Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Siti Nur Asyiffa - 5H - Chapter 22 Mindmap PDF
Uploaded by
AyunieazahaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Siti Nur Asyiffa - 5H - Chapter 22 Mindmap PDF
Uploaded by
AyunieazahaCopyright:
Available Formats
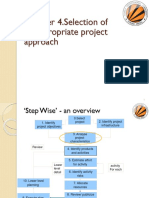
SD LIFE CYCLE
I. Systems Analysis
2. Conceptual Design
3. Physical Design
4. Implementation and Conversion
5. Operations and Maintenance WHY BEHAVIORAL PROB OCCUR?
throughout the life cycle, planning must be done & Fear Disruption
behavioral aspects of change must be considered Lack of top-mgt Manner change is
INVOLVEMENT IN SDLC support introduced
I. IS steering committee Bad prior experiences Biases & emotions
2. Project Development Team Poor communication Personal characteristics
3. Programmers
4. Systems Analysts
5. Management
6. Users
INTRO TO SYSTEMS DEVELOPMENT WAYS TO PREVENT
Management support Keep system simple
Two plans needed:
SD PLANNING
I. Project Development Plan
and Systems Analysis Satisfy user needs
Involve users
Keep open commu-
nication
Reduce fears Test system prior im-
Specific to a project & authored by the project team
2. Master Plan (CHAPTER 22) Avoid emotionalism plementation
Long-range & authored by steering committee
outlining prioritized projects & timetables
CAPITAL BUDGETING
I. Payback period
2. Net Present Value (NPV)
PLANNING TECHNIQUES
3. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
I. Program evaluation and review technique (P E R T)
used to identify critical paths, plan resources, FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS
estimate task duration & identify potential risks I. software product in terms of how much beneficial
2. Gantt chart product development will be for the org. in a
horizontal bar chart used to visually represent a practical POV
project plan over time 2. Below are 5 types of feasibility:
Economic Scheduling
Technical Operational
SITI NUR ASYIFFA BINTI MOHD AZAHA Legal
(2022787353)
AC220B5H
You might also like
- Chapter 05 Part 1Document16 pagesChapter 05 Part 1badigadprabidhik01No ratings yet
- Mod1TMC470 OMT570Lec1 4Ch3Process-1Document24 pagesMod1TMC470 OMT570Lec1 4Ch3Process-1Adarsh RaoNo ratings yet
- Objectives of The General Ledger SystemDocument3 pagesObjectives of The General Ledger SystemAnonymous iCFtw74QNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 WBSDocument15 pagesLecture 3 WBSShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Project Management Process Group (Online Class) - FGDDocument23 pages03 - Project Management Process Group (Online Class) - FGDGeofisika UINo ratings yet
- School App: Report - 03 Project Planning ReportDocument9 pagesSchool App: Report - 03 Project Planning ReportMarufa BadhonNo ratings yet
- What Is The Aim of Systems Engineering: C2 GeneralDocument34 pagesWhat Is The Aim of Systems Engineering: C2 GeneralUnarine MutshinyaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02 Project ManagementDocument8 pagesChapter 02 Project ManagementPatel RajNo ratings yet
- Guc 100 59 28201 2023-02-08T09 24 49Document17 pagesGuc 100 59 28201 2023-02-08T09 24 49Yomna ElmassryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.selection of An Appropriate Project ApproachDocument29 pagesChapter 4.selection of An Appropriate Project ApproachHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Task 3 Part A&C Implementation PlanDocument8 pagesTask 3 Part A&C Implementation PlanFitri AnaNo ratings yet
- LCC Book Chapter 6 P.C-A.C Asset ManagementDocument20 pagesLCC Book Chapter 6 P.C-A.C Asset ManagementJorge Perez DzulNo ratings yet
- Implementing The COSO 2013's New 17 Principles in AuditDocument23 pagesImplementing The COSO 2013's New 17 Principles in Audittunlinoo.067433100% (1)
- Proposed Project Cycle TemplateDocument11 pagesProposed Project Cycle TemplateAlessandra Mae SalvacionNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Ship Industrie 4Document18 pagesAutonomous Ship Industrie 4IdhamtanahbaruNo ratings yet
- 21mbac24-Tfb-Iat-2 - SeDocument3 pages21mbac24-Tfb-Iat-2 - SeHemanth SNo ratings yet
- 1-180-Adjie-Urplan-Its-Decision Support SystemDocument18 pages1-180-Adjie-Urplan-Its-Decision Support SystemStanislaus SangmanetaNo ratings yet
- Project Management A Managerial Approach-1Document11 pagesProject Management A Managerial Approach-1ousama aklanNo ratings yet
- 2 - What Is Project Management - Part 1Document8 pages2 - What Is Project Management - Part 1Ahmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2Jahanzaib Ashiq Jahanzaib AshiqNo ratings yet
- Sec 1Document5 pagesSec 1Hamza KarimallahNo ratings yet
- MYH Case StudyDocument62 pagesMYH Case Studyassignmentlink75% (16)
- Lec 23-25Document36 pagesLec 23-25api-19981384100% (1)
- PM - Pinto Chapter 5 NoteDocument12 pagesPM - Pinto Chapter 5 NoteSarthak ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Information System MNGTDocument28 pagesChapter 12 Information System MNGTShah AzNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Software Engineering - Isaac Computer ScienceDocument9 pagesApproaches To Software Engineering - Isaac Computer Science87shf2xx2jNo ratings yet
- EIS Summary NotsDocument62 pagesEIS Summary NotsKESHAV DroliaNo ratings yet
- Conversion Cycle (Process Cost) : Rizal Technological UniversityDocument25 pagesConversion Cycle (Process Cost) : Rizal Technological UniversityHatdogNo ratings yet
- Sen Part 2Document8 pagesSen Part 2ray654301No ratings yet
- W2-2 Clarify The Process - Final CandidateDocument48 pagesW2-2 Clarify The Process - Final CandidateNicolaNo ratings yet
- Massmarts Internal Audit IT Auditing ManualDocument25 pagesMassmarts Internal Audit IT Auditing ManualbturkistaniNo ratings yet
- It 101410 AppendixqDocument4 pagesIt 101410 AppendixqPaulina OssandonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document72 pagesChapter 10Carlfornia Vutomi MinyukuNo ratings yet
- Sadp Unit 2 ModifiedDocument3 pagesSadp Unit 2 ModifiedKesava 1642No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument23 pagesAssignmentDhanlaxmiNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis and Design: Software Development Life CycleDocument37 pagesSystems Analysis and Design: Software Development Life CycleTACN-2C-19ACN Nguyen Tien DucNo ratings yet
- 12 A) SPMDocument7 pages12 A) SPMTeju MelapattuNo ratings yet
- CITPM Body of Knowledge 4th Edition PDFDocument117 pagesCITPM Body of Knowledge 4th Edition PDFUber101No ratings yet
- IT General Controls - John Gatto (Part 3)Document32 pagesIT General Controls - John Gatto (Part 3)Adil SufyanNo ratings yet
- Systems Analysis: 1. Analytical 2. InterpersonalDocument10 pagesSystems Analysis: 1. Analytical 2. InterpersonalJARELL HANZ DAMIANNo ratings yet
- Project Scope Management 1Document48 pagesProject Scope Management 1Isla, Ana ValerieNo ratings yet
- Lec 3Document12 pagesLec 3raja sohaib qayyumNo ratings yet
- SESSION NO. 4 Onwards (Week 2 Onwards) : Rizal Technological UniversityDocument5 pagesSESSION NO. 4 Onwards (Week 2 Onwards) : Rizal Technological UniversityKelvin CaldinoNo ratings yet
- SPM Unit 1Document12 pagesSPM Unit 1samblaster252001100% (1)
- The Construction Management Process at Various Phases of The ProjectDocument39 pagesThe Construction Management Process at Various Phases of The ProjectJairus MadridNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Project ManagementDocument21 pagesGroup 8 - Project ManagementGanesh SarodeNo ratings yet
- Acquisition, Development and Implementation of Information SystemsDocument32 pagesAcquisition, Development and Implementation of Information SystemsSatrughan ThapaNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument8 pagesNotesniczNo ratings yet
- Standardizing Documentation For Internal Controls GuideDocument29 pagesStandardizing Documentation For Internal Controls Guidemr auditorNo ratings yet
- Project Cost Management: 1 Plan Cost MGMT 2 Estimate CostDocument23 pagesProject Cost Management: 1 Plan Cost MGMT 2 Estimate CostsahilkaushikNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV Audit Maintenance Warranty English 2017Document35 pagesChapter IV Audit Maintenance Warranty English 2017Javier Gaete ObrequeNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Project Planning: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesUnit 8 Project Planning: ObjectivesSayan RoyNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document20 pagesCH 2ARRAHMANNo ratings yet
- System Life Cycle Methodologies: Management Information Systems 8/E Raymond Mcleod, Jr. and George SchellDocument55 pagesSystem Life Cycle Methodologies: Management Information Systems 8/E Raymond Mcleod, Jr. and George SchellAbdul LatifNo ratings yet
- PIA 2731, Lecture 1: The Project CycleDocument15 pagesPIA 2731, Lecture 1: The Project CycleMuhammad N BashashaNo ratings yet
- Notes-Project Management Lesson 1Document5 pagesNotes-Project Management Lesson 1Mary Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering UNIT-1: Elements OF A Software Process ORDocument18 pagesSoftware Engineering UNIT-1: Elements OF A Software Process ORlakshmiNo ratings yet
- IRMITKnowledge Topic AgileDocument14 pagesIRMITKnowledge Topic AgileJoel Colquepisco EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Managing Software Deliverables: A Software Development Management MethodologyFrom EverandManaging Software Deliverables: A Software Development Management MethodologyNo ratings yet
- Analysis within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 3 Activity Analysis — The DeliverablesFrom EverandAnalysis within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 3 Activity Analysis — The DeliverablesNo ratings yet