Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lab Albinism Biology - Canizales - 1 (A) - HSC01Y-1001 - S2
Lab Albinism Biology - Canizales - 1 (A) - HSC01Y-1001 - S2
Uploaded by
Arijan SchiffererOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lab Albinism Biology - Canizales - 1 (A) - HSC01Y-1001 - S2
Lab Albinism Biology - Canizales - 1 (A) - HSC01Y-1001 - S2
Uploaded by
Arijan SchiffererCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology - Canizales - 1(A) … Quizzes Lab: Albinism
Lab: Albinism
Due Mar 8 at 3pm Points 30 Ques!ons 17
Available a"er Mar 7 at 12am Time Limit None Allowed A"empts 3
Instruc!ons
HS.L3U1.25:
I can evaluate how mistakes during DNA replica!on can cause muta!ons.
I can explain the impacts of DNA muta!ons such as gene!c varia!on, adapta!ons, and gene!c
disorders.
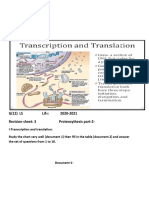
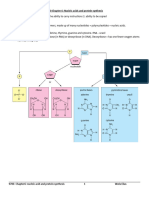
Direc!ons: In this ac!vity, you will learn about transcrip!on and transla!on, the process
that makes proteins! As you work through this assignment, you will also explore the
different muta!ons that can occur that result in albinism.
Take the Quiz Again
A#empt History
A"empt Time Score
LATEST A#empt 1 67 minutes 17.73 out of 30 *
* Some ques!ons not yet graded
Correct answers are hidden.
Score for this a#empt: 17.73 out of 30 *
Submi#ed Mar 7 at 9:39pm
This a#empt took 67 minutes.
Ques!on 1 1 / 1 pts
Transcrip!on is the process by which DNA is "read" by
messenger RNA (mRNA). mRNA obtains the message from DNA
for making proteins and carries the message to the ribosomes to
make proteins. In transcrip!on, mRNA copies the message in its
own unique language.
Normally when DNA is copied by DNA, the base adenine (A)
pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) with guanine (G); A-T
and C-G.
In RNA, there is no thymine, instead there is uracil (U)! In RNA,
the base pairs are as follows A-U and C-G.
When DNA is transcribed, A in DNA will transcribe into U in
RNA, but T in DNA will transcribe to A in RNA. C and G will
transcribe with each other.
See the example below: (keep this handy!)
DNA A T C G
mRNA U A G C
Check for understanding!
Transcribe the following: (do not include spaces!! Not case
sensi!ve)
DNA CAT
mRNA ???
GUA
Ques!on 2 1 / 1 pts
A"er the DNA has been transcribed (the message read and
copied) by mRNA, the message is then carried to the ribosomes
to be translated. Transla!on is the process by which proteins are
made following the message that was obtained by mRNA.
(Remember that the mRNA acts as a messenger for the DNA?) In
transla!on, ribosomes obtain the message from mRNA and
literally "translate" the message. If mRNA says "UAU", then that
message translates to the amino acid "tyrosine (tyr)".
The mRNA base pairs are read in codons, by groups of 3. If
mRNA has "UAUCGG", then the codons are read as "UAU-CGG".
This mRNA will result in the amino acids "tyr-arg". Amino acid
"tyr" for codon "uau" and "arg" for codon "cgg".
Many amino acids will eventually be put together to make a
protein that will result in your phenotype (physical appearance)!
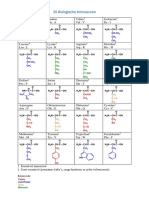
Since we are not tRNA, we will use an amino acid diagram (see
below) to help us translate the mRNA.
DNA TAT ACG
AUA
mRNA (first base
pair is "A", UGC
(transcrip!on)
second is "U",
third is "A")
amino acid
ile cys
(transla!on)
Check for understanding!
Translate the following
DNA CAT
mRNA GUA
amino acid ???
val
Ques!on 3 1 / 1 pts
Muta!ons occur frequently during the replica!on or
transcrip!on of DNA. Some muta!ons can lead to different
proteins to be created because the "message" has been messed
up, coding for another amino acid. Such muta!ons that can mess
up a message are inser!ons and dele!ons. These type of
muta!ons create a shi" in the reading frame (frameshi"
muta!on), thus the original codon will be shi!ed crea!ng a
different codon, thus a new message.
mRNA codons amino acids
original mRNA AUA-UGC-CCA ile-cys-pro
AUA-AUG-
inser!on CCC-A (inserted ile-met-pro
A)
AUA-GCC-CA
dele!on ile-ala
(deleted U)
Check for understanding!
What kind of frameshi" muta!on occurred below?
original UUUAGCUAU
muta!on UUAGCUAU
dele!on
nice! the 3rd "U" was deleted
inser!on
Ques!on 4 1 / 1 pts
Another type of muta!on that can occur is a subs!tu!on. Some
subs!tu!ons will result in a different amino acid, and some
subs!tu!ons will remain coding for the same amino acid as the
regular. If the subs!tu!on does not change the amino acid, then
the muta!on is considered "silent".
mRNA amino
sequence acids
ile-
original AUAUGCCCA cys- original
pro
different
met-
muta!on codon,
AUGUGCCCA cys-
1 different
pro
amino acid
silent
muta!on/no
ile- change in
muta!on
AUUUGCCCA cys- amino
2
pro acid/same
amino acids
as original
Check for understanding!
Which muta!on has a more drama!c effect on a protein?
inser!on/dele!ons because they shi" reading frames, rearranging whole
codons
subs!tu!ons because they affect a small point of a codon
Ques!on 5 2 / 2 pts
Individual 1 has a muta!on in the TYR (OCA1) gene.
The following original DNA strand is for gene TYR (OCA1):
TACGAGGACCGACAAAACATGACGGACGACACCTCAAAGGTCTGGAGGCGACC
Transcribe and translate the following original DNA. The first
codon has been done for you.
original
TAC GAG GAC
DNA
CUC CUG
mRNA AUG
amino leu leu
met
acids
**no spaces!! spelling counts! le#ers only!! For amino acids, you
can write the 3 le#er word (i.e. "met" for methionine) or the
en!re word (i.e. "methionine")
Answer 1:
cuc
Answer 2:
cug
Answer 3:
leu
Answer 4:
leu
Incorrect Ques!on 6 0 / 3 pts
The following is for gene TYR (OCA1):
original DNA: ACGGACGACACC
mutated DNA: ACGACGACACC
Transcribe and translate the mutated DNA.
mutated ACG ACG CAC
mRNA
amino thr thr his
acid
**no spaces!! spelling counts! le#ers only!! For amino acids, you
can write the 3 le#er word (i.e. "val" for valine) or the en!re
word (i.e. "valine")
22-23 - Mountain Ridge High…
Home
Announcements
Account Modules
Google Drive
Dashboard
SchoolCity Student
Grades 46
Courses
StudyMate
Calendar Student Tech Tips
Inbox
History
Studio
Help Answer 1:
ACG
Answer 2:
ACG
Answer 3:
CAC
Answer 4:
thr
Answer 5:
thr
Answer 6:
his
Ques!on 7 1 / 1 pts
What kind of muta!on occurred in individual 1's OCA1? Select 2
answers
original DNA: ACGGACGACACC
mutated DNA: ACGACGACACC
inser!on
dele!on
silent
frameshi"
subs!tu!on
Ques!on 8 1 / 1 pts
What kind of muta!on occurred here?
original DNA: GTAAAG
mutated DNA: GTTAAG
dele!on
inser!on
subs!tu!on
Ques!on 9 1 / 1 pts
Study the 2 DNA strands below:
original DNA GAGGAC
mRNA CUCCUG
amino acid leu-leu
mutated DNA GAGAAC
mRNA CUCUUG
amino acid leu-leu
What kind of muta!on occurred? select all that apply
frameshi"
neither
dele!on
inser!on
subs!tu!on
silent
Ques!on 10 1 / 1 pts
Study the 2 DNA strands below:
original DNA GAGGAC
mRNA CUCCUG
amino acid leu-leu
mutated DNA GAGAAC
mRNA CUCUUG
amino acid leu-leu
Which codon in the original DNA was affected?
GAC
GGA
GAGGAC
AGG
GAG
Ques!on 11 1 / 1 pts
Study the 2 DNA strands below for the TYRP-1 (OCA3) gene:
original DNA CTGAATTC
mRNA GACUUAAG
mutated DNA CTGTAATTC
mRNA GACAUUAAG
What kind of muta!on did individual 3 have? select all that
apply
You might also like
- Pre Test AnswersDocument3 pagesPre Test AnswersJohn Van Dave TaturoNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillDocument32 pagesProtein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillIMY PAMEROYANNo ratings yet
- Sequencing TechnologiesDocument25 pagesSequencing TechnologiesOhhh OkayNo ratings yet
- Video Recap of Dna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis by Amoeba Sisters 2Document2 pagesVideo Recap of Dna Vs Rna and Protein Synthesis by Amoeba Sisters 2api-2331875660% (2)
- ReplicationDocument45 pagesReplicationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- USMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideDocument137 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Biochemistry - Side by SideMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- I. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and GenesDocument12 pagesI. DNA, Chromosomes, Chromatin, and GeneshanzNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4&5 PDFJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Nesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 10th Edition Denise Anderson Sarah Salm Eugene NesterDocument9 pagesSolution Manual For Nesters Microbiology A Human Perspective 10th Edition Denise Anderson Sarah Salm Eugene NesterChristianColemannsja100% (38)
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- COT No. 2Document4 pagesCOT No. 2Rina RomanoNo ratings yet
- Fold Your Own DNADocument4 pagesFold Your Own DNANatividad Moreno RascónNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis (Gene Expression)Document63 pagesProtein Synthesis (Gene Expression)jaybeeclaireNo ratings yet
- Assesment For Dna and RnaDocument1 pageAssesment For Dna and RnaJemebel NosaresNo ratings yet
- Lab Albinism Biology - Canizales - 1 (A) - HSC01Y-1001 - S2 2Document1 pageLab Albinism Biology - Canizales - 1 (A) - HSC01Y-1001 - S2 2Arijan SchiffererNo ratings yet
- Transcription MsDocument12 pagesTranscription Msapi-44119921No ratings yet
- Protein-SynthesisDocument57 pagesProtein-SynthesisMA. FRITZIE DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Day 4Document8 pagesDay 4Kinberly AnnNo ratings yet
- Class 12 - Genetics NotesDocument1 pageClass 12 - Genetics NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument85 pagesTranscription and Translation: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionClydeNo ratings yet
- Week 1 of IGEMDocument68 pagesWeek 1 of IGEMXuejing DuNo ratings yet
- 3 57 3dnatranscription 090907150155 Phpapp02Document12 pages3 57 3dnatranscription 090907150155 Phpapp02Dev AshwaniNo ratings yet
- CENTRAL DOGMADocument14 pagesCENTRAL DOGMASecond BooksNo ratings yet
- HABB 213 Overal NotesDocument67 pagesHABB 213 Overal NotesAmandaNo ratings yet
- Genomics WondeDocument80 pagesGenomics WondezafuNo ratings yet
- IB BiologyDocument12 pagesIB BiologyMaria Corazon Leonor OtawaNo ratings yet
- 10 Gene Expression LecturesDocument61 pages10 Gene Expression LecturesTererai Lalelani Masikati HoveNo ratings yet
- RNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesRNA and Protein Synthesis WorksheetJo JoNo ratings yet
- 2.2 (Grade 8-Lesson 9 - PPT)Document60 pages2.2 (Grade 8-Lesson 9 - PPT)adelainne.mtNo ratings yet
- COMPETANCE BASED QUESTION Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument9 pagesCOMPETANCE BASED QUESTION Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceKarthika UmashankarNo ratings yet
- 2nd Bio AssgnmntDocument6 pages2nd Bio AssgnmntNitinmanubanshNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet: Science (Quarter III - Week 4)Document10 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet: Science (Quarter III - Week 4)MARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- From Genes To ProteinsDocument32 pagesFrom Genes To ProteinsVanessa QuinolNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument21 pagesProtein SynthesisAnthony MoloneyNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument3 pagesProtein Synthesis423003157No ratings yet
- Overview of Translation (Article) Khan AcademyDocument8 pagesOverview of Translation (Article) Khan AcademyMaria LoaizaNo ratings yet
- Biology 97 Extensive Study GuideDocument17 pagesBiology 97 Extensive Study GuidepwnageownsuNo ratings yet
- Transcription and TranslationDocument16 pagesTranscription and TranslationParth MishraNo ratings yet
- Gene ExpressionDocument46 pagesGene Expressionmohammed mahmoudNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Protein SynthesisDocument77 pages4.5 Protein SynthesisJagaηηath ΚabiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DNA Is The Genetic Material RNADocument49 pagesNucleic Acids: DNA Is The Genetic Material RNAAaron CzikNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 30oct13Document41 pagesLecture - 30oct13Dagon BrownNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis With Video LinksDocument31 pagesProtein Synthesis With Video LinksSmilingNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience Reviewerkarljosefdelacruz1017No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument26 pagesProtein SynthesisMary Jane M. MorenoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Transcription and Post Transcription ModificationsDocument73 pagesLecture 4 - Transcription and Post Transcription ModificationskibzwanjikuNo ratings yet
- General Biology TranscriptionDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology TranscriptionChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 4Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- RNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDDocument7 pagesRNA Protein Synthesis Gizmo COMPLETEDcokcreNo ratings yet
- 03 - 05 Transcription and Translation AssignmentDocument2 pages03 - 05 Transcription and Translation AssignmentKeara RaleighNo ratings yet
- 4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - TranscriptionDocument19 pages4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - Transcriptionlilpidas54No ratings yet
- Transcription & Translation Notes PDFDocument20 pagesTranscription & Translation Notes PDFManas RjNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument28 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- BS10003 - Transcription and Translation - December 2020Document38 pagesBS10003 - Transcription and Translation - December 2020dhiraj moreNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet 3 GDocument4 pagesRevision Sheet 3 GJoelle AssafNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 BIO 1510Document34 pagesChapter 15 BIO 1510Chachi CNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Guided Notes #2Document45 pagesUnit 6 Guided Notes #225210580No ratings yet
- Class 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDocument4 pagesClass 12-UNITS 3-4 NotesDimas HernadyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaDocument51 pagesLecture 4 - Mechanism of Transcription in BacteriaBakalJenazahNo ratings yet
- Translation Notes SheetDocument5 pagesTranslation Notes SheetKelsey BakerNo ratings yet
- Science of Living System: Arindam MondalDocument48 pagesScience of Living System: Arindam MondalSohini RoyNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Life: Transcription and TranslationDocument13 pagesCentral Dogma of Life: Transcription and TranslationLamia AkterNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentDocument27 pagesProtein Synthesis: ADA School Biology DepartmentAydan BadalliNo ratings yet
- M.I.T LessonsDocument12 pagesM.I.T LessonsChassy KammyNo ratings yet
- Protien SynthesisDocument20 pagesProtien Synthesisapi-277471896No ratings yet
- 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis: 1 FocusDocument7 pages12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis: 1 FocusMark HortizuelaNo ratings yet
- Biology Core Practical 6.1 DNA Amplification Using PCRDocument2 pagesBiology Core Practical 6.1 DNA Amplification Using PCRBenedicte Symcox100% (1)
- Antisense Oligonucleotide Biotechnology, Applications and FutureDocument29 pagesAntisense Oligonucleotide Biotechnology, Applications and FuturesurojitarpitaNo ratings yet
- Color Plates (1-60)Document12 pagesColor Plates (1-60)Gayle BocalaNo ratings yet
- PCR TouchdownDocument3 pagesPCR TouchdownDeepak Ranjan SahooNo ratings yet
- The Key Difference Between Essential and NonDocument2 pagesThe Key Difference Between Essential and NonRafael CurtesNo ratings yet
- CH 12 DNA Genetic Material PDFDocument93 pagesCH 12 DNA Genetic Material PDFasaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. The Three Suggested Models of DNA Replication. Grey Indicates The Original DNA Strands, and Blue Indicates Newly Synthesized DNADocument6 pagesFigure 1. The Three Suggested Models of DNA Replication. Grey Indicates The Original DNA Strands, and Blue Indicates Newly Synthesized DNAKempetsNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Fatty Acids Levels of Freeze-Dried Termite Queen Macrotermes Gilvus Hagen Using Gas Chromatography-Mass SpectrometryDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Fatty Acids Levels of Freeze-Dried Termite Queen Macrotermes Gilvus Hagen Using Gas Chromatography-Mass SpectrometryHarrizul RivaiNo ratings yet
- Bio PDF 1Document7 pagesBio PDF 1Shin3 KimNo ratings yet
- PCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocument5 pagesPCR and Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisEamon Barkhordarian100% (1)
- Biochemistry JSS Medical College: DR - Prashant VishwanathDocument68 pagesBiochemistry JSS Medical College: DR - Prashant VishwanathAravind VPNo ratings yet
- 9700 Chapter 6 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Study SheetDocument21 pages9700 Chapter 6 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Study Sheetwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- SsoFast EvaGreen - QuickGuide - August 2009Document2 pagesSsoFast EvaGreen - QuickGuide - August 2009dnajenNo ratings yet
- Probes and Primer Design Using Primer ExpressDocument15 pagesProbes and Primer Design Using Primer Expressbiosynthesis12No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 BT3040: Fathima Bensha M BS20B015Document7 pagesAssignment 1 BT3040: Fathima Bensha M BS20B015fathimabenshaNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: RNA and Protein SynthesisjNo ratings yet
- 20 Biologische Aminozuren: Asparaginezuur Asp DDocument2 pages20 Biologische Aminozuren: Asparaginezuur Asp Detienne.jooken8734No ratings yet
- Alien EncountersDocument5 pagesAlien EncountersHaley Hamill50% (2)
- Copy of BuildingDNASEDocument5 pagesCopy of BuildingDNASECARSON SCHMIDTNo ratings yet
- 06.11.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A&B) - Jee - Adv - 2018 - P1 - PTA-7 - KEY & SOLDocument12 pages06.11.22 - SR - STAR CO-SC (MODEL-A&B) - Jee - Adv - 2018 - P1 - PTA-7 - KEY & SOLOrganic PrasadNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code Introduction PDFDocument10 pagesGenetic Code Introduction PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Real Time PCRDocument4 pagesReal Time PCRRASHMI SINGHNo ratings yet