0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesExpt 13 Plane Transmission Grating
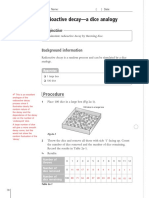
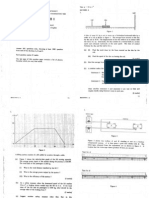
This experiment uses a plane transmission grating to determine the wavelengths of red and blue light. Students will measure the distance of bright fringes formed when red and blue light pass through the grating. From these measurements and the known grating slit separation, they can use the grating equation to calculate the wavelengths of red and blue light. The summary provides an overview of the key apparatus, procedures, and goals of the experiment to determine wavelengths of visible light using diffraction gratings.
Uploaded by
IkaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesExpt 13 Plane Transmission Grating
This experiment uses a plane transmission grating to determine the wavelengths of red and blue light. Students will measure the distance of bright fringes formed when red and blue light pass through the grating. From these measurements and the known grating slit separation, they can use the grating equation to calculate the wavelengths of red and blue light. The summary provides an overview of the key apparatus, procedures, and goals of the experiment to determine wavelengths of visible light using diffraction gratings.
Uploaded by
IkaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Introduction
- Apparatus
- Results
- Procedures
- Conclusion
- Discussion