Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Workshop - Plan (Another Copy)
Uploaded by
Ramo RimoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Workshop - Plan (Another Copy)
Uploaded by
Ramo RimoCopyright:
Available Formats
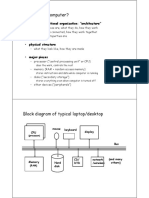
1/ Getting familiar with Neumann architecture and general purpose
computers:
Every system having ALU, memory, inputs, outputs and a transfer
function (in addition to other constraints) can be considered to be a
computation device (at the end, something is qualifying to be a computation
device if we can control the inputs, interpret the outputs, and be informed of
the internal functioning of the system.)
- we can get the change to brainstorm some examples: initial computation
with rocks, abacus , mechanical computation with Babbage analytical
machine.
- Discussing the point of discovery of electricity, and then electronics with the
discovery of transistor and finally the revolution that it brought to the field.
2/ One of the implementation of these computation devices (microcontrollers):
In this section, we discuss the general constraints imposed by
microcontrollers:
- power (static 5 volts input voltage), explain the bypass capacitor
- clock oscillator (we can get the general schema), search for the
interest of the capacitors on the sides of the oscillator
- a programming interface (USB peripheral) look for ICSP header and
native programming
- input and output interfaces
All of the above elements should be became familiar with
- Discussing the motivation for a micro-controller board (all the needs are
integrated into a single board)
- explain each of the parts independently (power and data interfaces)
3/ Introduction to schematics:
- getting the components placed (the ready file)
- getting the components wired.
- Understanding components
- Wires
- Nets
4/ Introducing PCBs (printed circuit boards):
- the historical aspects of electronic circuits (from wires to PCBs)
- a closer view to PCBs
- Traces
- Vias
- Pads
5/ Getting the PCB components placed and routed:
- Introducing the placement
- Some placement strategies
- Some routing strategies
- hands-on placement and routing
- consider elaborating a PDF file in which you indicate the most important
practices while routing the components
- you can consider adding a challenge at the end of each section.
6/ PCB Fabrication:
- All the files needed
- Gerber files and their utility
- Bill of materials
- Pick and place file
- performing the PCB fabrication online ()
TIP: while making the slides, consider organizing your slide in a form of
hierarchy.
a
lidzufp bslkdjf lkkjl
You might also like
- Week 5Document71 pagesWeek 5apoorvaNo ratings yet
- Internal Components of a ComputerDocument63 pagesInternal Components of a ComputerLester MagallonesNo ratings yet
- Serial Bus CommunicationDocument33 pagesSerial Bus CommunicationK k100% (1)
- Computer Architecture: Knowledge Level: BasicDocument130 pagesComputer Architecture: Knowledge Level: Basicrosev15No ratings yet
- Final Project Introduction To Computer System UnitDocument19 pagesFinal Project Introduction To Computer System UnitMuhammad Usman AkhterNo ratings yet
- Microcomputer Architecturei 1Document16 pagesMicrocomputer Architecturei 1Augustine NonsoNo ratings yet
- Workshop 20technolog 01.1Document7 pagesWorkshop 20technolog 01.1Akshat KulhariaNo ratings yet
- CHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY LAB MANUAL WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGYDocument63 pagesCHANDIGARH UNIVERSITY LAB MANUAL WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGYMehal KumarNo ratings yet
- Thisyear LectDocument420 pagesThisyear Lectsantosh vighneshwar hegdeNo ratings yet
- My Lecture1 Introductiona PDFDocument28 pagesMy Lecture1 Introductiona PDFchaitu4No ratings yet
- VHDL Quartus II LED Project & Combinational LogicDocument34 pagesVHDL Quartus II LED Project & Combinational LogicDaniaNo ratings yet
- ESD-Ch3 2018 P1 PDFDocument51 pagesESD-Ch3 2018 P1 PDFngoc an nguyenNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems Design (EEE 42101) - LecDocument18 pagesMicroprocessor Systems Design (EEE 42101) - Lecabdolmojeeb nourNo ratings yet
- Innovus Study Notes-CSDN BlogDocument6 pagesInnovus Study Notes-CSDN BlogAgnathavasiNo ratings yet
- Copyno1 Lastone February(Final)Document153 pagesCopyno1 Lastone February(Final)Sujala PatnaikNo ratings yet
- Arithmetic Logic UnitDocument26 pagesArithmetic Logic UnitZohaib MuhammadNo ratings yet
- cs1104 1Document45 pagescs1104 1Narvada KhedunNo ratings yet
- Pspice Tutorial - Workshop 2003Document58 pagesPspice Tutorial - Workshop 2003jodocsNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem - Module G11 (CSS)Document40 pages2nd Sem - Module G11 (CSS)Daniel Daryl CalingNo ratings yet
- 04cpu Part2Document12 pages04cpu Part2Rezaul karim ShiblyNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Information Technology and Computer OrganizationDocument11 pagesIntroduction to Information Technology and Computer OrganizationRonnn HhhhNo ratings yet
- Motherboard components explainedDocument3 pagesMotherboard components explainedGautam MandoliyaNo ratings yet
- COA Practical FileDocument39 pagesCOA Practical FileDeepak MishraNo ratings yet
- Comp Arch Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4Document161 pagesComp Arch Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Ch4Patricia Jane PerezNo ratings yet
- Contact: Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument14 pagesContact: Computer Organization and Architecturewooo24No ratings yet
- Tle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Document5 pagesTle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Rose FloresNo ratings yet
- Central Processing UnitDocument61 pagesCentral Processing UnitLasithaNo ratings yet
- U ProccessorsDocument487 pagesU ProccessorsAndrei Linca-Torje100% (1)
- What's in A Computer?: - Logical or Functional Organization: "Architecture"Document7 pagesWhat's in A Computer?: - Logical or Functional Organization: "Architecture"Gosaye DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture and Organization (Eeng 3192)Document34 pagesComputer Architecture and Organization (Eeng 3192)Esuyawkal AdugnaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Systems Servicing 11: Brief History of The MotherboardErickson JavonitallaNo ratings yet
- PSPICE TutorialDocument24 pagesPSPICE TutorialbjsimardNo ratings yet
- VHDL Tutorial-Part 1-Adc-SpiDocument7 pagesVHDL Tutorial-Part 1-Adc-Spihieuhuech1No ratings yet
- Passing Package CSDocument20 pagesPassing Package CSbharathkumar900845No ratings yet
- Ita1002 Digital-Computer-Fundamentals Eth 1.0 0 Ita1002Document2 pagesIta1002 Digital-Computer-Fundamentals Eth 1.0 0 Ita1002ShivamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document30 pagesLecture 2Hạnh Hoàng ĐìnhNo ratings yet
- Sitara Boot Camp 10 Uboot Linux Kernel Board PortDocument110 pagesSitara Boot Camp 10 Uboot Linux Kernel Board PortP MNo ratings yet
- SocDocument11 pagesSocshahd dawoodNo ratings yet
- Computer 1Document27 pagesComputer 1Oana StoiaNo ratings yet
- Computer EvolutionDocument27 pagesComputer EvolutionNihash Reddy0% (1)
- Computer Hardware and Networking SyllabusDocument5 pagesComputer Hardware and Networking SyllabusRiyas FasilNo ratings yet
- CAO Module 2 (Vinny)Document25 pagesCAO Module 2 (Vinny)40-Shruti ShindeNo ratings yet
- VLSI Project DescriptionDocument4 pagesVLSI Project DescriptionKishoreNo ratings yet
- Embedded Hardware Design Block DiagramDocument26 pagesEmbedded Hardware Design Block DiagramHoàng TrầnNo ratings yet
- PSPICE Tutorial 2Document25 pagesPSPICE Tutorial 2jamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1widiefreeNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- 9 TP Hardware & Networks IDocument2 pages9 TP Hardware & Networks IahmadzaatariNo ratings yet
- ECE 513 Microprocessor / Microcontroller Systems: By: Engr. Junard P. KaquilalaDocument34 pagesECE 513 Microprocessor / Microcontroller Systems: By: Engr. Junard P. KaquilalaGenesis AlquizarNo ratings yet
- PSPICE Tutorial Introduction Components Analyses DesignDocument25 pagesPSPICE Tutorial Introduction Components Analyses DesignVăn CôngNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Summary Notes Computer Science A Level OCRDocument5 pages1.1 Summary Notes Computer Science A Level OCRChi Nguyễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- Sitara Boot Camp Uboot Linux Kernel Board PortDocument111 pagesSitara Boot Camp Uboot Linux Kernel Board Porttuzarahul100% (2)
- LESSON 2 Basic Hardware Components of Computer SystemsDocument26 pagesLESSON 2 Basic Hardware Components of Computer Systemskate cacayNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Systems Design Lecture on 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument21 pagesMicroprocessor Systems Design Lecture on 8051 MicrocontrollerHassan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Printed Board Circuit Design (PCB) : Prabhanjan Kumar & Kumar GautamDocument18 pagesPrinted Board Circuit Design (PCB) : Prabhanjan Kumar & Kumar GautamvivNo ratings yet
- What's in A Computer?: - Logical or Functional Organization: "Architecture"Document8 pagesWhat's in A Computer?: - Logical or Functional Organization: "Architecture"Lakhvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 - MADocument6 pagesSheet 1 - MALê Mạnh KhánhNo ratings yet
- CS M151B / EE M116C: Computer Systems ArchitectureDocument29 pagesCS M151B / EE M116C: Computer Systems ArchitecturetinhtrilacNo ratings yet
- EE 271 Digital Circuits and Systems: Course Specification (Syllabus)Document41 pagesEE 271 Digital Circuits and Systems: Course Specification (Syllabus)R.R.S. SavichevaNo ratings yet
- 1) Lecture1Document32 pages1) Lecture1faxofi9132No ratings yet
- Workshop - Plan (Another Copy)Document2 pagesWorkshop - Plan (Another Copy)Ramo RimoNo ratings yet
- Workshop - Plan (Another Copy)Document2 pagesWorkshop - Plan (Another Copy)Ramo RimoNo ratings yet
- Workshop - Plan (Another Copy)Document2 pagesWorkshop - Plan (Another Copy)Ramo RimoNo ratings yet
- Workshop - Plan (Another Copy)Document2 pagesWorkshop - Plan (Another Copy)Ramo RimoNo ratings yet