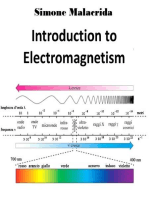
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Faraday
Uploaded by
Ramiro Ramirez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageMichael Faraday was a British scientist who studied electromagnetism and electrochemistry in the 19th century. His main discoveries included electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis by establishing the relationship between electricity, magnetism, and light. Faraday also discovered benzene, invented an early Bunsen burner, introduced terms still used today like electrode and ion, and was the first to hold the title of Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution of Great Britain.
Original Description:
Faraday
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMichael Faraday was a British scientist who studied electromagnetism and electrochemistry in the 19th century. His main discoveries included electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis by establishing the relationship between electricity, magnetism, and light. Faraday also discovered benzene, invented an early Bunsen burner, introduced terms still used today like electrode and ion, and was the first to hold the title of Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution of Great Britain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views1 pageFaraday
Uploaded by
Ramiro RamirezMichael Faraday was a British scientist who studied electromagnetism and electrochemistry in the 19th century. His main discoveries included electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis by establishing the relationship between electricity, magnetism, and light. Faraday also discovered benzene, invented an early Bunsen burner, introduced terms still used today like electrode and ion, and was the first to hold the title of Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal Institution of Great Britain.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Michael Faraday
September 22, 1791-Hampton Court, August 25, 1867)
Was a British scientist who studied electromagnetism
and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include
electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and
electrolysis.
Through his study of the magnetic field around a
conductor through which direct current flows, he laid
the foundations for the development of the concept
of electromagnetic field. He also established that
magnetism could affect light rays and that there was
an underlying relationship between the two
phenomena.
In the field of chemistry, Faraday discovered benzene, investigated chlorine
clathrate, invented an ancestor of the Bunsen burner, the oxidation number
system, and introduced terms such as anode, cathode, electrode, and ion. Finally,
he was the first to receive the title of Fullerian Professor of Chemistry at the Royal
Institution of Great Britain, which he would hold until his death.
Faraday made this discovery in 1845. It consists of the deviation of the plane of
polarization of light as an effect of a magnetic field, when passing through a
transparent material such as glass. It was the first known case of interaction
between magnetism and light.
You might also like
- Group 2Document9 pagesGroup 2Leanne TuasonNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument1 pageMichael FaradayValentina RoaNo ratings yet
- Michael Faraday Research PaperDocument6 pagesMichael Faraday Research Papergw0pajg4100% (1)
- FaradayDocument1 pageFaradayMainak Singha BarmaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Presentation Michael Faraday and His Contributions in The Field of Elctricity and ElectromagnetismDocument31 pagesGroup 3 Presentation Michael Faraday and His Contributions in The Field of Elctricity and ElectromagnetismIvan Salvador PapyrusNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument13 pagesMichael FaradayKyla MeiNo ratings yet
- Physicists: Group 3Document14 pagesPhysicists: Group 3Ebenezer RayosNo ratings yet
- My ProjectDocument1 pageMy ProjectOluwatumininu AlabiNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument2 pagesMichael FaradayPrincess Meth Catubigan SarominesNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument21 pagesNarrative ReportAngelo Celesena GalutNo ratings yet
- Michael Faraday - Group 2Document13 pagesMichael Faraday - Group 2Loraine Antonette CupoNo ratings yet
- MF SeminarDocument5 pagesMF SeminarJurica S MlincimaNo ratings yet
- Micael FaradayDocument2 pagesMicael Faradayanon_209478025No ratings yet
- Michael Faraday An English Scientist Who Contributed To The Study ofDocument2 pagesMichael Faraday An English Scientist Who Contributed To The Study ofJetro RosalesNo ratings yet
- Ancient and Classical History: Static ElectricityDocument15 pagesAncient and Classical History: Static ElectricityCarlos FightNo ratings yet
- Yadhu Krishnan - Michael Faraday and ElectricityDocument16 pagesYadhu Krishnan - Michael Faraday and ElectricityVishwanath J.R.No ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument15 pagesMichael FaradayMatthew FrederickNo ratings yet
- On Michael Farady by Aarushi PatidarDocument20 pagesOn Michael Farady by Aarushi PatidarAarushi Patidar100% (1)
- PHYSICSXIIDocument38 pagesPHYSICSXIISayantan DasNo ratings yet
- History of Elctronics by Ivy Dilla Btled 3bDocument11 pagesHistory of Elctronics by Ivy Dilla Btled 3bIvy DillaNo ratings yet
- History of ElctronicsDocument11 pagesHistory of ElctronicsIvy DillaNo ratings yet
- Ring of FireDocument5 pagesRing of FirePidotskiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Medan Elektromagnetik: Tokoh-Tokoh Yang Berjasa Di Bidang Elektromagnetik Dan MatematikDocument12 pagesTugas Medan Elektromagnetik: Tokoh-Tokoh Yang Berjasa Di Bidang Elektromagnetik Dan MatematikGagah Indrasmara Agityasaputra ST.MMNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument33 pagesMichael FaradayRezie Dampog DellavaNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument3 pagesMichael Faradaymarkmejia_025No ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument2 pagesMichael FaradayPrincess Faye V. PerezNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Pasig Jose St. Kapasigan, Pasig City College of EngineeringDocument6 pagesAssignment No. 1: Pamantasan NG Lungsod NG Pasig Jose St. Kapasigan, Pasig City College of EngineeringJessa Jabonete BrionesNo ratings yet
- Max Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert EinsteinDocument4 pagesMax Planck, in Full Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck: Albert Einsteinkat morenoNo ratings yet
- Electronic Waves Max PlanckDocument3 pagesElectronic Waves Max PlanckBliss GrandeNo ratings yet
- EM Wave TheoryDocument4 pagesEM Wave TheoryBlair RenceNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument54 pagesElectromagnetic WavesJoland MondaresNo ratings yet
- FaradayDocument2 pagesFaradaynazkasihNo ratings yet
- Brown Monochrome Simple Minimalist Presentation Template - 20231129 - 075306 - 0000Document9 pagesBrown Monochrome Simple Minimalist Presentation Template - 20231129 - 075306 - 0000Princess Maranan GargarNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument3 pagesMichael FaradayGaldinoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Michael FaradayDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Michael Faradayh07d16wn100% (1)
- The Nobel Prize in Physics 1901Document44 pagesThe Nobel Prize in Physics 1901Rudolf JasonNo ratings yet
- Rutherford, Radioactivity, and The Atomic NucleusDocument30 pagesRutherford, Radioactivity, and The Atomic NucleusanisdangasNo ratings yet
- The Five Scientist Behind Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument7 pagesThe Five Scientist Behind Electromagnetic SpectrumAnthony SantillanNo ratings yet
- 5 ScientistDocument3 pages5 ScientistEarrel Gianne Ibbay90% (10)
- MagnetismDocument3 pagesMagnetismArgel Linard Francisco MabagaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Milestone of ElectromagnetismDocument30 pagesDevelopmental Milestone of ElectromagnetismRamona EstevesNo ratings yet
- ElectronDocument15 pagesElectronMukhammad Hermawan Mochenk AwanNo ratings yet
- Sanu Chapri PhysicsDocument27 pagesSanu Chapri Physicslinkgogo69No ratings yet
- Electron 1561665Document18 pagesElectron 1561665johnny deppNo ratings yet
- Francis Aston and The Mass SpectrographDocument7 pagesFrancis Aston and The Mass SpectrographAhmed Ali SoomroNo ratings yet
- Basics of InductionDocument2 pagesBasics of InductionShahid AzizNo ratings yet
- Advanced Atomic TheoryDocument28 pagesAdvanced Atomic TheoryMohammed Sohail SamejaNo ratings yet
- A Timeline of Events in ElectromagnetismDocument7 pagesA Timeline of Events in ElectromagnetismGlenmar Alejandro VinegasNo ratings yet
- A Timeline of Events in Electromagnetism: 600 BCE: Sparking Amber in Ancient GreeceDocument7 pagesA Timeline of Events in Electromagnetism: 600 BCE: Sparking Amber in Ancient GreeceGlenmar Alejandro VinegasNo ratings yet
- The Five S Scien 2 PDFDocument6 pagesThe Five S Scien 2 PDFJit TrippinNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument107 pagesStructure of AtomDarshan Patil100% (1)
- The Contributions of Faraday and Maxwell to Electrical ScienceFrom EverandThe Contributions of Faraday and Maxwell to Electrical ScienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Xxi Century PhysicsDocument34 pagesXxi Century PhysicsDaniela SkellingtonNo ratings yet
- J.J. ThomsonDocument12 pagesJ.J. ThomsonVikram AnandNo ratings yet
- Maxwell, James Clerk PDFDocument4 pagesMaxwell, James Clerk PDFcreeshaNo ratings yet
- Michael FaradayDocument1 pageMichael FaradayduyNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument106 pagesStructure of AtomJayesh ChouhanNo ratings yet
- History of Electronics RushDocument36 pagesHistory of Electronics RushJiminah Yah100% (1)
- Structure of Atom (Historical Development)Document22 pagesStructure of Atom (Historical Development)Namish ManchandaNo ratings yet