Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Top 3 Civil Services in India: IAS, IPS, IFS
Uploaded by
Sapna DeviOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Top 3 Civil Services in India: IAS, IPS, IFS
Uploaded by
Sapna DeviCopyright:
Available Formats
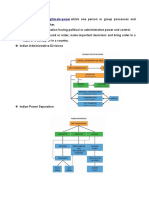
The IAS (Indian Administrative Service) was formally constituted in 1947, and is the premier service in India.
It offers an attractive and challenging career. Fame and glamour are also associated with this service. Even though most people tend to think being the DM or Collector is the most powerful and glamorous post, The IAS holds power at all levels. It is the service that is meant to place people straight at the top of any government organization and not the district alone. inspite of all the political interference if you are a determined person and diplomatic you can achieve anything for your country. The IAS or the Indian Administrative Service, handles affairs of the government. At the central level, this involves the framing and implementation of policy. At the district level, it is concerned with district affairs, including development functions. At the divisional level, the IAS officers look after law and order, general administration and development work. Members of the Indian Administrative Service hold various administrative posts like District Collector, Heads of Departments, Heads of Public Enterprises at the state level etc. They can also be posted on deputation to the Central Government to various posts. Being an 'All India Service', it follows the Cadre system. In this system officers are allotted to various state cadres and your service is allotted to that state. So for all practical purposes you belong to that state service and may be deputed elsewhere but you'll always be recognized by your parent cadre. These systems though very useful tend to positively and negatively affect careers. The cadre system is allotted on a basis of lottery and the toppers of each state may get a chance to get their home states if they have opted for such a preference. Indian Administrative Service Exams Indian Administrative Service Syllabus
The Indian Foreign Service [IFS] is a Central Service and the premier diplomatic service of our country. Members of the IFS, primarily represent the country in the international arena. The Indian Foreign Service deals with the country's external affairs, including diplomacy, trade and cultural relations. It is responsible for the administration and activities of Indian missions abroad, and for the framing and implementation of the Government's foreign policy. The service offers immense exposure to different political, social, ethnic and cultural milieu. An I.F.S officer can be posted in 160 odd Indian Embassies and Missions abroad. They can also be deputed to institutions like United Nations, UNESCO, World Bank, SAARC, etc. Back home, they can be posted in various parts of the country as Passport Officers. Even though many toppers at the civil services exams opt for the IAS, with limited vacancies the IFS is also a tough service to get. With India and Indians going global, this is the service which holds a lot of promise and glamour. The Indian Police Service [IPS] is primarily concerned with maintenance of Law and Order in the country. This is the premier uniformed civil service in the country. An I.P.S officer works for both the Central and State Governments. He serves the State Government in various capacities ranging from Assistant Superintendent of Police at the beginning of his career to the Director General of Police (who is the head of the police force in his state) at the stage of retirement. He can also serve the Central Government in various organizations like the Central Reserve Police Force, Border Security Force, Central Bureau of Investigation, Intelligence Bureau, Research and Analysis Wing (RAW) etc. The IPS (Indian Police Service) is responsible for public safety and security. The IPS mainly takes care of law and order, which, at the district level, is a responsibility shared with the IAS ; crime prevention and detection ; and traffic control and accident prevention and management. In order to fulfil these functions with greater efficiency, this service is divided into various functional departments, including : " Crime Branch, " Criminal Investigation Department (CID), " Home Guards, " Traffic Bureau. With changing times however, more and more IPS officers are serving in departments and areas that used to exclusively be the forte of IAS officers, just as the IAS officers now at times head departments like vigilance which were exclusively given to IPS officers. This widening of opportunities and exposure has made the IPS even more attractive. Again being an 'All India Service', it follows the Cadre system. In this system officers are allotted to various state cadres and your service is allotted to that state. So for all practical purposes you belong to that state service and may be deputed elsewhere but you'll always be recognized by your parent cadre. These systems though very useful tend to positively and negatively affect careers. The cadre system is allotted on a basis of lottery and the toppers of each state may get a chance to get their home states if they have opted for such a preference. The IPS is also filled through the civil services exam conducted by UPSC.
Indian P&T Accounts and Finance Service is a group A service. The senior most person of this service is the Deputy Director General who heads this organisation. The hierarchy: Assistant Chief Controllers of Imports and Exports > Deputy Chief Controller of Imports and Exports > Joint Chief Controller Imports and Exports or Chairman of a Public Sector unit. The Indian Audit and Accounts service is under the Control of the CAG. The Controller and Auditor General of India (CAG) is one of the Constitutional authorities, like the Chairman of UPSC or the Election Commissioner. He/she is responsible for maintenance of accounts in the states as well as Audit of Accounts of the Union as well as the State Governments. The post of Controller and Auditor General is not, reserved exclusively for officers of the IA&AS. Even officer of the IAS of sufficient experience and seniority may be appointed as the Controller and Auditor General. The services of officers of the IAAS are lent to State Government for functioning as Financial Advisers Chief Accounts Officers, Chief Internal Audit Officers and so on. The hierarchy: During the course of their probation, direct recruits to this service work as Assistant Accountant General. The hierarchy after that is: Deputy Accountant General > Senior Deputy Accountant General > Accountant General > Director of Audits > Additional CAG > Dy. CAG (equivalent in rank to a secretary to the Government of India).
The Indian Revenue Service has two wings, one being Income Tax and the other Customs and Central Exercise. The Indian Customs and Central Excise Service (IC&CES) is basically concerned with two main aspects, mainly Customs and Excise. While Customs is concerned with the checking and levy of duty on taxable goods brought into the country, the Excise department is involved with the taxation of goods manufactured within the country. The members of this service begin their Career as Assistant Collectors of Customs/Central Excise and may rise up in the hierarchy to the level of Chief Collector of Customs. The hierarchy: Probationers > Assistant Commissioners (Customs) > Deputy Commissioners (customs) > Additional Commissioners (Customs )> Commissioners (Customs) > member (Central Board of Excise and Customs) > Chairman (Central Board of Excise and Customs). The Central Excise Officers start as Assistant Commissioner (Central Excise). After that, the hierarchy follows as: Deputy Commissioners (Central Excise) > Additional Commissioner (Central Excise) > Commissioners (central Excise) > Member (Central Board of Excise and Customs) > Chairman (Central Board of Excise & Customs). Probationers to the customs service begin their field training at Madras while the excise officers may start service in any metropolitan town. Custom officers are posted at international airports and ports like, Mumbai, Calcutta, Chennai, Goa, etc. They could be posted at other border and coastal towns. Their principal duty is to levy customs' duty on goods, which are brought to the country. Customs & excise cadres are not watertight compartments. Officers are liable to transfer from one to another, depending upon their experience and the exigencies of the work. Chief Commissioner of Customs and Excise, with the pay of an Additional Secretary holds technical and administrative charges in all the regions, exercising overall supervision on the technical and administration work. The head of the administration is the Chairman Central Board of Excise and Customs.
The Indian Defence Accounts Service (IDAS) is responsible for maintaining the complete accounts of the Defence Services. The first position to be placed in after appointment is that of Assistant Controller of Defence Accounts. The defence accounts offices in cantonment, states and defence command headquarters are under the jurisdiction of the IDAS.
Indian Revenue Service This service deals with the matters concerning Income Tax. The members of this service, begin their career as Assistant Commissioners of Income Tax and may rise to the level of Chief Commissioners of Income Tax. With changing times however, more and more IRS officers are serving in departments and areas that used to exclusively be the forte of IAS officers. This widening of opportunities and exposure has made the IRS more attractive. Since there is no cadre system in this service you can expect to be posted anywhere in India and even your home state, which becomes a problem for many in the IAS or IPS. The tenures are also more stable with an average of 3 years unlike the other two services where one may not even complete a month and the average tenure is around a year or so. Officers of Indian Revenue Services (Income-tax) enter training at their academy at Nagpur. After training, they are posted as Assistant Commissioners either on assessment or other work. While the main work of the department is assessment and recovery of direct taxes, the department has specialized branches dealing with investigation of tax evasion, statistics, and so on with the help of Assistant Directors (of the same rank as Assistant Commissioners of Income-tax). The Assistant Commissioners/ Deputy Directors, Communication Chief Commissioners become members of Central Board of Direct Taxes. The head of the department is the Chairman of the Central Board of Direct Taxes, who is invariably a member of the Indian Revenue Services (Income-tax).
Indian Ordnance Factories Service
Ordinance factories manufacture equipment for the Defence Services. The Indian Ordnance Factories Service (IOFS) officers serve in these factories for a span of nearly 10 years. They may be asked to serve as commissioned officers of the Armed forces for 4 years. At the apex of the IOFS is the Chairman equivalent to a Secretary, followed by Members of the Ordinance Factories or Director General Ordinance Factories and then by General Manager. The senior and junior scale positions are like the other services.
Indian Postal Service
The Indian Postal Service also carries a lot of the aura of living in large bungalows etc. The only thing you miss sometimes is perhaps public exposure. This is however a service that gives you opportunities to do service to your nation by introducing newer and better schemes for the nation especially when communication is changing at a very fast pace. The hierarchy: Probationer > Senior Superintendent of Post Offices or Railway Mail in large district towns and Divisional Headquarters > Assistant Post Master General > Director > Post Master General of a 'Circle' > Senior Deputy Director Generals who are equivalent to Additional Secretary in a Ministry or member of Post and Telegraph Board (a total 8 in number) > Chairman of the Board.
Indian Civil Accounts Service
The separation of accounts from audit at the Union level has led to the creation of the new Indian Civil Accounts cadre. The Controller and Auditor General of India does not, however, control this cadre but the Secretary (Expenditure) in the Ministry of Finance (Government of India) exercises this function. The hierarchy: Assistant Controller of Accounts > Deputy Controller of Accounts > Controller of Accounts > Additional Controller General of Accounts > Controller General of Accounts (equivalent to Additional Secretary, to the Government of India.)
Indian Railway Traffic Service
The Indian Railway Traffic Services (IRTS) has two functions: (a) Commercial Transportation of objects by trains is the responsibility of the Commercial Division of the IRTS. (b) Operations: The Operations Department is in charge of the movement of trains. The hierarchy: Assistant Superintendent(Commercial/Operations) at Divisional Headquarters and after 4 years of service at the senior scale > Commercial/Operations Superintendent at the Divisional Headquarters > Senior Divisional OS/CS > Chief Commercial Superintendent OS/CS > Additional Chief Commercial Superintendent OS/ CS > Deputy Chief Commercial Superintendent OS/CS.
Indian Railway Accounts Service
The Indian Railway Accounts Service (IRAS) is in charge of all the accounts of the railways, i.e. income, expenditures, etc. The hierarchy: Financial Advisor cum Chief Accounts Officer of a zone > Senior Divisional Accounts Officers > Divisional Accounts Officers > Assistant Accounts Officers at Divisional Headquarters.
Indian Railway Personnel Service
Indian Railway Personnel Service involves tasks such as recruitment of all railway staff (inspectors, drivers, IRTS officers) and planning of recruitments, deciding promotions, postings, training, welfare, in fact all work concerning personnel. The hierarchy: Chief Personnel Officer > Chief Planning and Labour Officer > Additional Chief Planning Officer > Deputy Chief Planning Officer (Selection Grade) > Senior Divisional Personnel Officer > Divisional Personnel Officer > Assistant Personnel Officer >
Railway Protection Force (RPF)
The Railway Police Service (RPF) is responsible for the security of the railway tracks, personnel and equipment. The Director General is at the apex of the service. This post is equivalent to that of the Additional Secretary.
Indian Defence Estates Service
The management of cantonments is under the care of Defence Estate Service. The appointment on completion of probation is that of Executive Officer Class I or Class II of cantonments. The senior most position in this service is that of Director General Defence Estates.
Indian Information Service
The Indian Information Services (IIS) Officers are controlled by the Ministry of Defence (Directorate of Public Relations). The tasks Managing government's print media, electronic media, advertising agency, Union Ministeries (news desk),act as press advisors Constitute a press party Organise press conferences Control official media Organise festivals (national and international), etc
The work is interesting as it uses the flare for journalism, public relations and administration all together. There is a special requirement to enter this service. The officer needs to have some previous experience of work in a newspaper or news agency or ad agency. The promotional channel is more or less the same as that of other Services.
You might also like
- Civil Services: Indian Administrative Services (IAS)Document3 pagesCivil Services: Indian Administrative Services (IAS)Sny Kumar DeepakNo ratings yet
- All About IASDocument6 pagesAll About IASAnant SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Are You Looking For In A Career? Civil Services Offer Position, Respect & SecurityDocument2 pagesWhat Are You Looking For In A Career? Civil Services Offer Position, Respect & SecurityHimanshu BhandariNo ratings yet
- All India Services PDFDocument43 pagesAll India Services PDFAnilBabuNo ratings yet
- How Can I Become A Civil ServantDocument8 pagesHow Can I Become A Civil Servantrochak100No ratings yet
- How To Become Ias OfficerDocument6 pagesHow To Become Ias OfficerB ruikarNo ratings yet
- Eligibility To Become IAS Officer: Career As A IAS Officer About IAS OfficerDocument4 pagesEligibility To Become IAS Officer: Career As A IAS Officer About IAS Officersamiie30No ratings yet
- Fathana.j Agalya.sDocument14 pagesFathana.j Agalya.ssangimangibingobooNo ratings yet
- About Civil ServicesDocument3 pagesAbout Civil Servicesgmaruthi_1No ratings yet
- Kbs Sidhu IasDocument4 pagesKbs Sidhu Iaskbssidhu45No ratings yet
- IAS Officer HR PresentationDocument12 pagesIAS Officer HR PresentationFarukh ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Services: Unit 15 State and Public Service CommissionDocument12 pagesServices: Unit 15 State and Public Service CommissionM KIRAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Public Administration Unit-54 State Services and Public Service CommissionDocument12 pagesPublic Administration Unit-54 State Services and Public Service CommissionDeepika SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Authority? Authority Is The Which One Person or Group Possesses and Practices Over AnotherDocument11 pagesWhat Is Authority? Authority Is The Which One Person or Group Possesses and Practices Over AnotherMaharajNo ratings yet
- IPS: India's Elite Police ServiceDocument8 pagesIPS: India's Elite Police ServiceJohnVictorCahatianNo ratings yet
- Guide to the Indian Administrative Service (IASDocument43 pagesGuide to the Indian Administrative Service (IASmanjunath jekinakattiNo ratings yet
- What Does An IAS Officer DoDocument1 pageWhat Does An IAS Officer DoShruti MishraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Role of District CollectorDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Role of District CollectorMaharajNo ratings yet
- All India Services: Nature, Responsibilities and CadresDocument5 pagesAll India Services: Nature, Responsibilities and CadresspibluNo ratings yet
- Project Report On TaxationDocument51 pagesProject Report On Taxationanuragmishra211276% (38)
- UPSC Salary OverviewDocument3 pagesUPSC Salary OverviewDHURANDHAR BASESHANKARNo ratings yet
- Articles For IASDocument2 pagesArticles For IASLeslie PayneNo ratings yet
- IAS vs IPS: Key Differences Between the Two Top Civil ServicesDocument6 pagesIAS vs IPS: Key Differences Between the Two Top Civil ServicesPurnima SinghNo ratings yet
- PDF HistDocument4 pagesPDF HistAndrewNo ratings yet
- Indian Administrative Service - WikipediaDocument44 pagesIndian Administrative Service - WikipediaPankaj YadavNo ratings yet
- Kbs Sidhu CbiDocument9 pagesKbs Sidhu Cbikbssidhu78No ratings yet
- IPSProfile 180314 PDFDocument3 pagesIPSProfile 180314 PDFRakesh Ranjan JhaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of The OrganizationDocument11 pagesIntroduction of The OrganizationSharmilla RajendranNo ratings yet
- IAS Vs IPSDocument1 pageIAS Vs IPSShruti MishraNo ratings yet
- Wa0042.Document4 pagesWa0042.palneelakshi06No ratings yet
- Divisional CommissionerDocument3 pagesDivisional CommissionerDisha GogoiNo ratings yet
- Civil ServicesDocument7 pagesCivil ServicesPrasad AkkNo ratings yet
- District Administration POLITICAL SCIENCEDocument26 pagesDistrict Administration POLITICAL SCIENCEAnkushNo ratings yet
- VIKASH JINDAL SHARES INSIGHTS ON CIVIL SERVICES OPTIONSDocument6 pagesVIKASH JINDAL SHARES INSIGHTS ON CIVIL SERVICES OPTIONSSreekanth Reddy100% (1)
- Mba ProjectDocument47 pagesMba ProjectVaishnavi Santosh KatoreNo ratings yet
- Indian Administrative Service - Wikipedia PDFDocument136 pagesIndian Administrative Service - Wikipedia PDFBasanta KalitaNo ratings yet
- Groups of Css Exam Pakistan/ Css Exam Pakistan Posts/Jobs/VacanciesDocument1 pageGroups of Css Exam Pakistan/ Css Exam Pakistan Posts/Jobs/VacanciesJasim WazirNo ratings yet
- How to Have a Career in CustomsDocument4 pagesHow to Have a Career in Customsanosuyaroy28No ratings yet
- Incom Tax OrdinanceDocument6 pagesIncom Tax OrdinanceaghashabeerNo ratings yet
- Administrative Governance (Line and Staff)Document12 pagesAdministrative Governance (Line and Staff)Lavisha AroraNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Inspector (ITI)Document6 pagesIncome Tax Inspector (ITI)AshishNo ratings yet
- Indian Defense Estate Service (IDES)Document6 pagesIndian Defense Estate Service (IDES)Ishu BabyNo ratings yet
- BUREAUCRATIC REFORM IN INDIA - CAN THE SYSTEM BE CHANGEDDocument10 pagesBUREAUCRATIC REFORM IN INDIA - CAN THE SYSTEM BE CHANGEDAnkur SinhaNo ratings yet
- District Administration Since IndependenceDocument5 pagesDistrict Administration Since IndependencePrasad AkkNo ratings yet
- Govt JobsDocument16 pagesGovt Jobssurya putraNo ratings yet
- PA-SBCO Induction Training MaterialsDocument101 pagesPA-SBCO Induction Training Materialsvital polityNo ratings yet
- All Groups of CSS SummaryDocument9 pagesAll Groups of CSS SummaryNida NaeemNo ratings yet
- Carrers in Indian Postal ServiceDocument6 pagesCarrers in Indian Postal ServiceEntranzzNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of Police Agencies and Their JurisdictionDocument4 pagesHistorical Development of Police Agencies and Their JurisdictionNatasha Parfaniuc50% (2)
- Financial Institution: Debt Market Debt BondsDocument4 pagesFinancial Institution: Debt Market Debt BondsPriyanshu NankalNo ratings yet
- ObjectiveDocument3 pagesObjectiveArjun RichardNo ratings yet
- CA Vs CS: Which Career Has More Scope?Document2 pagesCA Vs CS: Which Career Has More Scope?Naineshp87No ratings yet
- Become a CID OfficerDocument6 pagesBecome a CID OfficerHimasri DhankaniNo ratings yet
- E-Filing of Income Tax ReturnDocument61 pagesE-Filing of Income Tax ReturnSilvi Khurana100% (2)
- Gazetted Officer (India) - WikipediaDocument5 pagesGazetted Officer (India) - WikipediaSuresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Free E Book IAS Planner PDFDocument58 pagesFree E Book IAS Planner PDFsrigandtp50% (6)
- Indian PostDocument45 pagesIndian PostManish BoliaNo ratings yet
- GST Tally ERP9 English: A Handbook for Understanding GST Implementation in TallyFrom EverandGST Tally ERP9 English: A Handbook for Understanding GST Implementation in TallyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Abyssinia Bank Charts Noteworthy Profit, Dividend ClimbDocument7 pagesAbyssinia Bank Charts Noteworthy Profit, Dividend ClimbBernabasNo ratings yet
- Business Organization TypesDocument36 pagesBusiness Organization TypesNatalie Tremblay100% (1)
- Abhishek Agrawal T-24 Test Analyst ResumeDocument4 pagesAbhishek Agrawal T-24 Test Analyst Resumesempoline12345678No ratings yet
- Acct 101 FinalDocument9 pagesAcct 101 FinalAndrea NingNo ratings yet
- Bernie MadoffDocument8 pagesBernie Madofflcorrente12No ratings yet
- SAP Contract Accounts Receivables and Payables - SAP Help Portal PageDocument2 pagesSAP Contract Accounts Receivables and Payables - SAP Help Portal Pagetekmoh1aNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 - Risk and Return: Past and PrologueDocument50 pagesChapter 05 - Risk and Return: Past and PrologueMarwa HassanNo ratings yet
- Score 75 Marks in DT IDT For Recording 1Document16 pagesScore 75 Marks in DT IDT For Recording 1saiNo ratings yet
- The Battle For Value FedEx UPSDocument23 pagesThe Battle For Value FedEx UPSHeo Mam100% (1)
- It o Calculus:, T) Depending On TwoDocument13 pagesIt o Calculus:, T) Depending On TwoTu ShirotaNo ratings yet
- Article by BLC - PLC - Mauritius - Corporate Governance & Directors Duties - Apr 2011Document24 pagesArticle by BLC - PLC - Mauritius - Corporate Governance & Directors Duties - Apr 2011Ak AshNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Intermediate Accounting 19th Edition by Stice PDFDocument18 pagesSolution Manual For Intermediate Accounting 19th Edition by Stice PDFADNo ratings yet
- BMBA Media Presentation July 2012Document4 pagesBMBA Media Presentation July 2012ShakilNo ratings yet
- Caltex Philippines, Inc. vs. Commission On AuditDocument41 pagesCaltex Philippines, Inc. vs. Commission On AuditJayson Francisco100% (1)
- Transfer of Intangible Property To Foreign Subsidiary - LTR 1321018Document24 pagesTransfer of Intangible Property To Foreign Subsidiary - LTR 1321018taxcrunchNo ratings yet
- Uy Tong vs. CA prohibits automatic property appropriationDocument2 pagesUy Tong vs. CA prohibits automatic property appropriationFai Meile100% (1)
- ENGG MNGT NEWpptDocument23 pagesENGG MNGT NEWpptRonald VilladolidNo ratings yet
- MSCI Feb11 IndexCalcMethodologyDocument103 pagesMSCI Feb11 IndexCalcMethodologybboyvnNo ratings yet
- Ia PPT 6Document20 pagesIa PPT 6lorriejaneNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A NegotiableDocument2 pagesCharacteristics of A NegotiableOmkar ShettyNo ratings yet
- Cost & Management Accounting - MGT402 Quiz 1Document63 pagesCost & Management Accounting - MGT402 Quiz 1Ayesha NaureenNo ratings yet
- Mas-1st-Pb-October-2022 - No AnsDocument13 pagesMas-1st-Pb-October-2022 - No AnsRizzaNo ratings yet
- Tax Rates 2009Document1 pageTax Rates 2009Ch Attique WainsNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoicesDocument5 pagesMultiple ChoicesAdlan AfnanNo ratings yet
- Reliable Taxi Service Business PlanDocument31 pagesReliable Taxi Service Business PlanHarry H Gaiya100% (2)
- Borkenstick Makes A Very Popular Undyed Cloth Sandal inDocument2 pagesBorkenstick Makes A Very Popular Undyed Cloth Sandal intrilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- 15P110 ShreyBhat GeneralDocument1 page15P110 ShreyBhat GeneralAnurag DeyNo ratings yet
- Applying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker 3rd Edition Test BankDocument13 pagesApplying International Financial Reporting Standards Picker 3rd Edition Test Banklisaclarkfgsocdkpix100% (33)
- Assignment 4.2 Accounting For Income TaxDocument2 pagesAssignment 4.2 Accounting For Income TaxMon RamNo ratings yet
- Cost of Capital Estimation TechniquesDocument16 pagesCost of Capital Estimation TechniquesVineet AgarwalNo ratings yet