0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views3 pagesElectronics Units & Prefixes Guide
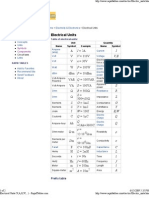
Common electronics units include volts (V) for electric potential difference, amperes (A) for electric current, watts (W) for power, joules (J) for energy/work/heat, coulombs (C) for electric charge, ohms (Ω) for resistance, farads (F) for capacitance, and henries (H) for inductance. Metric prefixes are used to augment these units to describe very large or small quantities, such as kilo (k) for 1,000, milli (m) for 1/1000, and micro (μ) for 1/1,000,000. The document provides examples of converting between units using these prefixes.
Uploaded by
Harsh PatelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views3 pagesElectronics Units & Prefixes Guide
Common electronics units include volts (V) for electric potential difference, amperes (A) for electric current, watts (W) for power, joules (J) for energy/work/heat, coulombs (C) for electric charge, ohms (Ω) for resistance, farads (F) for capacitance, and henries (H) for inductance. Metric prefixes are used to augment these units to describe very large or small quantities, such as kilo (k) for 1,000, milli (m) for 1/1000, and micro (μ) for 1/1,000,000. The document provides examples of converting between units using these prefixes.
Uploaded by
Harsh PatelCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd