Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology ss2
Uploaded by
Daniel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesOriginal Title
biology ss2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views2 pagesBiology ss2
Uploaded by
DanielCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
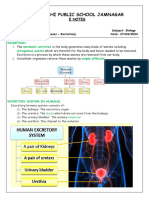
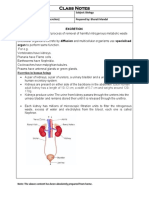
EXCRETION
Excretion is the process by which metabolic waste products are removed from the body of all living
things. Excretion is different from egestion which is the removal of solid waste (undigested food
substances i.e.faeces) through the anus. Excretion is necessary for the following reasons:
a. To avoid or prevent any harm that would be caused by any excretory product.
b. Some excretory products are poisonous to the body and should be removed.
c. To maintain water balance in the body (homeostasis).
d. To avoid interference of waste products with normal metabolic activities in the body.
EXCRETORY STRUCTURES AND WASTE IN ORGANISMS
TYPES OF EXCRETORY SYSTEMS
CONTRACTILE VACUOLE IN PROTOZOA
Contractile vacuole is a simple structure found in the cell of fresh water protozoa. Water constantly
enters the cell of a protozoan through the selectively permeable membrane because the cell is
hypertonic to its environment. As water enters the cell, a contractile vacuole is formed which collects
the water and expands, when it reaches the maximum size, it contracts and discharges the water
through a temporary break in the cell membrane at interval. Excretion of carbon dioxide and
ammonia is by diffusion through the cell membrane
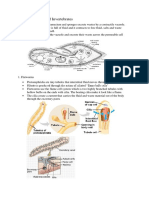
FLAME CELL IN FLATWORMS
The excretory system consists of two longitudinal canals with branched tubules which end in flame
cells. The flame cell has a large hollow called the cell lumen with bunch of flagella hung on it. Waste
product from the surrounding cells enters the flame cells. The flagella help to propel the fluid into the
tubules. The fluid passes into the exterior through a narrow tube called duct.
NEPHRIDIUM IN EARTHWORM
A pair of nephridia is found on each segment of the earthworm except the three and the last. Each
nephridium consists of a ciliated funnel, nephrostome which leads into a long coiled tube (narrow
and middle ciliated tubes, wide non-ciliated tubes and muscular tube). The tube opens to the exterior
as nephriodiophore (excretory pore). Waste product mainly urea is absorbed from blood capillaries
surrounding the nephridia. The fluid containing the waste through the long tube of the nephridia, salt
and other useful substances are reabsorbed through the wall of the tube. The unabsorbed substances
and water gather in the muscular tube and discharge to the exterior through the excretory pore.
MALPIGHIAN TUBULE IN INSECT
Malpighian tubules are found between the midgut (small intestine) and the hindgut (large intestine).
One end opens into the gut while the other end closed freely floats in the haemocoel. Nitrogenous
waste and water in the haemocoel are absorbed at the distal close end into the tubule. The waste is
converted into uric acid as it passes along the malpighian tubule towards the gut. A lot of water is
also reabsorbed so that by the time the uric acid reaches the proximal end, it is changed to solid
crystals. More water is reabsorbed in the rectum therefore concentrated urine leaves the body as
almost dried solid.
Classwork
SECTION A
1. The organelle which eliminates water from the body of protozoa is A. plasma membrane B.
contractile vacuole C. cell wall D. nucleus
2. In insects, the structure that performs the same function as the kidney in man is the A.
nephridium B. flame cell C. malpighian tubule D. trachea
3. The excretory structure in earthworm is the A. malpighian tubule B. nephridium C. kidney D.
flame cell
4. Flame cells are the A. excretory systems of worms B. excretory and respiratory systems of
flatworms C. excretory systems of flatworms D. secretory systems of flatworms
5. Which of these is a waste product of an insect? A. alkaloids B. uric acid C. sweat D.
mucilage
SECTION B
1) State the similarities and differences between excretory organs of a mammal and earthworm
2) State three factors that leads to the opening and closing of stomata.
3) List five excretory structures adapted to aquatic habitat
4) Mention four excretory waste in plants.
5) How are excretory products removed in amoeba and earthworm?
6) Describe the excretory structure in flatworm.
7) Define excretion.
8) Explain the necessity for an excretory system in animals.
9) Describe the mechanism of excretion in insects.
10) List five excretory product in plants.
11) Differentiate between excretion and egestion.
You might also like
- Chapter 4-Compare and Contrast-Transport EtcDocument34 pagesChapter 4-Compare and Contrast-Transport EtcCristel BautistaNo ratings yet
- ASTM E407-07 Standard Practice For Microetching Metals and AlloysDocument22 pagesASTM E407-07 Standard Practice For Microetching Metals and AlloysRifqiMahendraPutra100% (3)
- Class 10 Life ProcessDocument11 pagesClass 10 Life ProcessShubham Tiwari100% (2)
- Amisol Trio™: Skin Barrier and Hair ConditionerDocument18 pagesAmisol Trio™: Skin Barrier and Hair ConditionerCharlie MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chemtreat Challenges of Industrial Boiler Water TreatmentDocument17 pagesChemtreat Challenges of Industrial Boiler Water TreatmentKhondoker Nayeem ul haqueNo ratings yet
- Excretory System in Invertebrates NewDocument36 pagesExcretory System in Invertebrates Newudgfusgfusfgbsufgusd100% (8)
- 3RD Term S2 BiologyDocument26 pages3RD Term S2 Biologyask4oparahchigozieNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body Fluids HSBIO002Document34 pagesRegulation of Body Fluids HSBIO002REYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument8 pagesExcretory SystemShannen Christen NaraceNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - ExcretionDocument4 pagesLife Processes - ExcretionRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument2 pagesExcretionSD card 32 gbNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument21 pagesExcretory SystemAnin BertNo ratings yet
- Notes - Life Processes - Excretion - C-X - PART-IVDocument4 pagesNotes - Life Processes - Excretion - C-X - PART-IVdgera504No ratings yet
- The Excretory System in Swine and ChickensDocument4 pagesThe Excretory System in Swine and ChickensAbas S. AcmadNo ratings yet
- Ch 6 Life Processes NCERT Solutions (1)Document11 pagesCh 6 Life Processes NCERT Solutions (1)aalia hasanNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body FluidsDocument5 pagesRegulation of Body FluidsAlwìn GarciaNo ratings yet
- 10 BiologyDocument5 pages10 BiologyLegend 77 FFNo ratings yet
- 4. EXCRETORY SYS..SS2Document4 pages4. EXCRETORY SYS..SS2sunoyebimpeNo ratings yet
- 6 - Life Process (1)Document6 pages6 - Life Process (1)Saksham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesExcretory SystemAJAYI PETERNo ratings yet
- Sub Topics Covered:: Guidelines: Dear StudentsDocument6 pagesSub Topics Covered:: Guidelines: Dear StudentsSUHANEERIYANo ratings yet
- General Zoology Laboratory 1Document2 pagesGeneral Zoology Laboratory 1Luther Abaya MolinaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Compare and Contrast of The Process of Transport and CirculationDocument27 pagesWeek 3 Compare and Contrast of The Process of Transport and CirculationRAIZA MAE MIGUELNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Notes Grade 10Document6 pagesLife Processes Notes Grade 10Danny BlessyNo ratings yet
- X Life-Processes Excretion Module 1 of 3Document7 pagesX Life-Processes Excretion Module 1 of 3Tharika MahendranNo ratings yet
- Life ProoDocument6 pagesLife ProoItz me KARTIKKKNo ratings yet
- Wanater Canal System of SpongesDocument6 pagesWanater Canal System of SpongesAakash VNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument3 pagesExcretionsamNo ratings yet
- Canal System in Porifera: Ascon, Sycon and Leucon TypesDocument4 pagesCanal System in Porifera: Ascon, Sycon and Leucon TypesZotei RawihteNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedDocument12 pagesQ4 Week 3 4 GenBio2 EditedXyreen GalicinaoNo ratings yet
- Class X Biology: Life Processes Chapter NotesDocument18 pagesClass X Biology: Life Processes Chapter NotesSuresh Raghav50% (2)
- Regulation of Body FluidsDocument7 pagesRegulation of Body FluidsRuth FamillaranNo ratings yet
- Life Processess - Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesLife Processess - Lesson NotesshairyaNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument33 pagesPoriferaRushikesh pawar100% (1)
- ExcretionDocument5 pagesExcretionSaniya nebNo ratings yet
- Urinary System TermDocument30 pagesUrinary System TermRhahima SyafrilNo ratings yet
- X Bio Ch1 Life Processes Chapter Notes AugDocument18 pagesX Bio Ch1 Life Processes Chapter Notes AugAyush Pateria33% (3)
- Study Material Class XDocument14 pagesStudy Material Class XsaleemNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsDocument5 pagesLife Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsRajiv KabadNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument96 pagesGeneral BiologyrickyNo ratings yet
- SAJID FILE New CompleteDocument40 pagesSAJID FILE New Completejitendra kumarNo ratings yet
- ChopinDocument50 pagesChopinjojemjoeNo ratings yet
- Ist Term NotesDocument33 pagesIst Term NotesAyush KambojNo ratings yet
- Excretion: (A) Types of Animals On The Basis of Excretory Matter They ReleaseDocument6 pagesExcretion: (A) Types of Animals On The Basis of Excretory Matter They ReleasePrathmesh NamanNo ratings yet
- Excretion: (A) Types of Animals On The Basis of Excretory Matter They ReleaseDocument6 pagesExcretion: (A) Types of Animals On The Basis of Excretory Matter They ReleaseweyiNo ratings yet
- X Bio Ch1 Life Processes Chapter NotesDocument20 pagesX Bio Ch1 Life Processes Chapter NotesSurya Ravi0% (1)
- Canal System in PoriferaDocument6 pagesCanal System in Poriferasakibsharief911No ratings yet
- Excretory System of InvertebratesDocument3 pagesExcretory System of InvertebratesLingin LubisNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSESDocument6 pagesLIFE PROCESSESRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 10th Life ProcessDocument10 pages10th Life ProcessSunil SeerviNo ratings yet
- Life Processes-2Document10 pagesLife Processes-2Vipul BullaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument37 pagesBiologyThanosithebest12No ratings yet
- Excretion of WaterDocument5 pagesExcretion of WaterKamrul Alam MasumNo ratings yet
- Victoria JoiaDocument13 pagesVictoria JoiaJoia chipaique ChipaiqueNo ratings yet
- 1.6 EXCRETION-The Removal of WasteDocument13 pages1.6 EXCRETION-The Removal of WastesamiktshyagiriNo ratings yet
- Ex Cert IonDocument11 pagesEx Cert IonVicky BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Study of Human Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesStudy of Human Urinary SystemKʀɩsʜʌŋ ĸʀ ƦoƴNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange Frogs Cutaneous KeratinDocument4 pagesGas Exchange Frogs Cutaneous KeratinIAN NICOLETTE AUSTRIANo ratings yet
- Excretory System and OsmoregulationDocument10 pagesExcretory System and OsmoregulationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Science Definitions Form 3Document19 pagesScience Definitions Form 3api-261572669No ratings yet
- CQ Class10 Bio Life Processes T1Document8 pagesCQ Class10 Bio Life Processes T1Tapas Banerjee100% (1)
- PCOG LEC - Assignment 6 (Terpenoids and Resins)Document4 pagesPCOG LEC - Assignment 6 (Terpenoids and Resins)sadburgerNo ratings yet
- Chương 2 Cấu tạo và tính chất hóa lý hạt tinh bộtDocument82 pagesChương 2 Cấu tạo và tính chất hóa lý hạt tinh bộtTrungNo ratings yet
- Prominent Back Pressure ValvesDocument11 pagesProminent Back Pressure Valvesb wrNo ratings yet
- The Efficiency of Melanoidin Based-Waste Degradation With Different Biological MethodsDocument9 pagesThe Efficiency of Melanoidin Based-Waste Degradation With Different Biological MethodsTiaNo ratings yet
- Fill A Gap: Non Slump Flexible Acrylic Gap FillerDocument2 pagesFill A Gap: Non Slump Flexible Acrylic Gap FillerBianca Therese TorresNo ratings yet
- Vinnapas Solid Resins Brochure 2016 - 7409 - ENDocument24 pagesVinnapas Solid Resins Brochure 2016 - 7409 - ENJohnNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Et 2Document19 pagesLab Report Et 2Peach BabyNo ratings yet
- MID TERM EXAM - CLASS X SCIENCE SET ADocument6 pagesMID TERM EXAM - CLASS X SCIENCE SET AAnishika100% (1)
- Dura-Plate 301 L KDocument4 pagesDura-Plate 301 L KhainguyenbkvhvNo ratings yet
- O Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsDocument10 pagesO Level Bio - Chapter 1 - CellsTakudzwa ZvidzaNo ratings yet
- TDS Drewplus L-1311SDocument1 pageTDS Drewplus L-1311SIridian Cano CeronNo ratings yet
- Study On Important Biochemical Quality Parameters in Black TeaDocument15 pagesStudy On Important Biochemical Quality Parameters in Black TeaBagmishNo ratings yet
- New Testing ChargesDocument11 pagesNew Testing ChargesRay MrinalNo ratings yet
- Ren 2018Document4 pagesRen 2018Vaisakh KpNo ratings yet
- UV Absorbers / Stabilizers: Uses in The Supply ChainDocument2 pagesUV Absorbers / Stabilizers: Uses in The Supply ChainEMS 4AYDNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChemistryDocument4 pagesEngineering ChemistrySaha naNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steels: Types 321, 347 and 348Document9 pagesStainless Steels: Types 321, 347 and 348Lei WuNo ratings yet
- 48.0 - Spray Finishing v3.0 EnglishDocument16 pages48.0 - Spray Finishing v3.0 EnglishchumairabbasNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Teknik Reaksi KimiaDocument36 pagesRangkuman Teknik Reaksi KimiaRahmanda LuthfiaNo ratings yet
- Role of OxygenDocument14 pagesRole of OxygenrainrulletNo ratings yet
- Wa0036.Document2 pagesWa0036.GMHSS VehariNo ratings yet
- Full Paper: Chelvam Venkatesh, Prabal P. Singh, Hiriyakkanavar Ila, and Hiriyakkanavar JunjappaDocument9 pagesFull Paper: Chelvam Venkatesh, Prabal P. Singh, Hiriyakkanavar Ila, and Hiriyakkanavar JunjappaPrabal P SinghNo ratings yet
- Abstract: The New Compounds of Salicylic Acid Derivatives, 2 - (3 - (Chloromethyl) Benzoyloxy) Benzoic AcidDocument8 pagesAbstract: The New Compounds of Salicylic Acid Derivatives, 2 - (3 - (Chloromethyl) Benzoyloxy) Benzoic AcidFebria AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- FPA Fire Warden HandbookDocument62 pagesFPA Fire Warden HandbookSophie-Louise MercedesNo ratings yet
- PCM Moineau MR MVDocument6 pagesPCM Moineau MR MVendi suhendi awansyahNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Electrode Potential: Nernst EquationDocument10 pagesEquilibrium Electrode Potential: Nernst EquationSmruthi SuvarnaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High AlertDocument2 pagesDaftar Obat High AlertStore ApotekerNo ratings yet