100% found this document useful (1 vote)
116 views2 pagesUnderstanding Project Management Basics
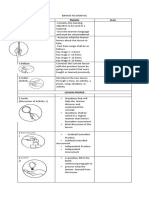
The document defines a project and outlines the key phases of project management:
1) A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end, undertaken to create a unique product or service. It has characteristics of being unique, temporary, and focused on achieving specific goals.
2) The core phases of project management include initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closing. In the planning phase, tasks and resources are identified and a project plan is created.
3) During execution, the project plan is implemented and work is performed while monitoring progress and making adjustments. The goal is to deliver the project objectives within time, cost, and quality targets.
Uploaded by
Czamille Rivera GonzagaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
116 views2 pagesUnderstanding Project Management Basics
The document defines a project and outlines the key phases of project management:
1) A project is a temporary endeavor with a defined beginning and end, undertaken to create a unique product or service. It has characteristics of being unique, temporary, and focused on achieving specific goals.
2) The core phases of project management include initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closing. In the planning phase, tasks and resources are identified and a project plan is created.
3) During execution, the project plan is implemented and work is performed while monitoring progress and making adjustments. The goal is to deliver the project objectives within time, cost, and quality targets.
Uploaded by
Czamille Rivera GonzagaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd