Professional Documents
Culture Documents
It All Started With A Big Bang!: Learning Activity Sheets
Uploaded by
nicOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
It All Started With A Big Bang!: Learning Activity Sheets
Uploaded by
nicCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEETS
GRADE 11/12 – PHYSICAL SCIENCE
Name: Date: Rating/Score:
IT ALL STARTED WITH A BIG BANG!
Part I: Stellar Crossword.
Directions: Fill out the crossword puzzle using the clues provided below.
3 4
6 7
10
Across Down
3 A model of the early universe; It 1 The element forms when two hydrogen
explains the continuous expansion isotopes fuse
of the universe 2 The element from space that is pulled by
6 Atoms of the same atomic number gravity to turn into a protostar
but of different atomic mass 4 A device used to speed up the protons to
8 The number of protons in an atom overcome the repulsion between the
Atomic _________ protons and the target atomic nuclei;
9 Refers to the elements with proton Particle _________
number greater than 92 5 The formation of the capture of free
10 The formation of new nuclei in the electrons by the cations in a plasma
early stages of the development of 7 A one-dimensional point where all
the universe matters and density are concentrated
Specific Week: Week 1 (LAS 1)
Target Competencies: Give evidence for and describe the formation of heavier elements during star formation
and evolution (S11/12PS-IIIa-2); Explain how the concept of atomic number led to the
synthesis of new elements in the laboratory (S11/12PS-IIIb-11)
(This is a Government Property. Not for Sale.)
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEETS
GRADE 11/12 – PHYSICAL SCIENCE
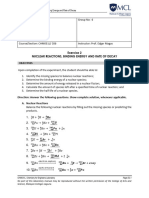
Part II: Trace the Reaction!
A. Directions: Trace the nuclear reactions happening in an average star during proton-
proton chain reaction by completing the following nuclear equations. Answer the
questions that follow.
1
1
1H + 11H → ___ + +10e + ν 1H + 11H → ___ + +10e + ν
e+ ν e+ ν
2
2
1H + 11H → ___ + γ 1H + 11H → ___ + γ
γ γ
3 3 1 1
2He + 2He → ___ + 1H + 1H
Legend:
Proton Neutron e+ Positron ν Neutrino γ Gamma Ray
Guide Questions:
1. What are the products formed and emitted when two protons fuse?
2. What will be formed when a protium and a deuterium fuse together?
3. Which isotope of helium is the final product of proton-proton chain reaction?
4. How does an electron differ from a positron?
5. Why is proton-proton chain reaction important in stellar formation and evolution?
Specific Week: Week 1 (LAS 1)
Target Competency: Give evidence for and describe the formation of heavier elements during star formation
and evolution (S11/12PS-IIIa-2)
(This is a Government Property. Not for Sale.)
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEETS
GRADE 11/12 – PHYSICAL SCIENCE
B. Directions: Trace the nuclear reactions happening in a massive star during Carbon-
Nitrogen-Oxygen (CNO) cycle by completing the following nuclear equations. Briefly
discuss what happens in each reaction.
1 12
2 13
6C + ___ → 137N + γ 7N → ___ + +10e + ν
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
4 3 13
___ + 1
1H →
15
8O +γ 6C + 11H → ___ + γ
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
5 6 15 12
15
8O → 157N + ___ + ν 7N + 11H → ___ + 6C
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
_____________________________ _____________________________
Guide Questions:
1. What is the common end-product of proton-proton chain reaction and CNO cycle?
2. Why is CNO cycle important in stellar formation and evolution?
Specific Week: Week 1 (LAS 1)
Target Competency: Give evidence for and describe the formation of heavier elements during star formation
and evolution (S11/12PS-IIIa-2)
(This is a Government Property. Not for Sale.)
LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEETS
GRADE 11/12 – PHYSICAL SCIENCE
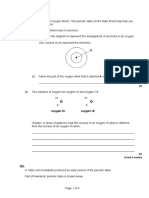
Part III: What’s My Number?
Directions: Complete the table provided below. Answer the questions that follow.
Element/ Atomic Mass Element/ Atomic Mass
Isotope Number Number Isotope Number Number
Hydrogen-1 1 1 Carbon-12 ___ 12
Hydrogen-2 1 ___ Carbon-13 6 13
Hydrogen-3 1 3 Carbon-14 6 ___
Helium-3 2 3 Uranium-235 92 235
Helium-4 2 ___ Uranium-238 92 ___
Guide Questions:
1. Define isotopes in terms of atomic number and mass number.
2. How is atomic number related to the identity of the atom?
3. What might happen if the relationship between atomic number and the identity of the atom
is not established?
EXIT SLIP
How does the lesson change your view about the Big Bang Theory?
Specific Week: Week 1 (LAS 1)
Target Competency: Explain how the concept of atomic number led to the synthesis of new elements in the
laboratory (S11/12PS-IIIb-11)
(This is a Government Property. Not for Sale.)
You might also like
- 15 Day Detox ChallengeDocument84 pages15 Day Detox ChallengeDanii Supergirl Bailey100% (4)
- Workbook Group TheoryDocument62 pagesWorkbook Group TheoryLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Delusion in SocietyDocument2 pagesDelusion in SocietyGasimovskyNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 GranulopoiesisDocument9 pagesLecture2 GranulopoiesisAfifa Prima GittaNo ratings yet
- Leadership Styles-Mckinsey EdDocument14 pagesLeadership Styles-Mckinsey EdcrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- Core ValuesDocument1 pageCore ValuesIan Abel AntiverosNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument7 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha SolomonNo ratings yet
- SDO Navotas GenChem2 SHS 1st2ndsem - FVDocument100 pagesSDO Navotas GenChem2 SHS 1st2ndsem - FVAborita KenshienNo ratings yet
- Activity On Noli Me TangereDocument5 pagesActivity On Noli Me TangereKKKNo ratings yet
- Ions and Isotopes PracticeDocument3 pagesIons and Isotopes PracticeJhey EmNo ratings yet
- Phy Sci PrelimDocument3 pagesPhy Sci PrelimMa'am DonnaNo ratings yet
- 1 Laws Physcie 1STQTRDocument5 pages1 Laws Physcie 1STQTRKayzelle RefamonteNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Physical Science Module UpdatedDocument52 pagesQuarter 3 Physical Science Module UpdatedansalerochNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 Physical Science Module UpdatedDocument52 pagesQuarter 3 Physical Science Module UpdatedNica Angela Anzures HUMSS 10BNo ratings yet
- Physical Science SummativeDocument3 pagesPhysical Science Summativejannette jane davidNo ratings yet
- 17Document5 pages17chelcea estrabelaNo ratings yet
- San Miguel Village School 2 Periodical Examination Science Grade 9-HumilityDocument2 pagesSan Miguel Village School 2 Periodical Examination Science Grade 9-HumilityChristian Jaylo HambreNo ratings yet
- G6 - Term 3 - Final Exam - Revision PackDocument26 pagesG6 - Term 3 - Final Exam - Revision Packelhassan.ali2020No ratings yet
- Phy Sci CH 1 QuizDocument4 pagesPhy Sci CH 1 QuizAlv CoperoNo ratings yet
- 4th Sequence Chemistry BonchouDocument3 pages4th Sequence Chemistry BonchouNgah Lilwaine MNo ratings yet
- 1ST Summ 1ST QTRDocument3 pages1ST Summ 1ST QTRmanilynmugatarNo ratings yet
- Two-Fold Numerical Solutions and Simulation of A Double PendulumDocument6 pagesTwo-Fold Numerical Solutions and Simulation of A Double PendulumInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangeDocument2 pagesPhase ChangeKiara LorenaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics Summary Notes: Atomic StructureDocument2 pagesNuclear Physics Summary Notes: Atomic StructureShelly AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument11 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- GenPhy Q2 Module3Document16 pagesGenPhy Q2 Module3mccloud2ordenizaNo ratings yet
- C3 Atomic Structure 2Document57 pagesC3 Atomic Structure 2Cassandra mwangiNo ratings yet
- 2022 FinalDocument4 pages2022 Finaljaychoi67No ratings yet
- Study On The Atomic Term Symbols For F (M Free Ion) ConfigurationDocument9 pagesStudy On The Atomic Term Symbols For F (M Free Ion) ConfigurationbbtbadalNo ratings yet
- SHS - 2020 2021 - Q1 Law - W1 2 - Physical Science FinalDocument8 pagesSHS - 2020 2021 - Q1 Law - W1 2 - Physical Science FinalKayzelle RefamonteNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure EWDocument7 pagesAtomic Structure EWMagical UnicornNo ratings yet
- Science 9 ChemistryDocument3 pagesScience 9 ChemistryBenedick Zorilla ZaspaNo ratings yet
- CHM031L - Exercise 2 - Group 6Document5 pagesCHM031L - Exercise 2 - Group 6Prince KJNo ratings yet
- Physical Science QuizDocument2 pagesPhysical Science QuizApril Mae ArcayaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Periodic Trends ActivityDocument6 pagesChemistry Periodic Trends ActivityocNo ratings yet
- Oxygen-16 Oxygen-18Document9 pagesOxygen-16 Oxygen-18Mohammed Rabee alzaabiNo ratings yet
- MIT5 35F12 Module 2LS1Document9 pagesMIT5 35F12 Module 2LS1Angela StefanNo ratings yet
- Solving Numerically Ermakov-Type Equation For Newtonian Cosmology Model With VortexDocument7 pagesSolving Numerically Ermakov-Type Equation For Newtonian Cosmology Model With VortexScience DirectNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM - PHY SCI Set ADocument4 pagesMIDTERM - PHY SCI Set ANini VillezaNo ratings yet
- PPE Prep Qs Year 10Document11 pagesPPE Prep Qs Year 10Methyl OrangeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Higher Past Papers by TopicDocument334 pagesAdvanced Higher Past Papers by TopicSkandar TajNo ratings yet
- Exercises PolsDocument8 pagesExercises PolsAshutosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 3RD Periodcial ExamDocument3 pages3RD Periodcial ExamAileen gay PayunanNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 DynamicsDocument4 pagesQuiz 2 DynamicsIrina StefaniaNo ratings yet
- Polar BondsDocument8 pagesPolar BondsAnthony JohanNo ratings yet
- Chem 12123123Document4 pagesChem 12123123ZombieSlayer1730No ratings yet
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Chem 2nd Quarter w4 w5Document28 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET Chem 2nd Quarter w4 w5ilostmyselfintothewoodsNo ratings yet
- Physics Stellar Evolution: NameDocument10 pagesPhysics Stellar Evolution: Nameglobal chronic careNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesPhysical Science Midterm ExamManuel Paulo AcogidoNo ratings yet
- SHS Sy2021-2022 Q3law W1-2 General-Chemistry-ValidatedDocument8 pagesSHS Sy2021-2022 Q3law W1-2 General-Chemistry-Validatedjohnrobertdeocampo84No ratings yet
- Midterm 2Document10 pagesMidterm 2timNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Q3 - Las 4 RTPDocument4 pagesScience 8 - Q3 - Las 4 RTPAprilyn CollanoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Iit Jee Formula Page 1 5Document5 pagesChemistry Iit Jee Formula Page 1 5maddy449No ratings yet
- 3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NameDocument81 pages3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NamesuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- Summative Test 1&2Document2 pagesSummative Test 1&2Jessa Mae CasipongNo ratings yet
- SLG HomeworkDocument12 pagesSLG HomeworkMethyl OrangeNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicDocument21 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicdissaoctafianellisNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Atomic StructurearyanNo ratings yet
- Year 5 Finals Assessment ScienceDocument7 pagesYear 5 Finals Assessment ScienceSarah KhanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Week CLEDocument8 pages2nd Quarter Week CLEchino chanNo ratings yet
- Grav PhetDocument3 pagesGrav PhetpiaNo ratings yet
- GR 9 NS November Exam 2023Document10 pagesGR 9 NS November Exam 2023kotolograceNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Angular Momentum: UIC Physics Department Physics 141 Laboratory ManualDocument4 pagesConservation of Angular Momentum: UIC Physics Department Physics 141 Laboratory ManualDeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 18 19 Modern Chemistry Online Chapter 5 Study Guide Review PDFDocument6 pages18 19 Modern Chemistry Online Chapter 5 Study Guide Review PDFAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- 6.1.e Ox-Red WSDocument9 pages6.1.e Ox-Red WSscispenceNo ratings yet
- Cooperative Learning: Complied By: ANGELICA T. ORDINEZADocument16 pagesCooperative Learning: Complied By: ANGELICA T. ORDINEZAAlexis Kaye GullaNo ratings yet
- CV Augusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaDocument4 pagesCV Augusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaAugusto Brasil Ocampo MedinaNo ratings yet
- Oxford EAP B1 Pre-Intermediate Student - S Book 2Document167 pagesOxford EAP B1 Pre-Intermediate Student - S Book 2Thư Dương Thị AnhNo ratings yet
- Bolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartDocument2 pagesBolt Grade Markings and Strength ChartGregory GaschteffNo ratings yet
- Nanolithography - Processing Methods PDFDocument10 pagesNanolithography - Processing Methods PDFNilesh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- ELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1Document10 pagesELEVATOR DOOR - pdf1vigneshNo ratings yet
- Week-3-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-11-15-DllDocument12 pagesWeek-3-Q1-Gen Chem-Sep-11-15-DllJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- Siemens Make Motor Manual PDFDocument10 pagesSiemens Make Motor Manual PDFArindam SamantaNo ratings yet
- Micro Lab Midterm Study GuideDocument15 pagesMicro Lab Midterm Study GuideYvette Salomé NievesNo ratings yet
- Apron CapacityDocument10 pagesApron CapacityMuchammad Ulil AidiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - ReviewerDocument6 pagesLesson 3 - ReviewerAdrian MarananNo ratings yet
- What Are The Spacer Bars in RC Beams - QuoraDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Spacer Bars in RC Beams - QuoradesignNo ratings yet
- EqualLogic Release and Support Policy v25Document7 pagesEqualLogic Release and Support Policy v25du2efsNo ratings yet
- Continue Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesDocument7 pagesContinue Practice Exam Test Questions Part 1 of The SeriesKenn Earl Bringino VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Latched, Flip-Flops, and TimersDocument36 pagesLatched, Flip-Flops, and TimersMuhammad Umair AslamNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedDocument4 pagesQuarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedJigz FamulaganNo ratings yet
- Jakub - BaZi CalculatorDocument3 pagesJakub - BaZi Calculatorpedro restinxNo ratings yet
- Literatura Tecnica 3Document10 pagesLiteratura Tecnica 3Christian PerezNo ratings yet
- QuexBook TutorialDocument14 pagesQuexBook TutorialJeffrey FarillasNo ratings yet
- Physics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Document1 pagePhysics Blue Print 1 Class XI Half Yearly 23Nilima Aparajita SahuNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1Document3 pagesPerformance Task 1Jellie May RomeroNo ratings yet
- India TeenagersDocument3 pagesIndia TeenagersPaul Babu ThundathilNo ratings yet
- The Covenant Taken From The Sons of Adam Is The FitrahDocument10 pagesThe Covenant Taken From The Sons of Adam Is The FitrahTyler FranklinNo ratings yet