Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Practical Relative Velocity & Acceleration PDF
Uploaded by
Keshav PagarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical Relative Velocity & Acceleration PDF
Uploaded by
Keshav PagarCopyright:
Available Formats
KOM
Practical No:
Title: - To solve two problems on velocity and acceleration analysis using relative
velocity and acceleration method.
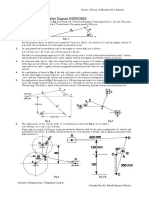
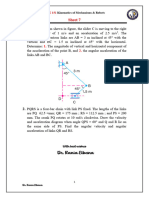
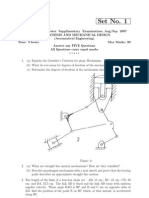
1. An engine mechanism is shown in Fig. The crank CB = 100 mm and the
connecting rod BA = 300 mm with centre of gravity G, 100 mm from B. In the
position shown, the crankshaft has a speed of 75 rad/s and an angular acceleration
of 1200 rad/s2. Find:1. velocity of G and angular velocity of AB, and 2.
acceleration of G and angular acceleration of AB.
2. PQRS is a four bar chain with link PS fixed. The lengths of the links are PQ= 62.5
mm ; QR = 175 mm ; RS = 112.5 mm ; and PS = 200 mm. The crank PQ rotates at
10 rad/s clockwise. Draw the velocity and acceleration diagram when angle QPS =
60° and Q and R lie on the same side of PS. Find the angular velocity and angular
acceleration of links QR and RS.
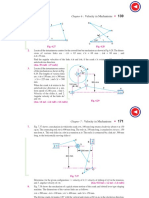
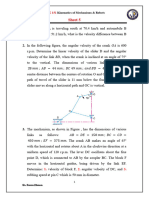
3. In the mechanism, as shown in Fig. the crank OA rotates at 20 r.p.m. anticlockwise
and gives motion to the sliding blocks B and D. The dimensions of the various
links are OA = 300 mm; AB = 1200 mm; BC = 450 mm and CD = 450 mm. For
the given configuration, determine : 1. velocities of sliding at B and D, 2. Angular
velocity of CD, 3. linear acceleration of D, and 4. angular acceleration of CD.
Prof. Pagar K. R. Mechanical Department, GCOERC, Nashik Page 1
KOM
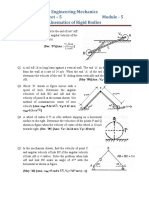
4. In the toggle mechanism shown in Fig., the slider D is constrained to move on a
horizontal path. The crank OA is rotating in the counter-clockwise direction at a
speed of 180 r.p.m. increasing at the rate of 50 rad/s2. The dimensions of the
various links are as follows: OA = 180 mm ; CB = 240 mm ; AB = 360 mm ; and
BD = 540 mm. For the given configuration, find 1. Velocity of slider D and
angular velocity of BD, and 2. Acceleration of slider D and angular acceleration of
BD.
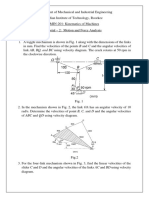
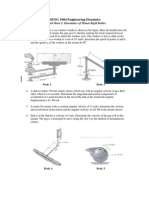
5. In the mechanism shown in Fig, the slider C is moving to the right with a velocity
of 1 m/s and an acceleration of 2.5 m/s2. The dimensions of various links are AB =
3 m inclined at 45° with the vertical and BC = 1.5 m inclined at 45° with the
horizontal. Determine: 1. The magnitude of vertical and horizontal component of
the acceleration of the point B, and 2. the angular acceleration of the links AB and
BC.
Prof. Pagar K. R. Mechanical Department, GCOERC, Nashik Page 2
You might also like
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetAgare Tube0% (1)
- Assignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFSarvesh ArbattiNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Theory of MachinesDocument4 pagesExercises: Theory of Machinesgangadharan tharumarNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration Diagram EXERCISESDocument2 pagesVelocity and Acceleration Diagram EXERCISESSpidyNo ratings yet
- Relative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsDocument9 pagesRelative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsSanket KumbharNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document4 pagesHW 4earn owinoNo ratings yet
- VelocitytutorialDocument4 pagesVelocitytutorialManoz Thapa KajiNo ratings yet
- 10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsDocument5 pages10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7b AccelerationDocument2 pagesTutorial 7b AccelerationGorkha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Batch-B2 Acceleration AnalysisDocument2 pagesBatch-B2 Acceleration AnalysisAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Dynamics ProblemsDocument6 pagesMechanical Engineering Dynamics Problemsizel valerianoNo ratings yet
- Question Bank KOMDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank KOMMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Kamalesh DfcNo ratings yet
- Kinema TicsDocument2 pagesKinema TicsMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsDocument29 pagesUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument2 pagesTheory of MachineRıshabhBhawarNo ratings yet
- Adams Lab ProblemsDocument10 pagesAdams Lab ProblemsAcchyutjhNo ratings yet
- Acceleration in MechanismsDocument38 pagesAcceleration in Mechanismsmurali_330No ratings yet
- Assignment-3 Date of Submission: 07-01-2022Document2 pagesAssignment-3 Date of Submission: 07-01-2022Vasthadu Vasu Kannah DLNo ratings yet
- At 6032 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment 1Document1 pageAt 6032 - Mechanics of Machines - Assignment 1Vinod BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Acceleration analysis tutorialDocument3 pagesAcceleration analysis tutorialdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- EJERCICIOS MECANISMOS - Javier Fuentes CDocument10 pagesEJERCICIOS MECANISMOS - Javier Fuentes CVictor MartinezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 KDMDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 KDMvishalNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Kinematics TutorialDocument2 pagesMechanism Kinematics TutorialAbhishek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 5: Example 15.1Document10 pagesExperiment No 5: Example 15.1dhuridevendra1984No ratings yet
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Document6 pagesME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rigid BodyDocument4 pagesKinematics of Rigid BodyAbishek AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeHarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Part 2Document3 pagesSheet 2 Part 2Fouad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankmunirajNo ratings yet
- KOM Unit-3Document9 pagesKOM Unit-3puneethNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Acceleration ExamplesDocument38 pagesMechanism Acceleration ExamplesApple VidalNo ratings yet
- Kom CTDocument3 pagesKom CTUmesh Kumar GanjirNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Continuous Assessment TestDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinery Continuous Assessment TestshiekziaNo ratings yet
- Relative Velocity MethodDocument10 pagesRelative Velocity MethodOneplus entartainmentNo ratings yet
- Sheet7Document1 pageSheet7Mahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- Kom Assignment IDocument4 pagesKom Assignment IChadaram Jagadish JagadishNo ratings yet
- MENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsDocument3 pagesMENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- Velocity - Acceleration DiagramDocument9 pagesVelocity - Acceleration DiagramvisheshNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 1Document3 pagesPractice Problems 1Shivam JainNo ratings yet
- Sheet5Document3 pagesSheet5Mahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Velocity AnalysisDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 Velocity Analysisdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 5wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Problem Sheet Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesEngineering Mechanics Problem Sheet Kinematics of Rigid BodiesLeo TallerNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Common QuestionsDocument7 pagesModule 5 Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Common QuestionsLeo TallerNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Tom Assignment and TutorialDocument6 pagesTom Assignment and TutorialAkshay MishraNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration AnalysisDocument6 pagesVelocity and Acceleration AnalysisPrithviNo ratings yet
- Linear Velocity, V, of A Point Is The Linear Displacement of That Point Per Unit Time. RecallDocument24 pagesLinear Velocity, V, of A Point Is The Linear Displacement of That Point Per Unit Time. RecallKarthikeyanRamanujamNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms and Mechanical DesignDocument9 pagesMechanisms and Mechanical DesignNizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- AccelerationDocument8 pagesAccelerationapshah08No ratings yet
- Quiz KomDocument5 pagesQuiz Komchellakutti tNo ratings yet
- Tom-Assignment 1Document2 pagesTom-Assignment 1jamunaa83No ratings yet
- Activities 1 DynamicsDocument6 pagesActivities 1 DynamicsDiego PulidoNo ratings yet
- MCQ MechanismsDocument22 pagesMCQ Mechanismstvkbhanuprakash100% (1)
- E Are Free To Rotate On The Axis P. The Compound Gear B and C Rotate Together On TheDocument2 pagesE Are Free To Rotate On The Axis P. The Compound Gear B and C Rotate Together On ThekookoNo ratings yet
- TOM Question BankDocument10 pagesTOM Question BankMadhan Kumar GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- CH7 Velocity in Mechanisms Relative Velocity MethoDocument32 pagesCH7 Velocity in Mechanisms Relative Velocity MethoAliNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationDocument63 pagesVelocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationMPee Finance SumerpurNo ratings yet