Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 6179316044578947755
Uploaded by
Kartik ElectricalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 6179316044578947755
Uploaded by
Kartik ElectricalCopyright:
Available Formats
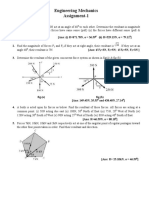
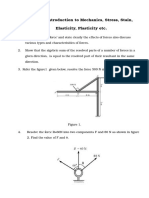
F O RC E S Y S T EM S AN D R ESU L T AN T
1. For the hook loaded as shown in figure, what is the net applied force along the axis of hook i.e. AB
direction.
2. Determine the net applied force on the block along the inclined plane for the arrangement shown in
figure. Weight of the block is 100 𝑁.
3. A belt is wrapped over a pulley as shown in figure. Tension applied at each end of the belt is given
in figure. Neglecting the weight of the belt, what is the net force applied by the belt on the pulley in
radial direction 𝑟.
4. A structural member is subjected to force 1000 𝑁 as shown in figure. Given that 𝐴𝐵 = 2 𝑚 and 𝐵𝐶 =
1 𝑚. Determine the moment of 1000 𝑁 force about point 𝐴.
5. A column is subjected to a force 600 𝑁 at the end of cable as shown in figure. Neglecting the weight
of components, determine the net moment at point 𝐴 of the column.
6. A uniform rod 𝐴𝐵𝐶 of weight 1200 𝑁 is shown in figure. Given that 𝐴𝐵 = 3 𝑚 and 𝐵𝐶 = 2 𝑚.
Determine the moment of this weight force about point 𝐴.
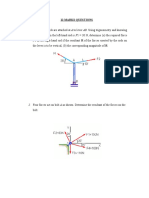
7. A hook is subjected to three forces as shown in figure. Determine the magnitude of the resultant
force. Also determine the angle of resultant force from 𝑥 axis.
8. Forces 𝑃, 2𝑃, 𝑃, 𝑃 and 2𝑃 act from one vertex of a regular hexagon to second, third, fourth, fifth and
sixth corner respectively. Determine the magnitude of resultant force.
9. A frame is subjected to four forces as shown in figure. 𝐴𝐵 = 𝐵𝐶 = 𝐶𝐷 = 𝐷𝐸 = 𝑎. The resultant force
intercepts vertical arm at a distance 𝑥 along line 𝐶𝐵𝐴. Determine 𝑥.
10. A beam is subjected to three forces as shown in figure. Determine the distance from left support at
which the resultant force of applied forces intercepts the beam.
11. A system of forces acting on a lamina is shown in the given figure. If the resultant of the force
system will meet 𝐴𝐵 at a point 𝑥 distance from B, determine 𝑥.
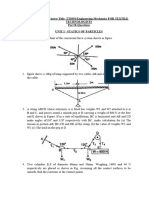
E Q U ILI BR I UM
12. Two drums are supported as shown. Weight and radius of drum 𝐴 are 1200 𝑁 and 300 𝑚𝑚
respectively. Weight and radius of drum 𝐵 are 1800 𝑁 and 400 𝑚𝑚 respectively. Determine the contact
reaction between drums.
13. Consider a rigid weightless bar fixed at 𝐴 and supporting a drum of weight 500 𝑁 by a cable as
shown in figure. Given that 𝐴𝐵 = 300 𝑚𝑚 and 𝐵𝐶 = 200 𝑚𝑚 and radius of the drum is 100 𝑚𝑚.
Determine the tension in cable.
14. A 1200 𝑁 bar 𝐴𝐵𝐶 is supported by a cord as shown in figure. Determine tension in the cord. The
length of rod 𝐴𝐵𝐶 is 240 𝑚𝑚.
15. Let a drum of radius 100 𝑚𝑚 and weight 500 𝑁 is now kept in the space between wall and bar 𝐴𝐵𝐶
of previous problem. Considering all surfaces as smooth, determine the tension in the cord. The length
of rod 𝐴𝐵𝐶 is 240 𝑚𝑚.
16. A homogenous rod 𝐴𝐷𝐶 of total weight 𝑊 is supported as shown in figure. Determine the tension in
cable 𝐴𝐵𝐶.
17. For the system loaded and supported as shown in figure, 𝐴𝐶 = 𝐵𝐶 = 200 𝑚𝑚 and 𝐶𝐷 = 𝐷𝐸 = 100 𝑚𝑚.
Weight of the cylinder is 1000 𝑁 and bars 𝐴𝐶𝐷 and 𝐵𝐶𝐸 are weightless. Considering smooth surfaces,
determine the tension in rope connecting 𝐴 and 𝐵. Cylinder radius is 100 𝑚𝑚.
18. Determine the mass of each of the two blocks if they cause a sag of 𝑠 = 0.5 𝑚 when suspended from
the rings at 𝐴 and 𝐵.
19. Figure shows a hollow weight free to slide along a vertical guide, with no friction between guide
and hollow weight. When the weight is released from the position 𝐴 as shown in figure, it starts
sliding downward. Spring is at its natural length when the weight is at position 𝐴. The weight finally
comes in equilibrium when it reaches to position 𝐵. What is the value of weight?
20. Consider a block of weight 200 𝑁 resting over a smooth inclined plane as shown in figure. Stiffness
of the spring is 240 𝑁/𝑚. Determine the natural (undeformed) length of the spring.
T W O & T HR EE F ORC E M EM B E R S
21. Consider a frame loaded as shown in figure. Neglecting weight of the members, determine the
direction of resultant reaction at pin 𝐵.
22. If the homogeneous triangular plate of weight 𝑊 shown in figure is held in equilibrium by the
cord, determine (i) angle 𝜃 that cord must make for equilibrium. (ii) tension in cord. Given that 𝐴𝐵 =
180 𝑚𝑚 and 𝐵𝐶 = 120 𝑚𝑚. The angle of inclined plane is such that normal reaction at point 𝐶 passes
through centroid of the triangular plate.
23. Changu is trying to move a wheel of weight 𝑊 over a block by applying a horizontal force as
shown in figure. Given that ℎ = 𝑟/3 and 𝑎 = 2𝑟/3, determine the force 𝑃 required to push the wheel just
over the block.
24. Neglecting weight of members for the system shown in figure, determine the magnitude and
direction of resultant reaction at pin 𝑂.
A N S WE R S
1. 333.67 𝑁 13. 484.12 𝑁
2. 143.185 𝑁 𝑢𝑝 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑛𝑒 14. 519.615 𝑁
3. 437.5 𝑁 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑦 𝑖𝑛𝑤𝑎𝑟𝑑 15. 936.282 𝑁
4. 2000 𝑁𝑚 16. 𝑊/2
5. 900 𝑁𝑚 17. 1144.37 𝑁
6. 2520 𝑁𝑚 18. 23.22 𝑁
7. 48.173 𝑘𝑁, 12.28° 𝐶𝑊 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 + 𝑋 19. 500√3 𝑁
8. 5.1111𝑃 20. 1.77 𝑚
9. 7.46𝑎 21. 45°
10. 2.5 𝑚 22. (𝑖) 33.69° (𝑖𝑖) 0.6𝑊
11. 0 𝑚 23. 𝑊√5
12. 909.3266 𝑁 24. 501 𝑁 𝑎𝑡 56.3° 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 ℎ𝑜𝑟𝑖𝑧𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑙
You might also like
- Force Systems and EquilibriumDocument7 pagesForce Systems and EquilibriumSachin bhaskar malgaveNo ratings yet
- CA4 Statics and Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument22 pagesCA4 Statics and Dynamics of Rigid BodiesEduard Joseph Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DEI Technical College Applied Mechanics Question BankDocument10 pagesDEI Technical College Applied Mechanics Question BankRaNo ratings yet
- Practice Numericals On MOSDocument14 pagesPractice Numericals On MOSBinil Varghese AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Anna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsDocument12 pagesAnna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Axial LoadingDocument8 pagesAxial LoadingPrince SinghNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 PDFDocument3 pagesExercise 4 PDFchetanNo ratings yet
- Engineering MEchanics Part - BDocument38 pagesEngineering MEchanics Part - BPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Part B question BankDocument9 pagesPart B question BankSriram SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Torsion Analysis of Various Shaft Cross SectionsDocument9 pagesTorsion Analysis of Various Shaft Cross SectionsShivamSinghNo ratings yet
- Shearing Forces in BeamsDocument9 pagesShearing Forces in BeamsKheshav JhundooNo ratings yet
- Shear and Bending 23 - 08 - 2021Document9 pagesShear and Bending 23 - 08 - 2021cos thetaNo ratings yet
- STATICS ProblemsDocument6 pagesSTATICS Problemsdesertfox1943No ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question BankSatyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Force and FrictionDocument7 pagesAssignment 1 Force and Frictionrajiv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- RMK Engineering College mechanical engineering tutorial problemsDocument22 pagesRMK Engineering College mechanical engineering tutorial problemskalirajgurusamy33% (3)
- Correl 2 Until MidtermsDocument23 pagesCorrel 2 Until MidtermsKimberly TacaisanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question BankKrishna MurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignments EMDocument19 pagesAssignments EMrajiv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems - Set 05 Beam Analysis and Stress CalculationsDocument8 pagesPractise Problems - Set 05 Beam Analysis and Stress Calculationsrohit kumarNo ratings yet
- HeyaDocument46 pagesHeyaJeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- PHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2harshitaNo ratings yet
- 12 MarksDocument23 pages12 Markslakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Btes103 203 em QBDocument10 pagesBtes103 203 em QBSurajNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS EXAM REVIEWDocument8 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS EXAM REVIEWAntonette LimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Design of Short Columns Subject To Axial and BendingDocument39 pagesLecture 8 - Design of Short Columns Subject To Axial and BendingMarcelo AbreraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 MOSDocument47 pagesAssignment 1 MOSGaurav RajNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument42 pagesEngineering Mechanicsrommel satajoNo ratings yet
- Final Structure LabDocument38 pagesFinal Structure LabNurul Syuhada0% (1)
- Multiple Choice 0Document43 pagesMultiple Choice 0Dave SalvadorNo ratings yet
- PinoyBix Engineering MechanicsDocument59 pagesPinoyBix Engineering MechanicsChris Balmaceda100% (1)
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 1 5Document7 pagesTutorials 1 5faizankhan260690No ratings yet
- MCQ in Engineering Mechanics Part 1 ECE Board ExamDocument11 pagesMCQ in Engineering Mechanics Part 1 ECE Board ExamJi KanNo ratings yet
- Forces and Equilibrium Assignment ProblemsDocument9 pagesForces and Equilibrium Assignment ProblemsParth PawarNo ratings yet
- Tutorials and Solution InstructionsDocument25 pagesTutorials and Solution InstructionsDanin kimNo ratings yet
- Calculus-Base Physics 1Document24 pagesCalculus-Base Physics 1dun lelNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation DesignDocument57 pagesPile Foundation DesignMoe AlDirdeeryNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set03Document5 pagesPractise Problems Set03rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- As 123Document4 pagesAs 123anurag kumarNo ratings yet
- Structural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Document6 pagesStructural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Michael BlairNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium Ex.Document15 pagesStatic Equilibrium Ex.Marc Harold ChuaNo ratings yet
- Forces Moments Equilibrium StabilityDocument3 pagesForces Moments Equilibrium StabilityMushabe MelisaNo ratings yet
- Static Mechanical System Section1: Stress, Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument17 pagesStatic Mechanical System Section1: Stress, Shear Force and Bending MomentHadhi Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- PRE-BOARDS-TUTORIAL-3Document56 pagesPRE-BOARDS-TUTORIAL-3vandiazvanNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsDocument14 pagesEquivalent Force Systems and Free Body Diagrams Solved ProblemsYun RamNo ratings yet
- Practise Problems Set01Document7 pagesPractise Problems Set01rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 PDFDocument8 pagesExercise 1 PDFLeong Yue HanNo ratings yet
- T4 ForcesDocument5 pagesT4 ForcesyanasakaranNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument24 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesAhsan TariqNo ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1reddiNo ratings yet
- Forces and Equilibrium in Mechanics ProblemsDocument17 pagesForces and Equilibrium in Mechanics Problemsbaig79No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Booked Railway Ticket DetailsDocument2 pagesBooked Railway Ticket DetailsKartik ElectricalNo ratings yet
- 11265/Mml Abkp Express Second Sitting (2S)Document2 pages11265/Mml Abkp Express Second Sitting (2S)Kartik ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Interim Tiger Report Signals Bigger Gain Some WarningsDocument8 pagesInterim Tiger Report Signals Bigger Gain Some WarningsKartik ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Electrician PEBDocument15 pagesElectrician PEBKartik ElectricalNo ratings yet
- 4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μDocument23 pages4.1 The Plausibility of µ as a Value for a Normal Population Mean μTolesa F BegnaNo ratings yet
- Extruded Aluminum Enclosures: 1455 SeriesDocument8 pagesExtruded Aluminum Enclosures: 1455 SeriesYaju JotosNo ratings yet
- American Hospital Supply Corporation Case Study-Surojit SahaDocument6 pagesAmerican Hospital Supply Corporation Case Study-Surojit Sahasurojitsaha15094No ratings yet
- Simulation of Methanol Synthesis in Packed Bed Reactor Based On Gas From Biomass GasificationDocument9 pagesSimulation of Methanol Synthesis in Packed Bed Reactor Based On Gas From Biomass GasificationHaris Surya HidayatNo ratings yet
- JPEG Standard: ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG10Document31 pagesJPEG Standard: ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG10bumerrNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 PDFDocument5 pagesNotes 2 PDFJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Jongka:the Traditional Korean Family: Exploring Jongka Food in The Context of Korean Food CategoriesDocument14 pagesJongka:the Traditional Korean Family: Exploring Jongka Food in The Context of Korean Food CategoriesSözen BayraktarNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Contemp World - BSA2Document7 pagesModule 4 - Contemp World - BSA2Marian AntipoloNo ratings yet
- Effect of COVID-19 On Global Supply ChainDocument4 pagesEffect of COVID-19 On Global Supply ChainInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Revit 2020 StructureDocument36 pagesRevit 2020 StructurejonrasNo ratings yet
- Week - 5 (Deep Learning) Q. 1) Explain The Architecture of Feed Forward Neural Network or Multilayer Perceptron. (12 Marks)Document7 pagesWeek - 5 (Deep Learning) Q. 1) Explain The Architecture of Feed Forward Neural Network or Multilayer Perceptron. (12 Marks)Mrunal BhilareNo ratings yet
- VSTEP Writing Preparation PDFDocument39 pagesVSTEP Writing Preparation PDFNgân Hà Tô100% (1)
- Report on Seminar Submitted by Akshata on MicrogridsDocument12 pagesReport on Seminar Submitted by Akshata on MicrogridsNitin Kakad73% (11)
- Stockhausen Cuatro Criterios de La Música ElectrónicaDocument44 pagesStockhausen Cuatro Criterios de La Música ElectrónicaFa SolisNo ratings yet
- 5239 PLC SplitterDocument3 pages5239 PLC SplittermksayshiNo ratings yet
- Project Review: Arun III Hydroelectric Project: Background Location and AccessibilityDocument2 pagesProject Review: Arun III Hydroelectric Project: Background Location and AccessibilitySachin ChakradharNo ratings yet
- PA 201 Course SyllabusDocument9 pagesPA 201 Course SyllabusFayyaz DeeNo ratings yet
- CHOOSING NAIA PaperDocument6 pagesCHOOSING NAIA PaperElyssa DaggettNo ratings yet
- Social DimensionDocument23 pagesSocial DimensionMichelle Quiambao Serdon100% (1)
- Manual E7370Document12 pagesManual E7370Carlos Rodríguez MartínNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head: SpecificationsDocument5 pagesCylinder Head: SpecificationsFares100% (1)
- History of AsphaltDocument3 pagesHistory of AsphaltRonald CostalesNo ratings yet
- Re-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsDocument8 pagesRe-Test SUBJECT-English Core Class - Xi Time: 2 Hrs. M.M: 50 General InstructionsSunilDwivediNo ratings yet
- 4 6023697383601211598 PDFDocument232 pages4 6023697383601211598 PDFmahshid kianiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of FirearmsDocument9 pagesAnatomy of Firearmswerdna67No ratings yet
- Sist Elec. D6KDocument2 pagesSist Elec. D6KJose Luis Aguero PomachaguaNo ratings yet
- Bonifacio Elementary School Answer SheetDocument17 pagesBonifacio Elementary School Answer Sheetaries sumalbagNo ratings yet
- Evolution - The Dissent of DarwinDocument7 pagesEvolution - The Dissent of DarwinluminitalupuliasaNo ratings yet
- DNV Otg - 02 Floating Liquefied Gas Terminals - tcm4-460301Document128 pagesDNV Otg - 02 Floating Liquefied Gas Terminals - tcm4-460301Jeril PhilipNo ratings yet
- Verb Tense Grade 9Document2 pagesVerb Tense Grade 9tba.shraddhaNo ratings yet