Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Managerial Economy
Uploaded by
asafu jonathanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Managerial Economy
Uploaded by
asafu jonathanCopyright:
Available Formats
Economic Integration,is an arrangement among nation that includes the reduction or
elimination of trade barriers and the coordination of monetary and fiscal policies. Economic integration
aim to reduce cost for both consumers and producers and to increase trade between the countries
involved in the agreement.Economic integration sometimes refered as regional integration.The
following below are the forms of an economic integration.
Simple free-trade area,
Is among of form of an economic integration is a simple free-trade area. In this form attention is focused
almost exclusively on a reduction of the tariffs and quotas that restrict trade. Emphasis is placed almost
entirely on increasing the exchange of goods. The articulation of transnationalized production chains,
trade in services, labour mobility, and more-sophisticated forms of economic integration are not an
explicit goal and emerge as merely tangential to the primary goal of securing access to foreign markets
for domestic firms.
Second-generation free-trade area,
In a second-generation free-trade area, the basic nature of simple free trade is expanded to include
trade in non-goods such as services. Where a simple free-trade area need only address the question of
tariffs and quotas, the trade in services and a widening of trade in goods raises questions of regulatory
convergence and the harmonization of rules of operation and governance. At this stage, attention needs
to be turned to such things as the transferability of professional certifications as well as questions of
labour mobility, particularly for the highly skilled professions such as legal, accounting, technology, and
medical services.
Common market,
The idea of a common market grows from the possibilities presented by the adoption of a common
external tariff. As trade flows increase and factor inputs imported into the integrating economies begin
to circulate freely, production chains crossing the intra-regional national boundaries begin to form. This
results in sustained pressure to reduce the costs of transporting finished and semi-finished goods
between the states participating in the integration project.The solution is the harmonization of border
procedures, which in its ultimate form leads to the virtual elimination of national boundaries as internal
barriers to trade and the formation of a free-flowing regional economic space.
Monetary union,
With the evolution of a common market and the concomitant surge in intra-regional trade comes a new
source of expenses for business: the costs of transnational transactions. Even though borders may be
open to the free transit of goods and services, the need to constantly engage in foreign exchange
operations to settle payments as well as the differing relative costs caused by different national
economic policies impose a constant financial and administrative expense on firms operating within the
region.
Economic community or union,
In an economic community or union, the logic of common external tariff, regulatory approximation, and
harmonization of macroeconomic policy is taken to its full conclusion through the construction of an
overarching governance framework that imposes a common economic policy system on all countries in
the region. In effect the member states surrender a significant degree of economic sovereignty to the
whole in the expectation of significantly expanded opportunities presented by a much larger, fully
integrated economic space facilitating the full mobility of finished products, factors of production, and
labour.
The political factor,
Although economic integration lead to regionalism as a method of organizing interstate relations that
focus on economic question, it is in the end a politically motivate concept. States do not fall into
economic regionalism by accident. Rather, they engage in long, sustained, and highly technical
discussion to carefully delimit the policy and geographical boundaries of the region. Management of the
region, irrespective of the extent to which it has resulted in economic integration, also emerges as a
potential source of sustained political tension between member states.
Externalization,
Although rarely explicitly framed as the need to externalize the rationale for politically contentious
policies, economic integration has emerged as a device used on the domestic political stage.
Culmination;Economic integration have great important since it allows countries to specialize and trade
without government interference, which can benefit all economies. It results in a reduction of costs and
ultimately an increase in overall wealth.Trade costs are reduced, and goods and services are more
widely available, which leads to a more efficient economy. An efficient economy distributes capital,
goods, and services into the areas that demand them the most.
You might also like
- Economic Integratio1Document23 pagesEconomic Integratio1Bhushan KharatNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic Cooperation and IntegrationDocument32 pagesRegional Economic Cooperation and IntegrationshiblysdqNo ratings yet
- Assignment FinalDocument34 pagesAssignment FinalSaina KennethNo ratings yet
- Success Factors: European Coal and Steel Community European Economic CommunityDocument12 pagesSuccess Factors: European Coal and Steel Community European Economic CommunityVandanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Regional Economic IntegrationDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Regional Economic IntegrationMaximusNo ratings yet
- Concept of Economic IntegrationDocument31 pagesConcept of Economic IntegrationNilin Shetty71% (7)
- Final Copy of Econghghomic ItegrationDocument20 pagesFinal Copy of Econghghomic ItegrationSneha BandarkarNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic BlocDocument18 pagesRegional Economic BlocAdesola OyeneyeNo ratings yet
- Group 1 TRADE BLOCSDocument4 pagesGroup 1 TRADE BLOCSGalindo, Justine Mae M.No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The Levels of Economic IntegrationDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The Levels of Economic IntegrationMartha L Pv RNo ratings yet
- Economic Integration LevelDocument2 pagesEconomic Integration LevelKhan AliNo ratings yet
- Regional Integrations IBMDocument64 pagesRegional Integrations IBMdileepsuNo ratings yet
- Controles de Lectura p.49Document5 pagesControles de Lectura p.49Karen SNo ratings yet
- What is Regional Integration? Explained in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesWhat is Regional Integration? Explained in 40 CharactersHambisa ShiferawNo ratings yet
- Impact of MNC in Indian EconomyDocument38 pagesImpact of MNC in Indian EconomySantosh Gunwant PandareNo ratings yet
- Regional Trade Blocks Promote Economic GrowthDocument7 pagesRegional Trade Blocks Promote Economic GrowthSukumar ThamilmaniNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document5 pagesLecture 1TOLENTINO, Joferose AluyenNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument5 pagesIntroKalis WaranNo ratings yet
- Economic integration stages and objectivesDocument7 pagesEconomic integration stages and objectivesranjitsinghaNo ratings yet
- Arab Academy For Science Technology & Maritime Transport-MBADocument6 pagesArab Academy For Science Technology & Maritime Transport-MBAWessam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Final On Economic IntDocument10 pagesFinal On Economic IntVandanaNo ratings yet
- DEBUTON Assign1 FinalsDocument2 pagesDEBUTON Assign1 Finalsshems DebutonNo ratings yet
- DEBUTON Assign1 FinalsDocument2 pagesDEBUTON Assign1 Finalsshems DebutonNo ratings yet
- What is Economic IntegrationDocument2 pagesWhat is Economic IntegrationAmmad Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Economic Integration: Galin Stefanov, PHD D. A. Tsenov Academy of Economics, Svishtov, BulgariaDocument17 pagesEconomic Integration: Galin Stefanov, PHD D. A. Tsenov Academy of Economics, Svishtov, BulgariaAntonia Tat�No ratings yet
- Amity Law School: Economics ProjectDocument16 pagesAmity Law School: Economics Projectprithvi yadavNo ratings yet
- Economic Integration Is An Agreement Among Countries in A Geographic Region To Reduce and Ultimately RemoveDocument2 pagesEconomic Integration Is An Agreement Among Countries in A Geographic Region To Reduce and Ultimately RemoveNaveen Jacob JohnNo ratings yet
- Why Country Formed EIDocument5 pagesWhy Country Formed EIKalis WaranNo ratings yet
- IBT001Document7 pagesIBT001Necy AlbuenNo ratings yet
- Types of Economic IntegrationDocument18 pagesTypes of Economic IntegrationAshish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Trade Facilitation: ... An Introduction To The Basic Concepts and BenefitsDocument6 pagesTrade Facilitation: ... An Introduction To The Basic Concepts and BenefitsSangini24No ratings yet
- 5ITB Economic Integration Among CountriesDocument3 pages5ITB Economic Integration Among Countriesbrigitte.banitogNo ratings yet
- Free Trade Area: Diana TamayoDocument2 pagesFree Trade Area: Diana TamayoDianaTamayoNo ratings yet
- Stages of Economic Integration from Autarky to Fully Integrated Economic UnionDocument2 pagesStages of Economic Integration from Autarky to Fully Integrated Economic UnionLanphuong BuiNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic Groupings of The Oic CountriesDocument48 pagesRegional Economic Groupings of The Oic CountriesngayaNo ratings yet
- 6.regional Economic IntegrationDocument2 pages6.regional Economic IntegrationJelena LjubojevicNo ratings yet
- 4-Trading BlocksDocument6 pages4-Trading BlocksHenry dragoNo ratings yet
- Multi Layer Regional PactsDocument3 pagesMulti Layer Regional PactsHussain Mohi-ud-Din QadriNo ratings yet
- REGION IntegrationDocument16 pagesREGION IntegrationApu ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- AsianDocument1 pageAsiankamalsharaffNo ratings yet
- Agreement (FTA), Which Eliminates Tariffs, Import Quotas, and Preferences On Most (If NotDocument3 pagesAgreement (FTA), Which Eliminates Tariffs, Import Quotas, and Preferences On Most (If NotBandi VargaNo ratings yet
- Globalization and Regional Grouping: Amity Law SchoolDocument10 pagesGlobalization and Regional Grouping: Amity Law SchoolAarti MaanNo ratings yet
- Why services liberalization boosts economiesDocument4 pagesWhy services liberalization boosts economiesMariam MathenNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3a MARKET INTEGRATIONDocument16 pagesLESSON 3a MARKET INTEGRATIONTRISHA MAE DUMENCELNo ratings yet
- Regional Economic IntegrationDocument15 pagesRegional Economic IntegrationKaechelle Marie MorilloNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World 1Document15 pagesContemporary World 1Ciedelle Honey Lou DimaligNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Export-Led GrowthDocument10 pagesAdvantages of Export-Led Growthaman mittalNo ratings yet
- Forms of IntegrationDocument11 pagesForms of IntegrationOlgaNo ratings yet
- isayevDocument6 pagesisayevsingerngoctrinh657No ratings yet
- Module 4Document47 pagesModule 4bitbknNo ratings yet
- Regional Integration Defined and ExplainedDocument9 pagesRegional Integration Defined and ExplainedjashanNo ratings yet
- COMESA Customs Union Functions and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesCOMESA Customs Union Functions and ObjectivesEthel LunguNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Regional Economic IntegrationDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Regional Economic Integrationfrancis albaracinNo ratings yet
- The Advantages of International RelationsDocument5 pagesThe Advantages of International Relationsrafunzel nathalieNo ratings yet
- Meaning: Economic Integration Is The Unification of Economic Policies Between Different States ThroughDocument6 pagesMeaning: Economic Integration Is The Unification of Economic Policies Between Different States ThroughswatiNo ratings yet
- Political AssignmentDocument6 pagesPolitical AssignmentNoor ul emanNo ratings yet
- Case 3 Economic IntegrationDocument4 pagesCase 3 Economic IntegrationLina Marcela AlzateNo ratings yet
- Economic IntegrationDocument2 pagesEconomic IntegrationAlina BanuNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- NARL3 Ry WL Iuca KEJDocument5 pagesNARL3 Ry WL Iuca KEJdineshNo ratings yet
- Item No. Part No. Name of Part Material No. Reqd DescriptionDocument3 pagesItem No. Part No. Name of Part Material No. Reqd Descriptionmantilla7No ratings yet
- Draft Resolution TemplateDocument5 pagesDraft Resolution TemplateMuhammad ArielNo ratings yet
- HJKJK PDFDocument1 pageHJKJK PDFDocumentaries onlineNo ratings yet
- Komatsu 27R8-7Document264 pagesKomatsu 27R8-7ВикторNo ratings yet
- Orpys Львов Ukraine Online fassou.paradisiaque2018@gmai 621427888 Online fassou.paradisiaque2018@gmai 621427888Document1 pageOrpys Львов Ukraine Online fassou.paradisiaque2018@gmai 621427888 Online fassou.paradisiaque2018@gmai 621427888Fassou LamahNo ratings yet
- Invoice Letter 11 Nov 2021Document8 pagesInvoice Letter 11 Nov 2021Suvi AzkaNo ratings yet
- Investopedia Stock Simulator - Investopedia Stock Simulator - PortfolioDocument1 pageInvestopedia Stock Simulator - Investopedia Stock Simulator - PortfoliohpliveNo ratings yet
- Cma December, 2019 Examination Foundation Level Subject: 003. Quantitative TechniquesDocument4 pagesCma December, 2019 Examination Foundation Level Subject: 003. Quantitative TechniquesArafatNo ratings yet
- Business Environment in IndiaDocument4 pagesBusiness Environment in Indiarohitmahnot1989100% (2)
- Ricardian Model ExplainedDocument37 pagesRicardian Model ExplainedLiễu Uyên VũNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 My RoomDocument21 pagesUnit 2 My RoomSUIJI TVNo ratings yet
- FELIPE Week 7 Size ReductionDocument19 pagesFELIPE Week 7 Size ReductionRaymond FelipeNo ratings yet
- Hadee Lutful & Co.: Presented byDocument7 pagesHadee Lutful & Co.: Presented byColors of LifeNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement ReceiptDocument10 pagesAcknowledgement ReceiptLevinson RubioNo ratings yet
- S-56ACIT v. Narendra I BhuvaDocument16 pagesS-56ACIT v. Narendra I BhuvaeurokidsshastringrjodNo ratings yet
- Both The QueriesDocument2 pagesBoth The Querieskalumuri NivedhaNo ratings yet
- Garden Rail - N°291 - 2018-11Document64 pagesGarden Rail - N°291 - 2018-11Valery GagichNo ratings yet
- PropertyDocument6 pagesPropertyKarthick KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line Reliability and Security PDFDocument350 pagesTransmission Line Reliability and Security PDFgulatimanish1985No ratings yet
- Sirona Invoice 1702366155-93Document1 pageSirona Invoice 1702366155-93mugentsukiyomi31No ratings yet
- Proposal For Testing Services: 1) Water Test For Drinking/Domestic PurposeDocument2 pagesProposal For Testing Services: 1) Water Test For Drinking/Domestic Purposeexam robotNo ratings yet
- New Carens Price List 1-4-2022Document1 pageNew Carens Price List 1-4-2022Toyesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Best Illume Lights Spotlight FeaturesDocument16 pagesBest Illume Lights Spotlight FeaturesgemrisNo ratings yet
- Mini CerditaDocument6 pagesMini CerditaKaren OssesNo ratings yet
- Case EuroDisneyDocument28 pagesCase EuroDisneyEsthefania Rodriguez PalominoNo ratings yet
- Zomato BillDocument1 pageZomato Billhrh84v4j8kNo ratings yet
- Components of Dutiable ValueDocument25 pagesComponents of Dutiable ValueJemimah MalicsiNo ratings yet
- Suchitra Kanuparthi, Member (J) and Chandra Bhan Singh, Member (T)Document17 pagesSuchitra Kanuparthi, Member (J) and Chandra Bhan Singh, Member (T)himeesha dhiliwalNo ratings yet
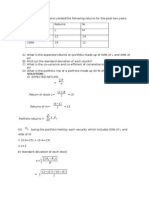
- Stocks Land M Have Yielded The Following Returns For The Past Two YearsDocument4 pagesStocks Land M Have Yielded The Following Returns For The Past Two YearsDharmendra Behera75% (4)