Professional Documents
Culture Documents
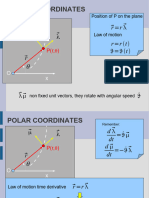
Kinema Tics
Uploaded by
MuntoiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinema Tics
Uploaded by
MuntoiaCopyright:
Available Formats
A.Y.
2020/21 Applied Mechanics kinematics
1
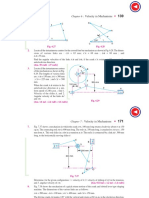
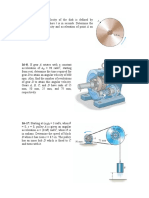
Slider-crank (1.7 Raparelli Ferraresi)
In the mechanism shown in figure, the crank OB rotates around the
fixed pivot O with constant angular velocity 1. is the angle
between the crank and the horizontal axis, as indicated in figure.
Data:
l=250 mm; r=100 mm; 1=100 rad/s; =135°/90°/180°
Determine:
the velocity of point B; the velocity of point A; the acceleration of
point B; the acceleration of point A
[=135° vB=10 m/s, vA=9,16 m/s, aB=1000 m/s2, aA=725,1 m/s2
=90° vB=10 m/s, vA=10 m/s, aB=1000 m/s2, aA=436 m/s2
=180°vB=10 m/s, vA=0, aB=1000 m/s2, aA=1400 m/s2]
2
Rigid body (1.6 Raparelli Ferraresi)
The plane rigid body ABCD shown in figure has rectangular shape
and slides along two orthogonal runners. The points A and B are
always in contact with the runners.
Data: =3 rad/s (counter-clockwise); =30°; AB=CD=1m;
AD=CB=0.5m.
Determine:
velocities of A and C;
the position of instantaneous center of zero velocity;
the value of in which the horizontal velocity component of
D is null.
[VA=1.5 m/s, VC=2.25 m/s, XK=0.87m, YK=0.5m, *=26.57°]
3
Four-bar linkage (1.11 Raparelli Ferraresi)
In the configuration of the figure the crank 1 is horizontal and its
angular velocity 1 is constant and counter-clockwise. The bar 3
is vertical.
Determine the angular velocities and the angular accelerations of
bars 2 and 3 in this configuration.
Data:
1 = 2 rad/s; OA = 100 mm; BD = 75 mm.
[2=0.857 rad/s; 3=0.428 rad/s;
=0.104 rad/s2, =4.23 rad/s2]
4
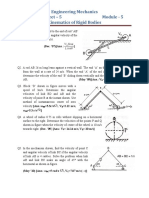
Piston rod-crank
The crank 1, of length R, rotates around at the fixed pivot O with
angular velocity n1 and angular acceleration . The connecting
rod 2, of length L, is hinged at body 1 in pivot A and at slider 3 in
pivot B. The body 3 slides along the horizontal groove.
Data:
R=0.21m; L=0.61m; 1=45°; 2=30°; n1=1500 rpm;
=1000rad/s2.
Determine:
The velocity and the acceleration of point B;
The angular velocity and the angular acceleration of body 2.
[VB=9.86 m/s, aB=4466m/s2, 2=44.17rad/s, =5526 rad/s2]
5
Wheels with connecting rod (1.17 Raparelli Ferraresi)
The two wheels 1 and 2 are connected by the bar AC and roll
without sliding on the floor.
The velocity of the centre A of the wheel 1 is 5 m/s constant in the
right direction.
Data:
AC=800 mm; r= 250 mm; BC= 200mm
In case of =0, determine:
the angular velocity of AC; the velocity of C; the velocity of B
[AC=0; vC= 5 m/s; vB= 2,78 m/s]
A.Y. 2020/21 Applied Mechanics kinematics
6
Cart in curve
A cart describes a curve of radius R=100 m with angular velocity
=0.2 rad/s and angular acceleration =0.1rad/s2.
On the cart, the sphere P runs inside a groove in radial direction.
In the configuration shown in figure PG = 50 cm, the relative
velocity of P with respect to G is Vr= 2 m/s and the relative
acceleration is ar=0,3 m/s2, with the same direction.
Determine the absolute velocity and acceleration of P.
[VP= 20.2 m/s; aP= 11.5 m/s2]
7
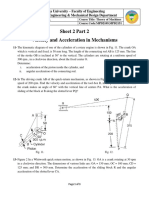
Quick return mechanism
Crank OP rotates with constant angular velocity = 157 rad/s.
Pivot P of the crank moves inside the groove of guide O1A.
With the assigned geometry shown in figure, determine angular
velocity 2 and acceleration of the oscillating guide, velocity
VA and acceleration aA.
Data:
OP = 0.305 m; O1A = 0.86 m; O1P = 0.61 m; O1O = 0.4 m.
[2= 62.3 rad/s; =1147.54 rad/s2; VA= 55 m/s; aA= 3400 m/s2]
8
Sliding vane compressor
The rotor rotates around its fixed centre O’ at the constant angular
velocity n = 2000 rpm. The vane can slide inside the radial groove
in the rotor. During rotation the vane remains in contact with the
fixed circular wall of the carter, of centre O. At the configuration
of the figure, determine the Coriolis acceleration of A.
Data: R=50 mm, OO’=10 mm, =45°
2
[aC= 707,7 m/s ]
9
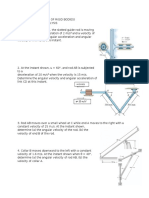
Piston rod-crank (type 2)
The crank 1 rotates in clockwise direction with constant angular
velocity 1=5 rad/s. The bar 2 slides inside the body 3 which can
rotate around the fixed pivot C. A reference system , is fixed to
the rod 2.
Data: OB=250 mm; OC=600 mm.
When =90° find:
the velocity of B;
the relative and the dragging velocities of C with respect to ,
;
the angular velocity and the angular acceleration of bar2.
[VB=1.25 m/s; VrC=1.154 m/s; VtC/B=0.481 m/s;
2=0.74 rad/s; =6.25 rad/s2]
10
Truck
The truck of figure is running at 70 km/h with a deceleration of 4
m/s2; in the same time the ladder is lifted and extended. The angle
is 30° and its time derivative is constant and equal to 8°/s, while
the ladder extension b is 1,5 m (d=6m), variable with velocity
=0,5 m/s and acceleration =-0,3 m/s2.
Find velocity and acceleration of the ladder end A with respect to
the truck and with respect to the ground.
[vAR= 1,16 m/s; vA= 19,4 m/s ; aAR= 0,47 m/s2; aA= 4,46 m/s2]
You might also like
- Mechanical Engineering Dynamics ProblemsDocument6 pagesMechanical Engineering Dynamics Problemsizel valerianoNo ratings yet
- Exercises: Theory of MachinesDocument4 pagesExercises: Theory of Machinesgangadharan tharumarNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document4 pagesHW 4earn owinoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Vel and Accln PDFSarvesh ArbattiNo ratings yet
- VelocitytutorialDocument4 pagesVelocitytutorialManoz Thapa KajiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 AE688Document7 pagesAssignment 03 AE688Mhmoud Al-TamimiNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis Worksheet PDF FreeHarsh VermaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMechanism of Machinery Velocity Analysis WorksheetAgare Tube0% (1)
- Tutorial 1 Velocity AnalysisDocument4 pagesTutorial 1 Velocity Analysisdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- Applied Dynamics Tut 4Document6 pagesApplied Dynamics Tut 4सुनिल दाहालNo ratings yet
- Kom Assignment IDocument4 pagesKom Assignment IChadaram Jagadish JagadishNo ratings yet
- Practical Relative Velocity & Acceleration PDFDocument2 pagesPractical Relative Velocity & Acceleration PDFKeshav PagarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5Document5 pagesTutorial Chapter 5wanpudinNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Rigid BodyDocument4 pagesKinematics of Rigid BodyAbishek AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Batch-B2 Acceleration AnalysisDocument2 pagesBatch-B2 Acceleration AnalysisAshutosh RautNo ratings yet
- Question Bank KOMDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank KOMMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Acceleration analysis tutorialDocument3 pagesAcceleration analysis tutorialdevraj subediNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines - I: Question Bank (Numericals) Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms: Graphical MethodsDocument18 pagesTheory of Machines - I: Question Bank (Numericals) Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms: Graphical Methodsvijaykumar327No ratings yet
- 10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsDocument5 pages10 Exercise 5 Acceleration Analysis of MechanismsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- MENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsDocument3 pagesMENG 1004 Engineering Dynamics Tutorial Sheet 2 Kinematics ProblemsMidnight_dreamerNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Acceleration Diagram EXERCISESDocument2 pagesVelocity and Acceleration Diagram EXERCISESSpidyNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsDocument29 pagesUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Problem Sheet Kinematics of Rigid BodiesDocument7 pagesEngineering Mechanics Problem Sheet Kinematics of Rigid BodiesLeo TallerNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Common QuestionsDocument7 pagesModule 5 Kinematics of Rigid Bodies Common QuestionsLeo TallerNo ratings yet
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Document4 pagesUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- EJERCICIOS MECANISMOS - Javier Fuentes CDocument10 pagesEJERCICIOS MECANISMOS - Javier Fuentes CVictor MartinezNo ratings yet
- Relative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsDocument9 pagesRelative Vel. and Accl. ProblemsSanket KumbharNo ratings yet
- Activities 1 DynamicsDocument6 pagesActivities 1 DynamicsDiego PulidoNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankmunirajNo ratings yet
- T4 - R1 - Kinematics of RB in 2D PDFDocument5 pagesT4 - R1 - Kinematics of RB in 2D PDFNurul AsyilahNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of MachineDocument25 pagesKinematics of MachineVidhiNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachineDocument2 pagesTheory of MachineRıshabhBhawarNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 Part 2Document3 pagesSheet 2 Part 2Fouad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Kamalesh DfcNo ratings yet
- 21 10 2021 6 1634817282934Document30 pages21 10 2021 6 1634817282934Bala VenkiNo ratings yet
- Assignment2ed PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment2ed PDFIza HamdanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Document11 pagesKinematics of Machinery May2006 Rr222105Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For DynamicsDocument4 pagesProblem Set For DynamicsSayan KarmakarNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines-Khurmi-116-120Document5 pagesTheory of Machines-Khurmi-116-120Star GlacierNo ratings yet
- Mech IV Sem Question BankDocument59 pagesMech IV Sem Question BankSivaNo ratings yet
- UC Berkeley ME 104 Engineering Mechanics Spring 2013 Homework SolutionsDocument3 pagesUC Berkeley ME 104 Engineering Mechanics Spring 2013 Homework SolutionsNhan ThanhNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems 1Document3 pagesPractice Problems 1Shivam JainNo ratings yet
- Problem SetDocument4 pagesProblem SetCalcifer da DemonNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet No 01Document3 pagesProblem Sheet No 01uzairNo ratings yet
- Sheet5Document3 pagesSheet5Mahmoud salahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document4 pagesTutorial 6ArvinNo ratings yet
- Velocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationDocument63 pagesVelocity and Accelerations in Planar Mechanisms, Coriolis Component of AccelerationMPee Finance SumerpurNo ratings yet
- ME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Document6 pagesME203 MOM July2013 Position Velo Tout01Kumar RajeshNo ratings yet
- Dyn Tutorial 5.1 PDFDocument3 pagesDyn Tutorial 5.1 PDFTareq SammarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7b AccelerationDocument2 pagesTutorial 7b AccelerationGorkha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Velocity and acceleration analysis of mechanismsDocument6 pagesVelocity and acceleration analysis of mechanismsAloysi DelouizaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery Continuous Assessment TestDocument2 pagesKinematics of Machinery Continuous Assessment TestshiekziaNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document9 pagesCH 16Amer JumahNo ratings yet
- ME203 MOM July16 IC&Acceleration Tutorial 02Document3 pagesME203 MOM July16 IC&Acceleration Tutorial 02Pradyumna KSNo ratings yet
- Phys10 Chap9 RotationOfRigidBodiesDocument6 pagesPhys10 Chap9 RotationOfRigidBodiesEngelbert Bicoy AntodNo ratings yet
- Clock Cleaning and Repairing - With a Chapter on Adding Quarter-Chimes to a Grandfather ClockFrom EverandClock Cleaning and Repairing - With a Chapter on Adding Quarter-Chimes to a Grandfather ClockRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cortante Utb 2020Document12 pagesCortante Utb 2020MuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics With FrictionDocument2 pagesDynamics With FrictionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics2 SlidesDocument17 pagesKinematics2 SlidesMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Rotors - SolutionDocument25 pagesTutorial Rotors - SolutionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Buckling Utb 2020Document12 pagesBuckling Utb 2020MuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Spanos Linear Prediction Theory For Digital Simulation of Sea WavesDocument7 pagesSpanos Linear Prediction Theory For Digital Simulation of Sea WavesMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Systems Modal AnalysisDocument22 pagesDynamic Systems Modal AnalysisMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Estructuras DosDocument11 pagesEstructuras DosMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Spanos ARMA Algorithms For Ocean Wave ModelingDocument10 pagesSpanos ARMA Algorithms For Ocean Wave ModelingMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Effective Breadth Rules ComparisonDocument9 pagesEffective Breadth Rules ComparisonMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Lin Methods of Stochastic Structural DynamicsDocument28 pagesLin Methods of Stochastic Structural DynamicsMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteDocument49 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Efficient technique determines ARMA algorithms for simulating stationary random processesDocument14 pagesEfficient technique determines ARMA algorithms for simulating stationary random processesMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial FEM - SolutionDocument18 pagesTutorial FEM - SolutionMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- SimulationofDeep WaterWavesBasedonDocument5 pagesSimulationofDeep WaterWavesBasedonMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Quentin Estimation and Prediction of Wave Inpit and System States Based On Local Hydropressure and Machinery ResponseDocument78 pagesQuentin Estimation and Prediction of Wave Inpit and System States Based On Local Hydropressure and Machinery ResponseMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- DDM - Mechatronics - Project 1Document3 pagesDDM - Mechatronics - Project 1MuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 1b - WhiteDocument12 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 1b - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 4 WhiteDocument61 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 4 WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 5 - WhiteDocument40 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 5 - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- FPGA and Structured ASIC - EnGDocument66 pagesFPGA and Structured ASIC - EnGMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 1aDocument36 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 1aMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteDocument49 pagesFluid Automation - Unit 3 - WhiteMuntoiaNo ratings yet
- My First Tutorial FpgaDocument52 pagesMy First Tutorial FpgaLongfet53No ratings yet