Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 - What Is Project Management - Part 1
Uploaded by
Ahmad JalamnehOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 - What Is Project Management - Part 1
Uploaded by
Ahmad JalamnehCopyright:
Available Formats
German Jordanian University
School of Management and Logistic Sciences
Management Sciences Department
Course:
Project Management MGT328
Chapter 2: What is Project Management?
Lecturer:
Omar M. Bwaliez
1 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
In This Chapter:
2.1 Introduction.
2.2 What is Project Management?
2.3 Project Management Organizations.
2.4 Project Management Process Groups.
2.4.1 Initiating Process Group.
2.4.2 Planning Process Group.
2.4.3 Executing Process Group.
2.4.4 Monitoring and Controlling Process Group.
2.4.5 Closing Process Group.
2.4.6 Project Management Process Group Interactions.
2.5 Project Management Knowledge Areas.
2.6 Project Management Process Groups and Knowledge Areas Mapping.
2.7 End-of-Chapter Quiz.
2 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
2.1 Introduction:
Implementing projects is not an easy process. It needs the skills, tools, and
techniques of multiple professions and organizations.
So, What is the best way to implement a project? The challenge is to manage the
required project inputs in order to achieve the project outputs. Project management is
one way to overcome that challenge.
The application of project management facilitates:
(1) Completion of project on time or earlier. [Time]
(2) Not exceeding the budget and other resources. [Cost]
(3) Meeting the specifications to the satisfaction of the customer. [Customer
satisfaction]
3 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
2.2 What is Project Management?
Definition of Project Management:
Project Management [] is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and
techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements.
The following figure illustrates some of
the most important tools used in project
management.
Managing a project typically includes:
1. Identifying requirements.
2. Addressing the various needs, concerns, and expectations of the stakeholders
as the project is planned and carried out.
3. Balancing the competing project constraints.
4 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
2.3 Project Management Organizations:
The complexity of the problems faced by the project manager results in a rapid
growth in the number of project-oriented organizations that has contributed to the
professionalization of project management and codified the areas of knowledge
required for competent project management.
The following are some of the major international project
management organizations:
1. The Project Management Institute (PMI). It was established in the United
States of America in 1969. Its mission is to foster the growth of project management
as well as building professionalism in the field through its many worldwide chapters,
its meetings and seminars around the globe, and its journals, books, and other
publications. The PMI has its project management body of knowledge (PMBOK).
2. The Association for Project Management (APM). It headquartered in the
United Kingdom, which started in the early 1970s and serves all of Europe. The
APM has its APM body of knowledge (APM BOK).
3. The International Project Management Association (IPMA). It headquartered
in Switzerland, which began in 1965 and serves a global constituency.
5 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
2.4 Project Management Process Groups:
Project management is accomplished through the appropriate application and
integration of five processes called project management process groups or simply
project management processes. They are:
Initiating (Start).
Planning (Plan).
Executing (Do).
Monitoring and Controlling (Check and act)
Closing (End).
A process group contains a set of interrelated actions and activities performed to
achieve a pre-specified product, service, or result. It is worth mentioning that all five
process groups are addressed in each project. Each process group is characterized by
its inputs, the tools and techniques that can be applied, and the resulting outputs. The
output of one process group generally becomes an input to another process group or
is a deliverable of the project.
6 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
2.4 Project Management Process Groups: cont.
Notes:
The project management process groups do not occur sequentially; they are overlapping
activities that occur throughout the project.
The application of the project management process groups is “iterative”, and many processes are
repeated during the project.
Project management process groups are not project life cycle phases. The project phase
describes what you need to do to complete the work, while the project management process group
describes what you need to do to manage the project.
The following chart can be used to learn the project management
process groups quickly and effectively. It helps you understand what
should be done when.
The following subsections identify and describe the five project
management process groups.
7 Omar Bwaliez 2020
Ch.2: What is Project Management?
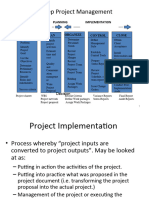
Project Management Process Groups Chart
MONITORING &
INITIATING PLANNING EXECUTING CLOSING
CONTROLLING
Measure performance
Execute the work according Confirm work is done to
Select project(s). Finalize requirements. against the performance
to the PM plan. requirements.
measurement baseline.
Determine variances and if
Create project scope Complete procurement
Select project manager. Request changes. they warrant a change
statement. closure.
request.
Determine company culture Determine what to Perform integrated change Gain formal acceptance of
Perform quality assurance.
and existing systems. purchase. control. the product.
Collect processes,
Complete final performance
procedures, and historical Determine team. Acquire final team. Approve or reject changes.
reporting.
information.
Understand the project’s Inform stakeholders of
Create WBS. Manage people. Index and archive records.
business case. approved changes.
Uncover initial Send and receive Update lessons learned
Create activity list. Create forecasts.
requirements and risks. information. knowledge base.
Create measurable Perform earned value
Create network diagram. Hold meetings. Hand of completed product.
objectives. analysis.
Estimate resources, time,
Develop project charter. Perform quality control. Release resources.
and cost.
Develop stakeholder Determine all roles and Report on project
management strategy. responsibilities. performance.
Develop final PM plan and
performance measurement Perform risk audits.
baseline that are realistic.
Gain formal approval of
the plan and hold kickoff Administer procurements.
meeting.
8 Omar Bwaliez 2020
You might also like
- Project Management Processes OverviewDocument88 pagesProject Management Processes OverviewrajimuruganNo ratings yet
- PMP Exam Notes (May 08th)Document21 pagesPMP Exam Notes (May 08th)Andrew Barclay100% (3)
- Project Scope ManagementDocument112 pagesProject Scope ManagementKelvin TingNo ratings yet
- Effecttive Project Management and New Product LaunchDocument20 pagesEffecttive Project Management and New Product LaunchAjayi Adebayo Ebenezer-SuccessNo ratings yet
- PMP Comprehensive NotesDocument29 pagesPMP Comprehensive NotesMohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- PPAM Final NotesDocument51 pagesPPAM Final NotesShimels ShitayeNo ratings yet
- Project Integration Management PlanDocument43 pagesProject Integration Management PlanBruce FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Brief PMPDocument11 pagesBrief PMPAliNo ratings yet
- PMP Comprehensive NotesDocument27 pagesPMP Comprehensive NotesAhmed Awed100% (1)
- Project Managementt200813 PDFDocument257 pagesProject Managementt200813 PDFL PatelNo ratings yet
- Project Scope Management Core FunctionsDocument30 pagesProject Scope Management Core FunctionsRifat Hasan RathiNo ratings yet
- Project Management Processes-Ch3Document88 pagesProject Management Processes-Ch3nihaj100% (1)
- Project Management ProcessesDocument11 pagesProject Management ProcessesBob DehnkeNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Dr. Donnie BoodlalDocument34 pagesProject Management: Dr. Donnie BoodlalRandy Sooknanan100% (1)
- Project Management Processes-Ch3Document88 pagesProject Management Processes-Ch3Carlos Aaron Chanta PerazaNo ratings yet
- GX Human Capital OverviewDocument2 pagesGX Human Capital OverviewEL ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Seven Essentials For Business Success - Lessons From Legendary ProfessorsDocument245 pagesSeven Essentials For Business Success - Lessons From Legendary ProfessorsahmetNo ratings yet
- Unit 6: Social EntrepreneurshipDocument20 pagesUnit 6: Social EntrepreneurshipcristianaNo ratings yet
- 5.project Scope ManagementDocument24 pages5.project Scope Managementsaikumar selaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Lifecycle GuideDocument35 pagesProject Management Lifecycle GuidehalinaNo ratings yet
- Project Management Fundamentals: Key Concepts and MethodologyFrom EverandProject Management Fundamentals: Key Concepts and MethodologyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Pertemuan 3 - Manajemen Konstruksi - Life Cycle ProjectDocument23 pagesPertemuan 3 - Manajemen Konstruksi - Life Cycle ProjectOzzy OjikNo ratings yet
- Project Management: K.ElamkumuthanDocument24 pagesProject Management: K.ElamkumuthanJeyanayagam JeyatheesNo ratings yet
- 13 - Stakeholder Management - 11 PDFDocument24 pages13 - Stakeholder Management - 11 PDFAnonymous j19GEvKNNo ratings yet
- Ippm01 Day 03Document13 pagesIppm01 Day 03Hatem AbdaliNo ratings yet
- General Project Management: Huawei ConfidentialDocument13 pagesGeneral Project Management: Huawei ConfidentialAjeng Sinta AwaliaNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Project Management ProfessionalDocument28 pagesDay 2 Project Management ProfessionalSuraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- #2 LifeCycle v001Document28 pages#2 LifeCycle v001rezaismiriadiNo ratings yet
- PMF-project Integration Mana - Bryan NguyenDocument31 pagesPMF-project Integration Mana - Bryan NguyenPablo CabotNo ratings yet
- Project Management Part 3Document43 pagesProject Management Part 3sundyveeraNo ratings yet
- Project Planning & Management: Lecturer: Eng - Abdifatah Omar AbdillahiDocument61 pagesProject Planning & Management: Lecturer: Eng - Abdifatah Omar Abdillahiabdikani abdilaahiNo ratings yet
- PM - Pinto Chapter 5 NoteDocument12 pagesPM - Pinto Chapter 5 NoteSarthak ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- CAPM Galway Day 2 Participant NotesDocument63 pagesCAPM Galway Day 2 Participant NotesAnna TrubetskayaNo ratings yet
- Project Monitoringand Control PMCDocument6 pagesProject Monitoringand Control PMCAhmedAliKhaskayaNo ratings yet
- Project DefinitionDocument2 pagesProject DefinitionCzamille Rivera Gonzaga100% (1)
- Project Management (University of Toronto) Project Management (University of Toronto)Document7 pagesProject Management (University of Toronto) Project Management (University of Toronto)HBHNo ratings yet
- Project Management - Lecture 1Document36 pagesProject Management - Lecture 1The KingNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4&5 - Schedule ManagementDocument126 pagesLecture-4&5 - Schedule ManagementSamar Fouad100% (1)
- The Construction Management Process at Various Phases of The ProjectDocument39 pagesThe Construction Management Process at Various Phases of The ProjectJairus MadridNo ratings yet
- Notes-Project Management Lesson 1Document5 pagesNotes-Project Management Lesson 1Mary Anne CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Part 1Document16 pagesChapter 05 Part 1badigadprabidhik01No ratings yet
- PJM5900 Week 3 - Foundations of Project Planning and Scope Management - 2021Document34 pagesPJM5900 Week 3 - Foundations of Project Planning and Scope Management - 2021DianaNo ratings yet
- 04 Project CycleDocument7 pages04 Project CycleAnikNo ratings yet
- m.m.ali@ess.aucegypt.edu بورج PMP Integrated ذيفنت سدنهم بورج بتكملا هحفص TSC بويت ويلا ىلع ضوعم دمحم سدنهم هانقDocument51 pagesm.m.ali@ess.aucegypt.edu بورج PMP Integrated ذيفنت سدنهم بورج بتكملا هحفص TSC بويت ويلا ىلع ضوعم دمحم سدنهم هانقAhmed Rahim IsmailNo ratings yet
- Initiating Planning Executing Monitoring & Controlling ClosingDocument6 pagesInitiating Planning Executing Monitoring & Controlling ClosingKshatrapati SinghNo ratings yet
- 10 - Communications Management - 12Document24 pages10 - Communications Management - 12Anonymous j19GEvKNNo ratings yet
- Chapter II PMDocument28 pagesChapter II PMalemneh bayehNo ratings yet
- (Pmbok® Guide) Sixth EditionDocument41 pages(Pmbok® Guide) Sixth EditionNaba majeadNo ratings yet
- Project and Site Management 1: DR Oluwole AjayiDocument28 pagesProject and Site Management 1: DR Oluwole AjayiGbemisola LawalNo ratings yet
- Integration ManamgementDocument1 pageIntegration Manamgementcarotenoid100% (1)
- Lecture 2 Project Management - 1a For StudentsDocument38 pagesLecture 2 Project Management - 1a For StudentsRathish RagooNo ratings yet
- PM Notes WordDocument257 pagesPM Notes Wordgkvimal nathanNo ratings yet
- DAY 8 PROJECT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENTDocument22 pagesDAY 8 PROJECT INTEGRATION MANAGEMENTAlok SharmaNo ratings yet
- Project Life CycleDocument13 pagesProject Life CycleHarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- SHAS4545 Space G4 S2-20202021 MOHAMAD ZULHELMI BIN AZHAR (SX160555KEES04)Document3 pagesSHAS4545 Space G4 S2-20202021 MOHAMAD ZULHELMI BIN AZHAR (SX160555KEES04)Nur FadzleynNo ratings yet
- Sample - PMP - Quick Reference - NDocument25 pagesSample - PMP - Quick Reference - NpentapentaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Project Management Process Group (Online Class) - FGDDocument23 pages03 - Project Management Process Group (Online Class) - FGDGeofisika UINo ratings yet
- PMP Prepare - PMBOK 5 Edition Project Integration ManagementDocument60 pagesPMP Prepare - PMBOK 5 Edition Project Integration ManagementAllwyn GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Project Scope ManagementDocument16 pagesProject Scope ManagementRonan Erickson CuaNo ratings yet
- Ccs 101 ExaminationDocument21 pagesCcs 101 ExaminationMichael Angelo MallariNo ratings yet
- Higher Nationals: Internal Verification of Assessment Decisions - BTEC (RQF)Document45 pagesHigher Nationals: Internal Verification of Assessment Decisions - BTEC (RQF)Master GamerNo ratings yet
- ITS Project Management MethodologyDocument34 pagesITS Project Management MethodologyAgroEmpresario ExportadorNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 1 (Project Integration Management)Document37 pagesKelompok 1 (Project Integration Management)Sponsorship Ini Lho ITSNo ratings yet
- First PPCDocument63 pagesFirst PPCAhmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1Ahmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- 2 - What Is Project Management - Part 3Document10 pages2 - What Is Project Management - Part 3Ahmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- 1 - What Is A Project - Part 1Document9 pages1 - What Is A Project - Part 1Ahmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- Project Management Planning ProcessesDocument13 pagesProject Management Planning ProcessesAhmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- Project Management Chapter on Organizational StructuresDocument14 pagesProject Management Chapter on Organizational StructuresAhmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- 1 - What Is A Project - Part 1Document9 pages1 - What Is A Project - Part 1Ahmad JalamnehNo ratings yet
- Brand Book 2022 (IIMBC)Document30 pagesBrand Book 2022 (IIMBC)Vibhanshujeet RaiNo ratings yet
- Imtcdl PCPMMDocument4 pagesImtcdl PCPMMIndrajit DashNo ratings yet
- Philippine Christian University: Module in Entrepreneurship (Grade 12)Document6 pagesPhilippine Christian University: Module in Entrepreneurship (Grade 12)Jude Michael G. PondalesNo ratings yet
- Shortlisted for WAT/PI at NMIMS MBA programsDocument2 pagesShortlisted for WAT/PI at NMIMS MBA programsSaumya BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Sonata SoftwareDocument232 pagesSonata SoftwareReTHINK INDIANo ratings yet
- ILAC International College 2019 BrochureDocument32 pagesILAC International College 2019 BrochureLorz CatalinaNo ratings yet
- Co-Operative Organizations As A Means of Poverty Alleviation and Rural Community Development in NigeriaDocument17 pagesCo-Operative Organizations As A Means of Poverty Alleviation and Rural Community Development in NigeriaOkafor PrinceNo ratings yet
- Professional Socialization and TrainingDocument8 pagesProfessional Socialization and TrainingMiliyonNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila (University of The City of Manila) PLM Business School Accounting DepartmentDocument10 pagesPamantasan NG Lungsod NG Maynila (University of The City of Manila) PLM Business School Accounting DepartmentAndrea BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution Technology Adopted and Its Influence On The Operational Performance of Hospitality Industry in Guiuan Eastern SamarDocument5 pagesIndustrial Revolution Technology Adopted and Its Influence On The Operational Performance of Hospitality Industry in Guiuan Eastern SamarPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNo ratings yet
- Starbucks - Creating The Ambience and Rekindling People's Thirst by Bringing The Brew To The WorldDocument13 pagesStarbucks - Creating The Ambience and Rekindling People's Thirst by Bringing The Brew To The WorldAlix BEDOUINNo ratings yet
- About CosmaDocument11 pagesAbout CosmaRamani ManiNo ratings yet
- Nisa Sukra Putri Resume - NewestDocument1 pageNisa Sukra Putri Resume - NewestThoriq FirstaNo ratings yet
- The Business Plan: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument8 pagesThe Business Plan: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinpriyankacharyaNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument87 pagesManagerial Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDarronNo ratings yet
- C9 Accounting - Finance Module 1 Final 2012Document75 pagesC9 Accounting - Finance Module 1 Final 2012Alexis ParrisNo ratings yet
- Causes and Effects of Ineffective Communication On Construction ProjectsDocument17 pagesCauses and Effects of Ineffective Communication On Construction Projectshamza.shaqfeh123No ratings yet
- Reflection JournalDocument2 pagesReflection JournalMeshack MateNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management 11 q1 Mod5 Nature of Planning Types and Levels of Plans v5Document25 pagesOrganization and Management 11 q1 Mod5 Nature of Planning Types and Levels of Plans v5Eizell Andrea S. LajaraNo ratings yet
- FDI's Latin American States of The Future 2018-19Document8 pagesFDI's Latin American States of The Future 2018-19Isaac CapitanachiNo ratings yet
- Claire Zavoyna 2024 ResumeDocument2 pagesClaire Zavoyna 2024 Resumeapi-486344993No ratings yet
- v1 Innovation in Marketing Assignment July 2022 FinalDocument12 pagesv1 Innovation in Marketing Assignment July 2022 FinalOladoyin TaiwoNo ratings yet
- BDocument186 pagesBapi-678150172No ratings yet
- Implementing entrepreneurship education to reduce graduate unemploymentDocument13 pagesImplementing entrepreneurship education to reduce graduate unemploymentCEO DimejiNo ratings yet
- Name Course 1st Sem 08-09 Breakdown of Fees Unit Amount OR# Date AmountDocument115 pagesName Course 1st Sem 08-09 Breakdown of Fees Unit Amount OR# Date Amountalido_aiNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Net Present Value MethodDocument12 pagesBusiness Finance: Net Present Value MethodAngelica ParasNo ratings yet
- Games in Entrepreneurship EducationDocument19 pagesGames in Entrepreneurship EducationabdouNo ratings yet