Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bon 7
Uploaded by
Harold Hardy Godfrey0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageBon 7
Uploaded by
Harold Hardy GodfreyCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
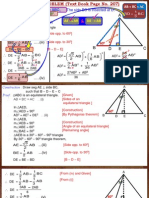
Let ABCD be a tetrahedron.
Prove that a=BC 2 + A D 2, b=C A2 + B D2, c= A B2 +C D2 are the
sides of a triangle. For which tetrahedron is this triangle equilateral?
Solution:
(I) Assume that a+ c ≤ b ⇔ B C 2+ A D2 + A B2 +C D2 ≤ C A 2+ B D2
⇔¿
⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗
⇔ A C 2−2 AC . AB + A B 2+ A D2 + A B2 + A D 2−2 AD . AC + A C 2 ≤ A C2 + A D2−2 AD . AB + A B2
⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗
⇔ ¿⇔ ¿(a contradiction: AB + AD − AC ≠ Oas ABCD is a tetrahedron)
Therefore, a + c > b. By the same argument, we get a + b > c and b + c > a. Therefore a, b, c
are the sides of a triangle
( II) a, b, c are the sides of an equilateral triangle ⇔ a=b=c
⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗ ⃗
a=b ⇔ B C 2+ A D2 =A B2 +C D2 ⇔ ¿⇔ AC (BC + BA )−AC ( DA + DC )=0
⃗ ⃗
⇔ AC . BD =0 ⇔ AC ⊥ BD By the same argument, we have b=c ⇔ BC ⊥ AD . Therefore,
ABCD is a Orthocentric tetrahedron
You might also like
- Bon 7Document1 pageBon 7Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Bon 7Document1 pageBon 7Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Apmo2022 SolDocument8 pagesApmo2022 SolShah Ahmed JubaerNo ratings yet
- 10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFDocument11 pages10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFAntonio Torres PeñaNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument11 pagesPythagoras Theoremss_733390583No ratings yet
- 3RD Term S2 MathematicsDocument31 pages3RD Term S2 MathematicsAdelowo DanielNo ratings yet
- Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2015: Junior Section ImportantDocument6 pagesHanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2015: Junior Section ImportantHung Son NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2015: Junior Section ImportantDocument6 pagesHanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2015: Junior Section ImportantApoorvaNo ratings yet
- Olympiad 2019 Geometry NotesDocument51 pagesOlympiad 2019 Geometry NotesDeepMath2006No ratings yet
- A Condition For A Circumscriptible Quadrilateral To Be CyclicDocument5 pagesA Condition For A Circumscriptible Quadrilateral To Be CyclicLuka KukricNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Olympiad, GeometryDocument18 pagesMathematics Olympiad, GeometryPrashant BhattNo ratings yet
- NS 4u Inequality Handout SolnDocument28 pagesNS 4u Inequality Handout SolnAlexander XieNo ratings yet
- MENSURATION Foundation BatchDocument68 pagesMENSURATION Foundation BatchDarvesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mensuration II (Important Results)Document13 pagesMensuration II (Important Results)Shubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- 373PR 02Document2 pages373PR 02George BasilaiaNo ratings yet
- AMM10930Document1 pageAMM10930이건행No ratings yet
- Solution of TrianglesDocument35 pagesSolution of TrianglesSankar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine RuleDocument4 pagesSine and Cosine RuleLeslie4892No ratings yet
- MC35 Geometry Ch10 Handout-209Document5 pagesMC35 Geometry Ch10 Handout-209SCARLETT CARSONNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument8 pagesPythagoras TheoremNur Ainaa MahayudinNo ratings yet
- TriangleDocument2 pagesTrianglehardikvimal52No ratings yet
- KV N JNVDocument4 pagesKV N JNVasb1922010No ratings yet
- Triangles SA1Document10 pagesTriangles SA1Daksh Bhardwaj VIII-A Roll No 2No ratings yet
- CBSE IX Congruence of Triangle Solved QuestionsDocument9 pagesCBSE IX Congruence of Triangle Solved Questionshimanshi swamiNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Oblique TrianglesDocument55 pagesSolutions of Oblique TrianglesElmer Kenneth100% (1)
- APMO 2013 - SolutionsDocument4 pagesAPMO 2013 - SolutionsQuang ĐàtNo ratings yet
- Solutions To The 80th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 7, 2019Document7 pagesSolutions To The 80th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 7, 2019Jkone ,No ratings yet
- Putnam Competition Saturday, 2019 ANSDocument6 pagesPutnam Competition Saturday, 2019 ANSMarcus TylerNo ratings yet
- Class - 9 - Nstse - PQP - 10 Papers - 2019-20 - 2 in A4 PDFDocument106 pagesClass - 9 - Nstse - PQP - 10 Papers - 2019-20 - 2 in A4 PDFriddhi100% (4)
- Math Club Junior 12 Aug (Complete)Document15 pagesMath Club Junior 12 Aug (Complete)Hazael NisharNo ratings yet
- 2010 Winter Camp - Mock Olympiad - SolutionsDocument5 pages2010 Winter Camp - Mock Olympiad - SolutionsAltananyNo ratings yet
- Prereq Quiz ReviewDocument2 pagesPrereq Quiz Reviewsathesnaidu11No ratings yet
- Las Math9 Q4 W6Document7 pagesLas Math9 Q4 W6Maxene Angelie RabanalNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument6 pagesMathsabhinavrohatgiNo ratings yet
- 7 Coordinate GeometryDocument4 pages7 Coordinate GeometryRoses Are RosieNo ratings yet
- Imp Theorems Class 12Document32 pagesImp Theorems Class 12dkhedka94No ratings yet
- A Test For OrthogonalityDocument3 pagesA Test For OrthogonalityUniverse gamerNo ratings yet
- NTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Document16 pagesNTSE Stage - 1 Mock Test - 3Apex Institute100% (1)
- 2008SummerCamp MockOlympiads SolutionsDocument11 pages2008SummerCamp MockOlympiads Solutionsdaud hasanNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions: The American Mathematical MonthlyDocument9 pagesProblems and Solutions: The American Mathematical MonthlyKhokon GayenNo ratings yet
- 06 10 14 - IMOGeom2Document13 pages06 10 14 - IMOGeom2Atithaya Chinchalongporn100% (1)
- 5.solutions of TriangleTheoryDocument19 pages5.solutions of TriangleTheorygryffindorstudent100% (1)
- CAT Quant Questions PDFDocument63 pagesCAT Quant Questions PDFSHREYA MAHESHWARINo ratings yet
- Solutions 1531-1540: Parabola Volume 53, Issue 3 (2017)Document5 pagesSolutions 1531-1540: Parabola Volume 53, Issue 3 (2017)MohammadNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument16 pagesJames Ruse 2008 Year 10 Maths Yearly & SolutionsRicha Ng50% (2)
- CBSE Class 10 - Trigonometry Exercise - MathematicsDocument8 pagesCBSE Class 10 - Trigonometry Exercise - MathematicsSmart eTeach100% (1)
- WS1 - VectorsDocument3 pagesWS1 - VectorsElaine BonaviaNo ratings yet
- Barycentric CoordinatesDocument17 pagesBarycentric Coordinatesmszlazak4179No ratings yet
- Solns of TriangleDocument11 pagesSolns of TrianglePrajuwalThakurNo ratings yet
- 01 (02) - Vector - Solved Example Module-6-ADocument10 pages01 (02) - Vector - Solved Example Module-6-ARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument18 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostMohd ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Answers To preMA3HL.1 - Feb 1, 2022Document7 pagesAnswers To preMA3HL.1 - Feb 1, 2022Syklone 03No ratings yet
- Topic: Triangles: AB BEDocument11 pagesTopic: Triangles: AB BEDaksh Bhardwaj VIII-A Roll No 2No ratings yet
- Dad S TheoremDocument17 pagesDad S TheoremyvazzocaanhdvpmlfmNo ratings yet
- Nsejs Geometry Sa2Document6 pagesNsejs Geometry Sa2gobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document36 pagesCH 8syedyaseen39375No ratings yet
- Abhay Mahajan: B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeDocument41 pagesAbhay Mahajan: B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeLakshya SehgalNo ratings yet
- Properties of Triangle - Exercise Module-2Document13 pagesProperties of Triangle - Exercise Module-2Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- 10005-PDF File-44405-2-10-20230330Document59 pages10005-PDF File-44405-2-10-20230330Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- 4534-PDF File-13398-1-10-20150323Document30 pages4534-PDF File-13398-1-10-20150323Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- BF02574063Document4 pagesBF02574063Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- 4104-PDF File-12544-2-10-20150105Document6 pages4104-PDF File-12544-2-10-20150105Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- 11377-PDF File-44402-1-10-20230329Document10 pages11377-PDF File-44402-1-10-20230329Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- 1314-PDF File-1393-1-10-20120117Document10 pages1314-PDF File-1393-1-10-20120117Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- Nam 42Document1 pageNam 42Harold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet
- De Hoc Ky 2 Toan 8 Nam 2022 2023 Truong Thcs Hoang Hoa Tham Ha NoiDocument1 pageDe Hoc Ky 2 Toan 8 Nam 2022 2023 Truong Thcs Hoang Hoa Tham Ha NoiHarold Hardy GodfreyNo ratings yet