Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
Anishka Josephine0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesForce causes motion or changes shape. Newton is the SI unit of force. Moment of force causes rotational motion when applied to a rigid body pivoted at an axis, and is measured as the product of the force magnitude and its perpendicular distance from the axis. The turning effect depends on both force magnitude and this perpendicular distance. The SI unit of torque is the Newton meter. The principle of moments states the sum of clockwise and anticlockwise torques equals zero.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentForce causes motion or changes shape. Newton is the SI unit of force. Moment of force causes rotational motion when applied to a rigid body pivoted at an axis, and is measured as the product of the force magnitude and its perpendicular distance from the axis. The turning effect depends on both force magnitude and this perpendicular distance. The SI unit of torque is the Newton meter. The principle of moments states the sum of clockwise and anticlockwise torques equals zero.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views14 pagesUntitled
Uploaded by
Anishka JosephineForce causes motion or changes shape. Newton is the SI unit of force. Moment of force causes rotational motion when applied to a rigid body pivoted at an axis, and is measured as the product of the force magnitude and its perpendicular distance from the axis. The turning effect depends on both force magnitude and this perpendicular distance. The SI unit of torque is the Newton meter. The principle of moments states the sum of clockwise and anticlockwise torques equals zero.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
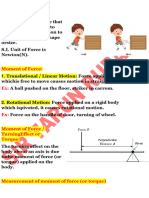
Force:
It is an external cause that causes a body in rest to move or body in
motion to rest or changes the shape or size.
S.I. Unit of Force is Newton (N).
Moment of Force:
1. Translational / Linear Motion: Force applied on a rigid body which is
free to move causes motion in straight path.
Ex: A ball pushed on the floor, striker in carrom.
2. Rotational Motion: Force applied on a rigid body which is pivoted, it
causes rotational motion.
Ex: Force on the handle of door, turning of wheel.
Moment of Force / Turning Effect or Torque:
The turning effect on the body about an axis is due to the moment of
force (or torque) applied on the body.
Measurement of moment of force (or torque)
The moment of a force (or torque) is equal to the product of the
magnitude of the force and the perpendicular distance of the line of
action of the force from the axis of rotation.
Factors affecting the turning of a body
The turning effect of a force on a body depends on the following two
factors:
(1) the magnitude of the force applied, and
(2) the perpendicular distance of the line of action of the force from the
axis of rotation (or pivoted point).
S.I. Unit of Torque: Nm
C.G.S. Unit: Dyne cm
Clockwise Moment is always NEGATIVE and Anticlockwise Moment is
always POSITIVE.
Ex: To open or shut a door,
Turning of hand flour grinder,
Turning of a steering wheel.
Principle of Moments:
Sum of Anticlockwise moments = Sum of Clockwise moments
OR
Algebraic sum of moments of all forces acting on a body about the axis
of rotation is 0.
You might also like
- Theory of MachinesDocument69 pagesTheory of MachinesAnil Lodwal100% (1)
- Force and Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesForce and Pressure Notesmatho logyNo ratings yet
- Torque and Rotation PhysicsDocument20 pagesTorque and Rotation PhysicsSaf Tanggo DiampuanNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter 2 (F4) Linear MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics: Chapter 2 (F4) Linear MotionKai YuanNo ratings yet
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- 559 ICSE ClassX Physics Force RN RWDDocument11 pages559 ICSE ClassX Physics Force RN RWDKeerthan Manjunath50% (2)
- Biomechanics and Sports PDFDocument31 pagesBiomechanics and Sports PDFAditi Pankaj100% (1)
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceradhikadaksh1983No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document73 pagesLecture 3HamzahNo ratings yet
- Force - Summary Notes: Noncontact Forces, E.g., Gravitational Force, Electrical Force, and Magnetic ForceDocument3 pagesForce - Summary Notes: Noncontact Forces, E.g., Gravitational Force, Electrical Force, and Magnetic ForceVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - ForceDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Forcekalpanapriyam213No ratings yet
- Vibration Is The Motion of Particle or A Body or System of Connected Bodies Displaced From The Position of EquilibriumDocument9 pagesVibration Is The Motion of Particle or A Body or System of Connected Bodies Displaced From The Position of EquilibriumrajuNo ratings yet
- Icse Physics NotesDocument110 pagesIcse Physics Notess9605519No ratings yet
- FORCE & PRESSURE NotesDocument1 pageFORCE & PRESSURE NotesPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Applications in Linear and Angular KineticsDocument30 pagesApplications in Linear and Angular Kineticsafifah temiziNo ratings yet
- Elements of A MomentDocument12 pagesElements of A MomentcrotoaslutNo ratings yet
- Genphysics1 Lesson 2Document19 pagesGenphysics1 Lesson 2Ariane AngelesNo ratings yet
- BM Lecture 1Document43 pagesBM Lecture 1Aggrey MukondeNo ratings yet
- Bio Physics Bio Static: Net Resulting Force 0 Net Torque 0Document4 pagesBio Physics Bio Static: Net Resulting Force 0 Net Torque 0Prabath Sameera WijerathneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13 VDocument5 pagesLecture 13 VLucian NicolauNo ratings yet
- Force, Work, Power & Energy (1) IcseDocument62 pagesForce, Work, Power & Energy (1) IcsesachiduthNo ratings yet
- Physics Class X Selina - ForceDocument18 pagesPhysics Class X Selina - ForceProteep MitraNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics: KinematicsDocument6 pagesBiomechanics: KinematicsNadziran EzizNo ratings yet
- Bio-Mechanics: USA Track & Field Level 1 Coaching SchoolDocument37 pagesBio-Mechanics: USA Track & Field Level 1 Coaching SchoolKoordinacijska Lestev Speed LadderNo ratings yet
- Bio MechanicsDocument5 pagesBio MechanicsAris SinagaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Structural DynamicsDocument22 pagesBasics of Structural Dynamicsdskumar49No ratings yet
- Introduction To MechanismsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To MechanismsAkash SoniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MechanismsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Mechanismsrajasekaran2323No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument66 pagesDocumentGarima KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Physics 134 Wk5 Topic: Moment of Force ObjectivesDocument3 pagesPhysics 134 Wk5 Topic: Moment of Force ObjectivesJhin KhadaNo ratings yet
- CH 10 Biomechanics and Sports Androbose - inDocument6 pagesCH 10 Biomechanics and Sports Androbose - inAadeesh SinghaiNo ratings yet
- FORCE JMDocument11 pagesFORCE JMapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Mechanical Principles: Syeda Amna Iqbal Lecturer Kinesiology BSPT, MSPT, DPTDocument23 pagesMechanical Principles: Syeda Amna Iqbal Lecturer Kinesiology BSPT, MSPT, DPTMuhammad Owais qarniNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument27 pagesKINEMATICSHhitika KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Linear Kinetics NotesDocument76 pagesChapter 12 Linear Kinetics NotesJason EdwardsNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument4 pagesPHYSICSjulianaquino1203No ratings yet
- Biomechanics: KinematicsDocument5 pagesBiomechanics: Kinematicsالقداري القداريNo ratings yet
- Lesson Note About ForceDocument6 pagesLesson Note About Forcemark joseph cometaNo ratings yet
- 1 Physical Principles: 1.1 Force and Torque 1.1.1 ForceDocument1 page1 Physical Principles: 1.1 Force and Torque 1.1.1 ForceBilla AjithNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document5 pagesLecture 14Lucian NicolauNo ratings yet
- Biomechanics in Physical Education Sports and ResearchDocument26 pagesBiomechanics in Physical Education Sports and ResearchEinn D. FloresNo ratings yet
- Dynamics M4Document29 pagesDynamics M4shilpaNo ratings yet
- Exp 4 DraftDocument5 pagesExp 4 DraftPoison PinkNo ratings yet
- Project T TTT TTTTTDocument4 pagesProject T TTT TTTTTNidhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vibration Example:-DealsDocument10 pagesVibration Example:-DealsmanishtopsecretsNo ratings yet
- Laws of - MottionDocument26 pagesLaws of - MottionnitikanehiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 and 5Document11 pagesUnit 3 and 5RayyanNo ratings yet
- What Is Projectile?Document19 pagesWhat Is Projectile?Rida KhanNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document5 pagesTask 1elking.ahmed1562002No ratings yet
- Instructional Material PhysicsDocument52 pagesInstructional Material PhysicsLester GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lectr 4 Angular KineticsDocument21 pagesLectr 4 Angular KineticsFareeha KausarNo ratings yet
- Project On Vibration Analysis: Guided ByDocument11 pagesProject On Vibration Analysis: Guided ByRajesh PradhanNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering B.E - Iii Year - V Semester Dynamics of Machines Unit I Force AnalysisDocument101 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering B.E - Iii Year - V Semester Dynamics of Machines Unit I Force Analysissuneel kumar rathoreNo ratings yet
- MS Point RKPSDocument12 pagesMS Point RKPSshivamkumar6203716No ratings yet
- Dynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldFrom EverandDynamic Deformation of Earth and Motion Effects Caused by Universe's Gravitational FieldNo ratings yet