0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views26 pagesPractice Assignment 1-Solutions
This document contains solutions to practice problems from the textbook Fundamentals of Electric Circuits. It includes problems related to calculating charge, current, power, and cost based on given circuit parameters like voltage, current over time, device power ratings, and electricity pricing. The problems cover basic circuit analysis concepts taught in an introductory course.
Uploaded by
Jingyu ZhangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views26 pagesPractice Assignment 1-Solutions
This document contains solutions to practice problems from the textbook Fundamentals of Electric Circuits. It includes problems related to calculating charge, current, power, and cost based on given circuit parameters like voltage, current over time, device power ratings, and electricity pricing. The problems cover basic circuit analysis concepts taught in an introductory course.
Uploaded by
Jingyu ZhangCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Problem 1: Number of Electrons: Determines the number of electrons represented by a given charge.
- Problem 2: Current Determination: Calculates the current flowing through an element from the charge flow function provided.
- Problem 3: Charge Calculation: Finds the charge flowing through a device given a current function.
- Problem 4: Charge Flow through a Conductor: Calculates the charge passing through a conductor in a specified time.
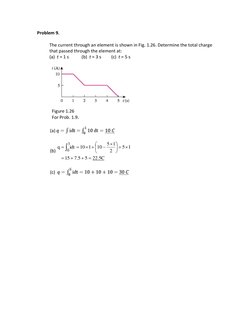
- Problem 5: Total Charge Transfer: Determines the total charge transferred over a short time interval.
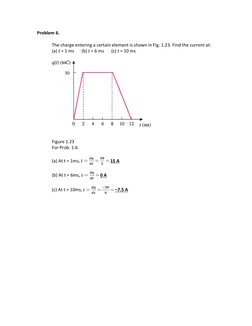
- Problem 6: Current from Charge Graph: Finds the current at specific times from a charge versus time graph.
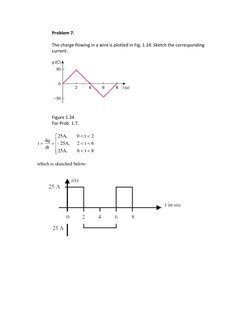
- Problem 7: Sketching Current from Charge: Sketches the current based on a plotted charge flow graph.
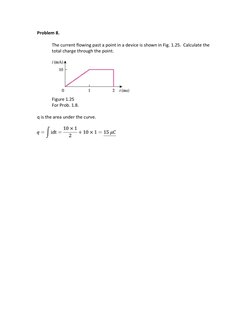
- Problem 8: Total Charge from Current: Calculates total charge through a point from a current graph.
- Problem 9: Charge through an Element: Determines charge passing through an element at various times.
- Problem 10: Charge from Lightning Bolt: Calculates charge deposited by a lightning strike on an object.
- Problem 14: Charge and Power Calculation: Calculates total charge and power consumed by a device.
- Problem 15: Power and Energy Absorption: Finds charge delivery and energy absorbed by a device terminal.
- Problem 16: Energy Absorption: Sketches power delivered and energy absorbed over time.
- Problem 21: Electrons in a Light Bulb: Calculates electrons flowing through a light bulb during operation.
- Problem 22: Charge from Lightning to Airplane: Calculates charge deposited on an airplane by a lightning bolt.
- Problem 24: Energy Cost for a Light Bulb: Finds the energy cost of operating a light bulb for one day.
- Problem 25: Toaster Energy Cost: Calculates the cost of using a toaster over one month, accounting for energy rates.
- Problem 29: Stove and Oven Electricity Cost: Finds the electricity cost of using a stove and oven combination for cooking.
- Problem 30: Monthly Energy Charge: Calculates how much a customer is charged for using electricity for a month.
- Problem 32: Time for Charge through Wire: Determines how long it takes for a specific charge to flow through a wire.
- Problem 35: Industrial Plant Energy: Calculates total energy consumed by an industrial plant as shown in a power graph.
- Problem 36: Battery Life and Current: Computes maximum current and life span of a lead-acid battery.
- Problem 37: Battery Charge Requirement: Calculates the total joules needed to recharge a battery.
- Problem 38: Motor Energy Output: Estimates energy delivered by a motor working for half an hour.
- Problem 39: Cost of Running a TV: Finds the cost in cents of running a TV without supervision.