Cells and Organelles - I"Volodymyr KravchenkoNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument21 pagesProkaryotes and EukaryotesJeff Hambre100% (2)
- Lecture 2Document46 pagesLecture 2Phạm ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Bio Lecture 2 Cell StructureDocument46 pagesBio Lecture 2 Cell StructureLương Bang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 1.2 IntroductionDocument8 pages1.2 IntroductionmiftahNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell OrganellesDocument53 pagesCell and Cell OrganellesShiffa SaheedNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2-GeneticsDocument15 pagesMODULE 2-GeneticsDivine Grace CincoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 Percep Med TermsDocument6 pagesNCM 116 Percep Med TermsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan BieneDocument1 pageLesson Plan BieneFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 2Document1 pageDrug Study 2Fayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative CareDocument13 pagesPost-Operative CareFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- A Case Study Presentation On: Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument63 pagesA Case Study Presentation On: Chronic Kidney DiseaseFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- I. Basic Tools Used in A Microbiology Laboratory.: Name: Course/Section: Lab Worksheet #: DateDocument14 pagesI. Basic Tools Used in A Microbiology Laboratory.: Name: Course/Section: Lab Worksheet #: DateFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- AsepticDocument2 pagesAsepticFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Loriega Faye Ann V. BSN-2D NCM-113Document1 pageLoriega Faye Ann V. BSN-2D NCM-113Fayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Force ProblemsDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Force ProblemsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 Force ProblemsDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics 1 Force ProblemsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Bag Technique ChecklistDocument3 pagesBag Technique Checklistsfd33% (3)
- Reflection Health IssueDocument1 pageReflection Health IssueFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Module Cell DisordersDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Module Cell DisordersFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology AssignmentDocument2 pagesPharmacology AssignmentFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Loriega Faye Ann V. BSN-1D: Types of Eating DisordersDocument8 pagesLoriega Faye Ann V. BSN-1D: Types of Eating DisordersFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Loriega Faye Ann V. BSN-1D: Types of Eating DisordersDocument8 pagesLoriega Faye Ann V. BSN-1D: Types of Eating DisordersFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Related Nursing Diagnosis Rev 10-15 (3) (1) - 1Document2 pagesNutrition Related Nursing Diagnosis Rev 10-15 (3) (1) - 1Fayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- CHN FamilydocxDocument3 pagesCHN FamilydocxFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument1 pageMaterialsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- IMCIDocument1 pageIMCIFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- IMCIDocument1 pageIMCIFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology AssignmentDocument2 pagesPharmacology AssignmentFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- A Family Case Study LORIEGADocument7 pagesA Family Case Study LORIEGAFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- I. Basic Tools Used in A Microbiology Laboratory.: Name: Course/Section: Lab Worksheet #: DateDocument14 pagesI. Basic Tools Used in A Microbiology Laboratory.: Name: Course/Section: Lab Worksheet #: DateFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- CHN Quiz Compilation FinalsDocument20 pagesCHN Quiz Compilation FinalsFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Reflection Health IssueDocument1 pageReflection Health IssueFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Loriega, Faye Ann V. BSN-2DDocument2 pagesLoriega, Faye Ann V. BSN-2DFayeann Vedor LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Family Case StudyDocument13 pagesFamily Case StudyKathleen Joy Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- 29 PerformanceAssessmentDocument22 pages29 PerformanceAssessmentDarmanNo ratings yet
- Prospectus: 1 ReservationsDocument8 pagesProspectus: 1 ReservationsvarunNo ratings yet
- Olimpiada de Limba Engleză - Liceu Etapa Locală - 15 Februarie 2020 Clasa A X-A, Secțiunea B Varianta 2Document4 pagesOlimpiada de Limba Engleză - Liceu Etapa Locală - 15 Februarie 2020 Clasa A X-A, Secțiunea B Varianta 2MidnightNo ratings yet
- Test - Reading Explorer 3 8A - QuizletDocument4 pagesTest - Reading Explorer 3 8A - QuizletTatjana Modea SibulNo ratings yet
- Wre MCQDocument136 pagesWre MCQsurendranath jadhavNo ratings yet
- AS Level Mathematics Statistics (New)Document49 pagesAS Level Mathematics Statistics (New)Alex GoldsmithNo ratings yet
- For 'Best Practices in O&M Safety' PDFDocument153 pagesFor 'Best Practices in O&M Safety' PDFSachinGoyalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Text and Cases 7th Edition Dess Solutions ManualDocument25 pagesStrategic Management Text and Cases 7th Edition Dess Solutions ManualNataliePowelljdmb100% (32)
- I Learned Chapter 8-The Power of GuidanceDocument1 pageI Learned Chapter 8-The Power of Guidanceapi-295870335No ratings yet
- Grade Thresholds - November 2018: Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709)Document3 pagesGrade Thresholds - November 2018: Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics (9709)redwanNo ratings yet
- What Is Emergency Lighting Circuit DiagramDocument14 pagesWhat Is Emergency Lighting Circuit DiagramjackNo ratings yet
- Rd6appspecDocument2 pagesRd6appspecravi00098No ratings yet
- Radiation Protection in Dental RadiologyDocument52 pagesRadiation Protection in Dental Radiologyivan dario ardila martinezNo ratings yet
- Geography Worksheet 1 Rural SettlementsDocument14 pagesGeography Worksheet 1 Rural SettlementsLelethuNo ratings yet
- Iefem English Guide Reported Speech 3Document6 pagesIefem English Guide Reported Speech 3Laury Yocely Perea MenaNo ratings yet
- A Settlement Prediction Model Considering Tidal Loading and Traffic LoadingDocument14 pagesA Settlement Prediction Model Considering Tidal Loading and Traffic LoadingSandro GuedesNo ratings yet
- Split Valuation SAPDocument7 pagesSplit Valuation SAPPramod ShettyNo ratings yet
- A Level Pure Unit 7 Parametric Equations QPDocument2 pagesA Level Pure Unit 7 Parametric Equations QPsaNo ratings yet
- Email Etiquettes: Click To Add TextDocument25 pagesEmail Etiquettes: Click To Add Textmanveen kaurNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thought Intelligence Fictional Intellectual Behave Exercise 1 ComputationDocument4 pagesEngineering Thought Intelligence Fictional Intellectual Behave Exercise 1 Computationposgas aceNo ratings yet
- Exp 3 Rahul Singh 2k20-A18-12Document8 pagesExp 3 Rahul Singh 2k20-A18-12Dummy Account-Rahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Practice For Group Work Week 2 Case 2.1 - Assigning Plants To Products (Better Products Company)Document2 pagesPractice For Group Work Week 2 Case 2.1 - Assigning Plants To Products (Better Products Company)Thu TrangNo ratings yet
- AE 2018-19 Syll PDFDocument118 pagesAE 2018-19 Syll PDFHARI KRISHNA SNo ratings yet
- Updated References PDFDocument8 pagesUpdated References PDFFrancine Dawn MoloNo ratings yet
- Various Executions MA: Series Foodstuffs ExecutionDocument17 pagesVarious Executions MA: Series Foodstuffs ExecutionKyriakos MichalakiNo ratings yet
- DLL-All Subjects - Week 7 Day 1Document5 pagesDLL-All Subjects - Week 7 Day 1Windel Beth Quimat ZafraNo ratings yet
- LEPTOSPIRADocument31 pagesLEPTOSPIRADinar NastitiNo ratings yet
- Free Downloads: Type Matters!Document3 pagesFree Downloads: Type Matters!Shinko Art Studio9% (11)
- Participatory Irrigation ManagementDocument11 pagesParticipatory Irrigation ManagementSidNo ratings yet
- Line Scan (Switch Hook) : NamesDocument3 pagesLine Scan (Switch Hook) : NamesUsairumNo ratings yet