Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DCC Report
Uploaded by
LynchXd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views7 pagesDCC Report
Uploaded by
LynchXdCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
BHARATI VIDYAPEETH INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
KHARGHAR
REPORT ON: BRIDGE NETWORK
Academic Year: 2022-23
Course: Data Communication & Computer Networking
Institute Code: 0027
Semester: 4
Under the Guidance of
Prof. Sujata Gawade
Submitted by: Arya Khandagale (8816)
Omkar Chavan (8842)
COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT
Introduction :-
In computer networking, a bridge is a device that connects
two or more network segments together. A bridge network is a
type of network configuration that uses bridges to connect
multiple network segments, allowing communication between
devices on different networks.
A bridge network operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of
the OSI model, and its primary function is to forward network
traffic between different network segments based on the
destination MAC (Media Access Control) address. When a
device sends data to another device on a different network
segment, the bridge network will forward the data to the
appropriate network segment based on the destination MAC
address.
Bridge networks can be used to extend the range of a network,
connect different types of networks together, or to segment a
larger network into smaller, more manageable segments. They
are commonly used in enterprise networks, where multiple
departments or floors of a building may have their own
network segments.
One of the benefits of using a bridge network is that it allows
for more efficient use of network bandwidth, as devices on
different segments can communicate directly with each other
without the need for data to be routed through a central router.
This can improve network performance and reduce latency.
Overall, bridge networks are an important tool in modern
computer networking, allowing for efficient and flexible
communication between different network segments.
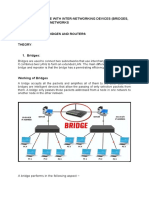
Working :-
A bridge network operates by examining the MAC addresses
of data packets as they pass through the network. When a
packet arrives at the bridge, it checks the destination MAC
address to determine which network segment the packet
should be forwarded to.
The bridge maintains a table of MAC addresses, known as a
MAC address table, which it uses to track the location of
devices on the network. When a device sends a packet, the
bridge adds the MAC address of the device to the MAC
address table, along with the network segment it is connected
to.If the destination MAC address is already in the MAC
address table and is on a different network segment than the
source device, the bridge will forward the packet to the
appropriate network segment. If the destination MAC address
is not in the table, the bridge will broadcast the packet to all
network segments except the one it was received on, in order
to find the destination device.
Once the destination device is found, its MAC address is
added to the table and subsequent packets to that device can
be forwarded directly.
Bridge networks can also be used to segment a larger network
into smaller, more manageable segments. This can improve
network performance by reducing the number of devices on
each segment and limiting the amount of traffic that needs to
be forwarded by the bridge.
Types of Bridge Network :-
1. Local Area Network (LAN) Bridge: This is the most
common type of bridge network and is used to connect two or
more LAN segments together. It operates at the data link layer
and forwards data based on MAC addresses.
2. Wireless Bridge: A wireless bridge connects two or more
wireless networks together, allowing devices on each network
to communicate with each other. It uses wireless signals to
transmit data between networks.
3. Virtual LAN (VLAN) Bridge: A VLAN bridge is used to
connect two or more VLANs together, allowing devices on
different VLANs to communicate with each other. It operates
at the data link layer and uses VLAN tags to identify which
VLAN a packet belongs to.
4. Remote Bridge: A remote bridge connects two LAN
segments that are geographically separated from each other
5. Transparent Bridge: A transparent bridge is a type of
bridge network that operates without requiring any
configuration from the user. It automatically forwards data
between different network segments based on MAC
addresses, without any user intervention.
6. Source Route Bridge: A source route bridge is used to
connect two or more networks that use different protocols or
have different addressing schemes.
Bridge Network :-
Advantages :-
1. Improved network performance: By forwarding packets
only to the appropriate network segment, bridge networks
reduce unnecessary traffic on the network and improve overall
network performance.
2. Increased network flexibility: Bridge networks can be used
to connect different types of networks together, allowing for
greater network flexibility and the ability to support a wider
range of devices.
3. Reduced network congestion: By limiting the amount of
broadcast traffic on the network, bridge networks reduce
network congestion and improve the efficiency of data
transmission.
4. Improved network security: Bridge networks can be used to
segment a larger network into smaller, more manageable
segments, which can improve network security by limiting the
potential impact of security breaches or network attacks.
5. Easy to set up and configure: Bridge networks are generally
easy to set up and configure, and do not require a lot of
additional hardware or software.
6. Cost-effective: Bridge networks are often a cost-effective
solution for connecting different network segments together,
as they do not require expensive routing equipment.
Disadvantages:-
1. Limited scalability: Bridge networks may become less
efficient as the number of connected network segments grows.
This can limit their scalability in larger networks.
2. Broadcast storms: If a device on the network generates a
large amount of broadcast traffic, it can create a broadcast
storm that can flood the entire network with unnecessary
traffic.
3. Single point of failure: A bridge network can be a single
point of failure for the entire network. If the bridge fails, all
devices on the network may lose connectivity.
4. Limited support for routing: Bridge networks only forward
data based on MAC addresses, and do not support the
advanced routing capabilities of more sophisticated
networking technologies, such as routers.
5. VLAN configuration complexity: VLAN bridges can be
more complex to configure and manage, especially in larger
networks with multiple VLANs.
6. Higher latency: Bridge networks may introduce additional
latency into the network, as packets must be processed by the
bridge before they can be forwarded to their destination.
Thank You…
You might also like
- Modeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTEFrom EverandModeling and Dimensioning of Mobile Wireless Networks: From GSM to LTENo ratings yet
- Lab DA-1Document27 pagesLab DA-1defristosNo ratings yet
- Cns Practical 4Document10 pagesCns Practical 4How to download AnythingNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks - Lecture NotesDocument42 pagesComputer Networks - Lecture NotesMehran Mustafa88% (17)
- Hardware & Network Servicing Level III: UC2: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocument80 pagesHardware & Network Servicing Level III: UC2: Determine Best Fit TopologyKinfe BeregaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 - DevicesDocument8 pagesUnit-4 - Devicesbobbysingh727272No ratings yet
- Computer Networking IMP Question and Answer SY BBA CA Sem IVDocument38 pagesComputer Networking IMP Question and Answer SY BBA CA Sem IVOM UTTARKARNo ratings yet
- LO3 Develop Topology EditedDocument38 pagesLO3 Develop Topology Editedbiruk mollaNo ratings yet
- Integrating Legacy and LAN/WAN Systems: Nathan J. MullerDocument19 pagesIntegrating Legacy and LAN/WAN Systems: Nathan J. MullerCentaur ArcherNo ratings yet
- Networks: Access Management: Class Notes # 6 Internetworking September 29, 2003Document7 pagesNetworks: Access Management: Class Notes # 6 Internetworking September 29, 2003utop8No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Part 1)Document5 pagesLesson 1 (Part 1)Rhealyn Galang BaduaNo ratings yet
- DevicesDocument29 pagesDevicesHabtamu Hailemariam AsfawNo ratings yet
- Different Types of BridgesDocument3 pagesDifferent Types of BridgesDinesh PudasainiNo ratings yet
- Networking Coursework. G5Document10 pagesNetworking Coursework. G5mbaziira eddyNo ratings yet
- Local Area Networks - InternetworkingDocument27 pagesLocal Area Networks - InternetworkingMohammed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Network Topology PDFDocument3 pagesNetwork Topology PDFLatonya ReidNo ratings yet
- AQA Computer Science A-Level 4.9.2 Networking: Advanced NotesDocument7 pagesAQA Computer Science A-Level 4.9.2 Networking: Advanced NotesShakila ShakiNo ratings yet
- Rail NetDocument24 pagesRail NetAugust mishraNo ratings yet
- Connecting DevicesDocument28 pagesConnecting DevicesNirmalNo ratings yet
- A Bridge Device Filters Data Traffic at A Network BoundarydDocument20 pagesA Bridge Device Filters Data Traffic at A Network BoundarydShall haileNo ratings yet
- Networking Coursework. G5.1Document13 pagesNetworking Coursework. G5.1mbaziira eddyNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument9 pagesNetwork Devicesellen_ramaNo ratings yet
- Unit-I PPT2 BasicsDocument34 pagesUnit-I PPT2 BasicsTejas MahadikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Network DevicesDocument42 pagesChapter 2: Network DevicesTamptress VampNo ratings yet
- Nguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingDocument13 pagesNguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingKatonguyenNo ratings yet
- 05 - Networking Components and Devices FDocument40 pages05 - Networking Components and Devices FBiniam NegaNo ratings yet
- CN Lab Exp 1 To 6Document37 pagesCN Lab Exp 1 To 6Ironheroo sivaNo ratings yet
- Network Types DevicesDocument4 pagesNetwork Types DevicesM.n KNo ratings yet
- 21bce8457 CN Lab2Document5 pages21bce8457 CN Lab2roopa KowshiNo ratings yet
- D PDFDocument29 pagesD PDFokienaNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument8 pagesNetwork DevicesSARLNo ratings yet
- Certificate: Dr. Jivraj Mehta Institute of Technology Mogar, AnandDocument75 pagesCertificate: Dr. Jivraj Mehta Institute of Technology Mogar, AnanddtNo ratings yet
- DCCNDocument5 pagesDCCNsurafel123emiruNo ratings yet
- Bridging and Switching BasicsDocument6 pagesBridging and Switching BasicsRicardo Herrera PradoNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Lec 8Document9 pagesComputer Network Lec 8Numan arshadNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingDocument6 pagesNetwork Essentials Fundamentals of NetworkingNaveen JhaNo ratings yet
- CN Connecting DevicesDocument3 pagesCN Connecting DevicesLife SayingsNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument6 pagesDocumentTANAKA ONIAS MANDIMUTSIRANo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeDocument6 pagesINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeAkriti SaxenaNo ratings yet
- CN Lab FinalDocument59 pagesCN Lab Finalreddy aditya456No ratings yet
- Networking Chap 3 4Document6 pagesNetworking Chap 3 4Aira DagumanNo ratings yet
- Note2 - Network DevicesDocument33 pagesNote2 - Network Devicesapi-26530736No ratings yet
- Practical 1: Study of Various Network Devices. 1. Repeater 2. Hub 3. Bridge 4. Switch 5. Router 6. ModemDocument13 pagesPractical 1: Study of Various Network Devices. 1. Repeater 2. Hub 3. Bridge 4. Switch 5. Router 6. ModemKikani JayanshuNo ratings yet
- DCN Unit-5Document15 pagesDCN Unit-5swanandghaskadviNo ratings yet
- CN AssignmentDocument4 pagesCN Assignmentgitu0744548No ratings yet
- "Devices For Connecting Network": Presented To The College of Computer Studies Data Communication and Networking 2Document9 pages"Devices For Connecting Network": Presented To The College of Computer Studies Data Communication and Networking 2Apple CamaliganNo ratings yet
- 2 Network DevicesDocument19 pages2 Network DevicesSourava Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Topology Omkar GhodkeDocument17 pagesTopology Omkar GhodkesrgrgggdsgNo ratings yet
- Mr. Nayneesh MishraDocument12 pagesMr. Nayneesh MishraPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Network DevicesDocument33 pagesNetwork Devicesapi-19739889No ratings yet
- Computer Networks KCDocument14 pagesComputer Networks KCKC ROCKNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 1Document18 pagesComputer Networks 1Edwin NfehNo ratings yet
- Networking Hardware and TopologiesDocument56 pagesNetworking Hardware and Topologiesskam zacNo ratings yet
- CN Exp1 60004200044 PDFDocument16 pagesCN Exp1 60004200044 PDFbhavik shahNo ratings yet
- Electronic Reservation ChartDocument66 pagesElectronic Reservation Chartasharmasp100% (1)
- Network Net Notes (3 Files Merged)Document17 pagesNetwork Net Notes (3 Files Merged)RohitNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Document9 pagesComputer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Pract 15&16Document1 pagePract 15&16LynchXdNo ratings yet
- Railway Management SystemDocument9 pagesRailway Management SystemLynchXdNo ratings yet
- Annexure IDocument2 pagesAnnexure ILynchXdNo ratings yet
- Annexure 2Document1 pageAnnexure 2LynchXdNo ratings yet
- Nat DCC Annexure 1-1Document1 pageNat DCC Annexure 1-1LynchXdNo ratings yet
- UndertakingDocument1 pageUndertakingLynchXdNo ratings yet
- Health & Performance Monitoring Using Active Magnetic BearingsDocument104 pagesHealth & Performance Monitoring Using Active Magnetic BearingsAbhinav RajNo ratings yet
- TNSTCDocument1 pageTNSTCMohamed MNo ratings yet
- 42mehd 24 11Document1 page42mehd 24 11Evin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Carte Tehnica Panou Fotovoltaic Cu Celule Policristaline Eging 250 WDocument1 pageCarte Tehnica Panou Fotovoltaic Cu Celule Policristaline Eging 250 WConstantin CilibiuNo ratings yet
- Tutoria Radio MobileDocument11 pagesTutoria Radio MobileGanti Nama Aja LahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NFFHT: Shyam Sunder Assistant Professor Mechanical EngineeringDocument44 pagesIntroduction To NFFHT: Shyam Sunder Assistant Professor Mechanical EngineeringTAPASVI BHATTNo ratings yet
- SDLP in Science July 18 2019Document5 pagesSDLP in Science July 18 2019Pinky MarieNo ratings yet
- Fluke Acess TemperatureDocument4 pagesFluke Acess TemperatureJuan José Villavicencio CantoNo ratings yet
- Principle of Virtual Work and Its ApplicationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Virtual Work and Its Applicationprem adhikari100% (1)
- Just Walk Across The RoomDocument8 pagesJust Walk Across The Roomstuutterrs100% (1)
- SC3 User Manual - V1.06 PDFDocument196 pagesSC3 User Manual - V1.06 PDFJoeNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Department Tracking Sheet OriginalCHARM2Document128 pagesLaboratory Department Tracking Sheet OriginalCHARM2Charmaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Bright: Insidecrochet - Co.ukDocument100 pagesBright: Insidecrochet - Co.ukЕкатерина Матушинец100% (2)
- Some Lower Bounds On The Reach of An Algebraic Variety: Chris La Valle Josué Tonelli-CuetoDocument9 pagesSome Lower Bounds On The Reach of An Algebraic Variety: Chris La Valle Josué Tonelli-CuetospanishramNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia NeonatorumDocument35 pagesAsphyxia NeonatorumMuhammad RagilNo ratings yet
- 20240119-AC MV Cable Schedule - R1Document1 page20240119-AC MV Cable Schedule - R1newattelectricNo ratings yet
- Sheet Service - SKT80SDocument3 pagesSheet Service - SKT80SAnanda risaNo ratings yet
- Monitoração E Diagnósticos de Pára-Raios A ZnoDocument7 pagesMonitoração E Diagnósticos de Pára-Raios A ZnoRamón MirelesNo ratings yet
- Dry-Heat Destruction of Destruction KineticsDocument5 pagesDry-Heat Destruction of Destruction KineticsFabioEspinolaNo ratings yet
- Latest CNC Cutting Design - Types, Materials and Installation - LivspaceDocument22 pagesLatest CNC Cutting Design - Types, Materials and Installation - Livspacesushil247No ratings yet
- EMI Unit 1Document98 pagesEMI Unit 1Anirudhh RaviNo ratings yet
- ISolutions Lifecycle Cost ToolDocument8 pagesISolutions Lifecycle Cost ToolpchakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Import Coordinates From Excel To AutoPIPEDocument23 pagesTutorial - Import Coordinates From Excel To AutoPIPEFabio MiguelNo ratings yet
- ProgrammableFlow Intro - Sep2011Document39 pagesProgrammableFlow Intro - Sep2011Serge StasovNo ratings yet
- Start Up Slug Catcher and Train 1Document43 pagesStart Up Slug Catcher and Train 1Larbi HammounNo ratings yet
- Hardware Catalog No Prices (PTHW0208.1C) PDFDocument11 pagesHardware Catalog No Prices (PTHW0208.1C) PDFAhmed TahaNo ratings yet
- Obturator / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument97 pagesObturator / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- (Ronald Weed, John Von Heyking (Eds.) ) Civil ReligiDocument375 pages(Ronald Weed, John Von Heyking (Eds.) ) Civil ReligiskaspeNo ratings yet
- Nutritional and Antinutritional Composition of Fermented Foods Developed by Using Dehydrated Curry LeavesDocument8 pagesNutritional and Antinutritional Composition of Fermented Foods Developed by Using Dehydrated Curry LeavesManu BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Differential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and The Pathogenesis of InflammationDocument14 pagesDifferential Release of Mast Cell Mediators and The Pathogenesis of InflammationklaumrdNo ratings yet
- Concise Guide to OTN optical transport networksFrom EverandConcise Guide to OTN optical transport networksRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZFrom EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsFrom EverandAlcatel-Lucent Service Routing Architect (SRA) Self-Study Guide: Preparing for the BGP, VPRN and Multicast ExamsNo ratings yet
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterFrom EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- The CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersFrom EverandThe CompTIA Network+ Computing Technology Industry Association Certification N10-008 Study Guide: Hi-Tech Edition: Proven Methods to Pass the Exam with Confidence - Practice Test with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsFrom EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationFrom EverandCCNA: 3 in 1- Beginner's Guide+ Tips on Taking the Exam+ Simple and Effective Strategies to Learn About CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) Routing And Switching CertificationNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachFrom EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNo ratings yet
- HACKING WITH KALI LINUX PENETRATION TESTING: Mastering Ethical Hacking Techniques with Kali Linux (2024 Guide for Beginners)From EverandHACKING WITH KALI LINUX PENETRATION TESTING: Mastering Ethical Hacking Techniques with Kali Linux (2024 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- FTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationFrom EverandFTTx Networks: Technology Implementation and OperationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionFrom EverandMastering Linux Security and Hardening - Second Edition: Protect your Linux systems from intruders, malware attacks, and other cyber threats, 2nd EditionNo ratings yet