Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gastrointestinal Drugs
Uploaded by
Uma CrespoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gastrointestinal Drugs
Uploaded by
Uma CrespoCopyright:
Available Formats
GASTROINTESTINAL DRUGS
DRUGS:
Digestion
Foods we eat needs to be converted into ANTACIDS
simplest form neutralizes stomach acid
o Carbs -> glucose available in OTC, pts self-treat
o Lipids -> fatty acids indication:
o Proteins -> amino acids o hyperacidity
Digestion needs help from enzymes EX o hyperphosphatemia (CKD pts) and
amylase breaks down starches to prevent formation of stones
monosaccharides o treats calcium deficiency
Mechanical digestion pushes food to stomach o stress ulcers – by glucocorticoid that
More chemical digestion happens in the increases glucose and GI secretions
stomach o constipation
adverse effects
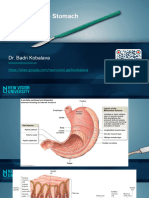
STOMACH o Magnesium – diarrhea
Secretes mucus, pepsinogen, and HCl acid. o Aluminum – constipation
pH ranges from 2-4 (lower = acidic; higher = Kremil-S combination of both
basic/alkalinic) o Aluminum – attracts phosphates if
EX of pH: taken for an extended period of time
o Urine = 6 (slightly acidic) o Carbonate – bloating and flatulence
o Blood = 7.35-7.45 (slightly alkalinic) Nx consideration:
o S. intestine mucus = 8 (basic/alkaline) o Administer apart from other meds pls
o 7 = neutral o Ensure therapeutic levels
Stomach wall is lined with mucus which o Diagnostic testing
protects stomach from acidity of HCl acid. o Prevent imbalances – acid base or
electrolyte imbalance
Acid Indigestion “Heartburn” o Bowel program – diarrhea and
Excessive acid that goes to esophagus constipation
Gastroesophageal / cardiac sphincter is o Adequate nutrition – fluid and
normally closed to prevent reflux or backflow electrolytes r/t diarrhea
of stomach contents back to esophagus o Support
Pts with heartburn – this sphincter remains o Education
open (due to wear and tear, excessive ALGINATES AND ANTIFOAMING AGENTS
production) o Combined with antacids
Esophagus does not have mucus lining = reflux
o Floats on stomach CONTENTS to form
of acid burns the lining of esophagus
a neutralizing layer
They are AKA cardiac due to anatomical
o Helps prevent acid reflux
location, almost same as heart location and
o Gaviscon
sometimes mistaken as chest pain.
o Simethicone – prevents formation of
ULCER occurs when stomach linings are
damaged gases and flatulence (by carbonates)
PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE HISTAMINE-2 ANTAGONISTS
Caused by many factors. Antihistamine – histamine 2 stimulates HCl
o Not eating production
Decrease HCl acid production
o H. pylori – lives in acidic environment
Selectively blocks H2 receptors on the parietal
Mucus lining of stomach in an area is
cells
THINNING and eventually nawawala then
Blocks production of HCl acid
creates a wound
Indications:
2 types:
o Short-term for ulcers
o gastric
o Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
o duodenal
o Stress induced ulcers
o Erosive GERD
o Heartburn, acid indigestion, sour
stomach
“-tidine”
Adverse Effects:
o Dizziness confusion
o Cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac arrest
o Diarrhea
o Impotence
o Rashes
Nx cons:
o Administer with or before meals at
bedtime
o Monitor pts if given IV doses – cardiac
arrhythmias
o Provide comfort, bathroom privileges,
assist c ambulation
o Reorient if CNS effects occur
o Support – answer questions and
educate
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS
Stops secretion/production of HCl acids
Blocks the final step of acid production as long
as you’re taking the drug
Gives time for stomach ulcers to heal
Indications:
o Esophagitis, heartburn, GERD
Advere effects
o Headache, dizziness, vertigo
o Diarrhea, abd pain, n/v
o URTI, cough
GI PROTECTANT (CYTOPROTECTIVE)
Coats any injured area in the stomach
Less contact to acid = healing
Sucralfate (Carafate) only GI protectant
available
Creates a viscuous substance – will act as
barrier
PROSTAGLANDINS
Protects stomach lining
By increasing mucus production
Misoprostol (Cytotec) – prostaglandin E
analogue
Misprostol – check for allergies/allergic
reactions
Contraindicated during pregnancy –
abortifacient (triggers/stimulates uterine
contraction)
You might also like
- Why Men Want Sex and Women Need Love by Barbara and Allen Pease - ExcerptDocument27 pagesWhy Men Want Sex and Women Need Love by Barbara and Allen Pease - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group62% (34)
- NURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubricDocument7 pagesNURS 366 Exam 1 Study Guide and RubriccmpNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument12 pagesGastrointestinal Disorderssophia yemane100% (4)
- EHEDG Guidelines by Topics 04 2013Document2 pagesEHEDG Guidelines by Topics 04 2013renzolonardi100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal TractDocument13 pagesGastrointestinal TractMarcel TabucolNo ratings yet
- Pcol 1 Sas 7Document9 pagesPcol 1 Sas 7HaruhNo ratings yet
- Git NotesDocument10 pagesGit NotesLucky GomezNo ratings yet
- MS Lec Gi P1Document6 pagesMS Lec Gi P1Julia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Management of Gastric AcidityDocument23 pagesManagement of Gastric AcidityDharline100% (1)
- Gastro Intestinal SystemDocument9 pagesGastro Intestinal SystemJe Lyn100% (1)
- Vaagdevi Phamacy CollegeDocument27 pagesVaagdevi Phamacy CollegeLalith VarmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Esophagus SG 2021 After Class FinalDocument28 pages1 Esophagus SG 2021 After Class FinalTyler YounNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Digestion and AbsorptionDocument115 pagesDisturbances in Digestion and AbsorptionGabrielle PamaNo ratings yet
- GIT Intensive ReviewerDocument9 pagesGIT Intensive ReviewerAllysa PrestonNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 2 Spesialit Obat Dan Alkes Obat Gastrointestinal 2023 NDocument66 pagesPertemuan 2 Spesialit Obat Dan Alkes Obat Gastrointestinal 2023 NAtika PutriNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer PowerPoint PresentationDocument40 pagesPeptic Ulcer PowerPoint Presentationbhavya khattriNo ratings yet
- 1 - Adult Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument17 pages1 - Adult Gastrointestinal DisorderNica EnriquezNo ratings yet
- MEDSURG 1 NotesDocument43 pagesMEDSURG 1 NotesNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- L28 - Esophageal DiseasesDocument16 pagesL28 - Esophageal DiseasesNimer Abdelhadi AliNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersDocument4 pagesMed Surg 2 - 10 Nursing Care of Clients With Biliary DisordersMaxinne RoseñoNo ratings yet
- VomitingDocument4 pagesVomitingMax BrownNo ratings yet
- Pharma Part 1 FinalsDocument6 pagesPharma Part 1 Finalsmelitonfred22No ratings yet
- Upper GI Tract (Stomach)Document5 pagesUpper GI Tract (Stomach)NAWAB PHOTOCOPYNo ratings yet
- Git ToprankDocument5 pagesGit ToprankJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument12 pagesGastrointestinal Disordershelloa100% (1)
- Nto Uchenna Note On GI SecretionsDocument10 pagesNto Uchenna Note On GI SecretionsNwaoha Chibuzor AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Bio 253 MidtermDocument17 pagesBio 253 MidtermJason ChuNo ratings yet
- Gastric Fluid AnalysisDocument3 pagesGastric Fluid AnalysisanonacadsNo ratings yet
- GI SimDocument5 pagesGI SimIyath SaeedNo ratings yet
- Common Pediatric DisordersDocument2 pagesCommon Pediatric DisordersJean ReyesNo ratings yet
- Acid Peptic DisordersDocument72 pagesAcid Peptic DisordersAteeq ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestin Al System: CBL On Peptic UlcerDocument37 pagesGastrointestin Al System: CBL On Peptic UlcerAbdul Rasheed Talha NaqshbandiNo ratings yet
- Gastric Fluid Analysis NotesDocument2 pagesGastric Fluid Analysis NotesanonacadsNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Obstruction and Equine Gastric Ulcer SyndromeDocument30 pagesEsophageal Obstruction and Equine Gastric Ulcer Syndromeannelle0219No ratings yet
- GIDocument7 pagesGIiheart musicNo ratings yet
- Gastro HistoryDocument4 pagesGastro HistoryAsma SikanderNo ratings yet
- MS-2 GallbladderDocument2 pagesMS-2 Gallbladderelijahdale.guillergan-05No ratings yet
- Study ExamDocument54 pagesStudy ExamQadri HaitamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Gastrointestinal SystemDocument4 pagesPharmacology of Gastrointestinal SystemZaira KimNo ratings yet
- SGD 16 Gi 1Document4 pagesSGD 16 Gi 1Kaedehara KazuhaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Nursing ReviewDocument50 pagesGastrointestinal Nursing ReviewRoby NgNo ratings yet
- Caccam, Christine Amor PDocument11 pagesCaccam, Christine Amor PChris Tine CaccamNo ratings yet
- Digest This!Document7 pagesDigest This!Dhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Esophageal PathologyDocument8 pagesEsophageal PathologyAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Presenting Symptoms:: Gastrointestinal HistoryDocument4 pagesPresenting Symptoms:: Gastrointestinal HistoryTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- Gerd and Hiatal HerniaDocument4 pagesGerd and Hiatal HerniaAmoroso, Marian Corneth D.No ratings yet
- GitDocument302 pagesGitjgcriste100% (7)
- Nyeri AbdomenDocument88 pagesNyeri AbdomenAngela Kristiana IntanNo ratings yet
- Surgery2 07 Stomach and Small IntestineDocument85 pagesSurgery2 07 Stomach and Small Intestinezein0217zienNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract: Monometric StudiesDocument9 pagesGastrointestinal Tract: Monometric StudiesJosh LimNo ratings yet
- 2300 - Module 8 - Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary EmergenciesDocument14 pages2300 - Module 8 - Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Emergenciesmegan.abbinkNo ratings yet
- GIT - Part IIDocument23 pagesGIT - Part IIDiyar ArifNo ratings yet
- Dysphagia Lesson 2Document40 pagesDysphagia Lesson 2Raina FujiyoshiNo ratings yet
- GI Review BulletsDocument19 pagesGI Review Bulletsjanet_alexisNo ratings yet
- Upper GI Guided NotesDocument9 pagesUpper GI Guided NotesVanessaNo ratings yet
- Bolus: DigestiveDocument4 pagesBolus: DigestiveJohnmer AvelinoNo ratings yet
- Gastro Reviewer FinalsDocument5 pagesGastro Reviewer Finalsadd.bdrcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Gastrointestinal Agents Reviewer PDFDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Gastrointestinal Agents Reviewer PDFdavenNo ratings yet
- Urea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsDocument6 pagesUrea/ Ammonia Tests: Primary Liver Function TestsMemory MahwendaNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux DiseaseDocument4 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Diseaseampogison08No ratings yet
- Antiulcer Chapter 40Document9 pagesAntiulcer Chapter 40triddle1969No ratings yet
- Sex - Assigned at Birth Gender - Used To Describe TraditionalDocument2 pagesSex - Assigned at Birth Gender - Used To Describe TraditionalUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Semi-Finals Pediatric NursingDocument12 pagesSemi-Finals Pediatric NursingUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemics DrugsDocument3 pagesAntihyperglycemics DrugsUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Pedia TranscriptDocument18 pagesPedia TranscriptUma CrespoNo ratings yet
- Ca 2013 39Document40 pagesCa 2013 39singh1699No ratings yet
- Notes, MetalsDocument7 pagesNotes, MetalsindaiNo ratings yet
- Method of Toxicity Test 1Document59 pagesMethod of Toxicity Test 1Widya AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- RDG UNIT 2 Skimming Class A 2021Document17 pagesRDG UNIT 2 Skimming Class A 2021Yuly Rumondang Wulan SiallaganNo ratings yet
- 00516-CLIA-Newsletter Jan 06Document4 pages00516-CLIA-Newsletter Jan 06losangelesNo ratings yet
- CAT Test Series - 2014Document2 pagesCAT Test Series - 2014dimevsnNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument10 pages1 SMAnindita GaluhNo ratings yet
- Nature and Nurture - How They Play A Role in Serial Killers and THDocument40 pagesNature and Nurture - How They Play A Role in Serial Killers and THJ.A.B.ANo ratings yet
- CH 10 - Reinforced - Concrete - Fundamentals and Design ExamplesDocument143 pagesCH 10 - Reinforced - Concrete - Fundamentals and Design ExamplesVeronica Sebastian EspinozaNo ratings yet
- TCM Reach TrucksDocument5 pagesTCM Reach TrucksMuhammad SohailNo ratings yet
- RIASEC Personality TestDocument2 pagesRIASEC Personality TestSarah Jane NomoNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering. 02 Soil CompressibilityDocument63 pagesFoundation Engineering. 02 Soil Compressibilitysammy lopezNo ratings yet
- Ancamine Teta UsDocument2 pagesAncamine Teta UssimphiweNo ratings yet
- Trane Air Cooled Scroll Chillers Installation Operation MaintenanceDocument276 pagesTrane Air Cooled Scroll Chillers Installation Operation MaintenanceBay Mưa100% (1)
- Pearls and Pitfalls in Emergency Radiology Variants and Other Difficult Diagnoses 2013Document389 pagesPearls and Pitfalls in Emergency Radiology Variants and Other Difficult Diagnoses 2013mmbire@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- NeoResin DTM Presentation 9-01Document22 pagesNeoResin DTM Presentation 9-01idreesgisNo ratings yet
- ProAct ISCDocument120 pagesProAct ISCjhon vergaraNo ratings yet
- Margarita ForesDocument20 pagesMargarita ForesKlarisse YoungNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Strength & HypertrophyDocument6 pagesEvidence-Based Strength & HypertrophyAnže BenkoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ImageDocument43 pagesContemporary ImageProf. L100% (1)
- 224 Chinese Healing ExercisesDocument4 pages224 Chinese Healing ExercisesKiné Therapeut-manuelle Masseur GabiNo ratings yet
- Unit Two The Health Benefits of Physical ActivityDocument10 pagesUnit Two The Health Benefits of Physical ActivityYoseph DefaruNo ratings yet
- Hiperparatiroidism SarcinaDocument7 pagesHiperparatiroidism SarcinaClaudia IrimieNo ratings yet
- Ergo 1 - Workshop 3Document3 pagesErgo 1 - Workshop 3Mugar GeillaNo ratings yet
- Preparing Polymers For The Jar TestDocument5 pagesPreparing Polymers For The Jar Testarvin4dNo ratings yet
- Pescatarian Mediterranean Diet Cookbook 2 - Adele TylerDocument98 pagesPescatarian Mediterranean Diet Cookbook 2 - Adele Tylerrabino_rojoNo ratings yet
- Transformers: Z Z Z S S Z S SDocument17 pagesTransformers: Z Z Z S S Z S SSreenivasaraoDharmavarapu100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical ReactionsDocument11 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q4 - Lessons 7 and 8) Electrochemical Reactionsprincess3canlasNo ratings yet