Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Words CH 1 Geo
Uploaded by
Aditi Singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesThe document summarizes different ways that resources can be categorized:
(1) Biotic resources come from living things, while abiotic resources come from non-living things like rocks and metals.
(2) Renewable resources can replenish, like forests, while non-renewable resources like fossils fuels cannot replenish within human timescales.
(3) Resources can be owned individually, by communities, nationally, or internationally depending on location and type of resource.
Original Description:
Original Title
KEY WORDS CH 1 GEO
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes different ways that resources can be categorized:
(1) Biotic resources come from living things, while abiotic resources come from non-living things like rocks and metals.
(2) Renewable resources can replenish, like forests, while non-renewable resources like fossils fuels cannot replenish within human timescales.
(3) Resources can be owned individually, by communities, nationally, or internationally depending on location and type of resource.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesKey Words CH 1 Geo
Uploaded by
Aditi SinghThe document summarizes different ways that resources can be categorized:
(1) Biotic resources come from living things, while abiotic resources come from non-living things like rocks and metals.
(2) Renewable resources can replenish, like forests, while non-renewable resources like fossils fuels cannot replenish within human timescales.
(3) Resources can be owned individually, by communities, nationally, or internationally depending on location and type of resource.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
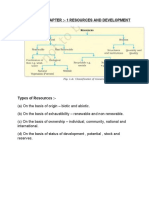
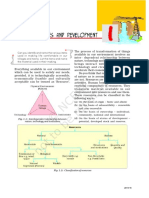
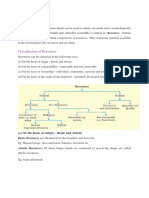
GEOGRAPHY CH-1 CLASS X KEYWORDS
(a) On the Basis of Origin – Biotic and Abiotic
Biotic Resources are obtained from the biosphere and have life.
Eg: Human beings, flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock etc.
Abiotic Resources: All those things which are composed of non-living things are called
abiotic resources.
Eg: rocks and metals.
(b) On the Basis of Exhaustibility – Renewable and Non-Renewable
The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical
processes are known as Renewable or Replenishable Resources. The renewable resource
may further be divided into continuous or flow.
Eg: Solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc.
Non-Renewable Resources occur over a very long geological time. These resources take
millions of years in their formation. Some of the resources like metals are recyclable and
some like fossil fuels cannot be recycled and get exhausted with their use.
Eg: Minerals and fossil fuels.
(c) On the Basis of Ownership – Individual, Community, National and International
Individual Resources are owned privately by individuals. In villages people own lands
whereas in urban areas people own plots, houses and other properties.
Eg: Plantation, pasture lands, ponds, water in wells etc.
Community Owned Resources are accessible to all the members of the community.
Eg: Grazing grounds, burial grounds, public parks, picnic spots, playgrounds etc.
National Resources are owned by a nation or country. All the minerals, water resources,
forests, wildlife, land within the political boundaries and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles
(22.2 km) from the coast termed as territorial water and resources therein belong to the nation.
Eg: Roads, canals, railways etc.
International Resources are regulated by international institutions. The oceanic resources
beyond 200 nautical miles of the Exclusive Economic Zone belong to open ocean and no
individual country can utilise these without the concurrence of international institutions.
(d) On the Basis of the Status of Development – Potential, Developed Stock and Reserves
Potential Resources are the resources which are found in a region but have not been utilised.
Eg: Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar
energy, but so far these have not been developed properly.
Developed Resources: Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have
been determined for utilisation. The development of resources depends on technology and
level of their feasibility.
Materials in the environment which have the potential to satisfy human needs but human
beings do not have the appropriate technology to access these, are called Stock.
Eg: Hydrogen can be used as a rich source of energy. But we do not have advanced
technology to use it.
Reserves are the subset of the stock, which can be put into use with the help of existing
technical ‘know-how’ but their use has not been started. These can be used for meeting future
requirements.
Eg: Water in the dams, forests etc. is a reserve which can be used in the future.
You might also like
- Resource: Concept and ClassificationDocument15 pagesResource: Concept and Classificationrevolvevijaya123No ratings yet
- Bhatnagar International School Paschim Vihar Class 10 - GeographyDocument13 pagesBhatnagar International School Paschim Vihar Class 10 - Geographykanica bathlaNo ratings yet
- Geography Session 1Document13 pagesGeography Session 1kanica bathlaNo ratings yet
- Geography Question Bank - 2Document63 pagesGeography Question Bank - 2K.R.Naghul PranavNo ratings yet
- Resources and Devolopment NotesDocument20 pagesResources and Devolopment NotesDanyaNo ratings yet
- Class X - Resources and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesClass X - Resources and DevelopmentAryavir SardanaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary IndiaDocument104 pagesContemporary Indiasgangwar2005sgNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCH-1 Resources and DevelopmentBaby QueenNo ratings yet
- Original 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesOriginal 1587566839 Resource and DevelopmentS KannanNo ratings yet
- Geo - NcertDocument98 pagesGeo - NcertMegan CruzNo ratings yet
- Class X Resources Lesson PDFDocument8 pagesClass X Resources Lesson PDFmalokailash09No ratings yet
- Resources NotesDocument11 pagesResources NotesMedhansh MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Land DegradationDocument8 pagesLand DegradationvikasNo ratings yet
- Jess 101Document13 pagesJess 101Shreya Sharma100% (1)
- Resources & Development Notes GRADE 10Document12 pagesResources & Development Notes GRADE 10Zara FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Resources & DevelopmentDocument10 pagesResources & Developmentdhdahanuwala100% (1)
- Resrc & DVPTDocument9 pagesResrc & DVPTRupam PatgiriNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1-Resources & DevelopmentDocument25 pagesCHAPTER 1-Resources & DevelopmentSangeeta SinghNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument32 pagesResources and DevelopmentSwastiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Sciences Geography: Chapter 1 Notes Resources and Development 1. ResourcesDocument8 pagesClass 10 Social Sciences Geography: Chapter 1 Notes Resources and Development 1. ResourcesSandhya SinghNo ratings yet
- Jess 101Document13 pagesJess 101wefWENo ratings yet
- Resource and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesResource and DevelopmentthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Resource DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResource DevelopmentSimrah RehanNo ratings yet
- Resource and Development Important NotesDocument3 pagesResource and Development Important NotesasgurudevNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development NotesDocument13 pagesClass 10 Geo. CH 1 - Resource and Development Notessadhna yadav100% (2)
- NCERT Book Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesNCERT Book Class 10 Social Science Contemporary India Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentSara GuptaNo ratings yet
- Resources and Development: by Adarsh - NJDocument27 pagesResources and Development: by Adarsh - NJAnkur ChopraNo ratings yet
- Grade X Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGrade X Geography Chapter 1 Resources and DevelopmentMohammed OwaisNo ratings yet
- CH - An Introduction To ResourcesDocument7 pagesCH - An Introduction To ResourcesshivamNo ratings yet
- NCERT-Contemporary India II - Class XDocument99 pagesNCERT-Contemporary India II - Class Xnikhilam.com67% (3)
- Contemporary India 7-CombinedDocument77 pagesContemporary India 7-CombinedShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Geography VS, S, L AqDocument27 pagesGeography VS, S, L AqJamunamary JamunamaryNo ratings yet
- Resource Planning Geography CHP 1Document4 pagesResource Planning Geography CHP 1charan dheepNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bokaro Steel City Class Viii-E SESSION-2021-22Document17 pagesDelhi Public School Bokaro Steel City Class Viii-E SESSION-2021-22Suraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesResources and Developmentpujal dabasNo ratings yet
- Our Resources. NotesDocument4 pagesOur Resources. NotesYrryr TryyeyrrNo ratings yet
- NCERT Book For Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 PDFDocument13 pagesNCERT Book For Class 10 Geography Chapter 1 PDFLiyakath AliNo ratings yet
- Jess 101Document13 pagesJess 101SWADSEH MONDALNo ratings yet
- Jess 101Document19 pagesJess 101SampathiNo ratings yet
- Resource and Development: Questions of 3/4 MarksDocument9 pagesResource and Development: Questions of 3/4 MarksLATHEKA SKNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument15 pagesNatural ResourcesSuryaSagarNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument30 pagesGeographyA:-Piyush ShirsekarNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Sector 46, Gurgaon Class 10 Chapter 1: Resources and Development (Minimum Learning Programme) Resources AreDocument11 pagesAmity International School, Sector 46, Gurgaon Class 10 Chapter 1: Resources and Development (Minimum Learning Programme) Resources AreRam KapoorNo ratings yet
- GeoDocument28 pagesGeoSakshi GoelNo ratings yet
- Class X: Chapter 1 (Resources and Development)Document10 pagesClass X: Chapter 1 (Resources and Development)Divyansh GargNo ratings yet
- Classification of ResourcesDocument11 pagesClassification of ResourcesbasilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Resources and Development: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - Resources and Development: Multiple Choice QuestionsreemNo ratings yet
- Types of ResourcesDocument2 pagesTypes of ResourcesdikshaNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument23 pagesResources and Developmentharshit kumarNo ratings yet
- Geo-10 2Document107 pagesGeo-10 2SonalikaNo ratings yet
- Resources and DevelopmentDocument22 pagesResources and DevelopmentArwaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyDocument18 pagesClassification of Resources: Notes Class 10 Chapter 1 - Resources and Development GeographyMANISH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Marine Sources of Energy: Pergamon Policy Studies on Energy and EnvironmentFrom EverandMarine Sources of Energy: Pergamon Policy Studies on Energy and EnvironmentNo ratings yet
- Industrialized Nature: Brute Force Technology and the Transformation of the Natural WorldFrom EverandIndustrialized Nature: Brute Force Technology and the Transformation of the Natural WorldNo ratings yet
- Marine Conservation Biology: The Science of Maintaining the Sea's BiodiversityFrom EverandMarine Conservation Biology: The Science of Maintaining the Sea's BiodiversityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Stage Inundation Relations: Part 630 Hydrology National Engineering HandbookDocument16 pagesStage Inundation Relations: Part 630 Hydrology National Engineering HandbookBernard OwusuNo ratings yet
- 911 MetallurgyDocument8 pages911 MetallurgyLopezNgelekaNo ratings yet
- বাংলাদেশ ভূমি পরিমাপের আদর্শ এককসমূহDocument31 pagesবাংলাদেশ ভূমি পরিমাপের আদর্শ এককসমূহmosammat sumaNo ratings yet
- Geotourisms Global GrowthDocument14 pagesGeotourisms Global GrowthHizkya HutagalungNo ratings yet
- 2 5233735348906903362Document13 pages2 5233735348906903362bnmfsajadNo ratings yet
- Poultry Farming ManureDocument13 pagesPoultry Farming ManureDeepak PradeepNo ratings yet
- Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating CreatingDocument2 pagesRemembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating CreatingMenard Licuanan RosalesNo ratings yet
- Grade-7 Biotic and Abiotic FactorDocument18 pagesGrade-7 Biotic and Abiotic FactorMira BagayNo ratings yet
- AAPG 2010 International Conference & Exhibition AnnouncementDocument76 pagesAAPG 2010 International Conference & Exhibition AnnouncementAAPG_EventsNo ratings yet
- SWMM Users Manual Version 5.2Document424 pagesSWMM Users Manual Version 5.2melasofiaNo ratings yet
- Nº SSR-1 NS-R-3 Draf R1 Site Evaluation For Nuclear Installations FRDocument33 pagesNº SSR-1 NS-R-3 Draf R1 Site Evaluation For Nuclear Installations FRdaniel addeNo ratings yet
- Pepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) Responses To Surface and Drip Irrigation in Southern TunisiaDocument4 pagesPepper (Capsicum Annuum L.) Responses To Surface and Drip Irrigation in Southern TunisiaShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Envi ScienceDocument13 pagesEnvi ScienceNestor Navarro Jr.No ratings yet
- Reservoir and Reservoir FluidDocument51 pagesReservoir and Reservoir FluidFaisal FadilahNo ratings yet
- Disaster & Its TypesDocument21 pagesDisaster & Its Types17mohammed kaifNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Fly LevellingDocument4 pagesIntroduction of Fly LevellingSudhir BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Spatial Analysis of Important Bird Area Boundaries in The Philippines: Gaps and RecommendationsDocument35 pagesSpatial Analysis of Important Bird Area Boundaries in The Philippines: Gaps and RecommendationsHeza LeighNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia Harnica - Sea of Ivae v2Document62 pagesEncyclopedia Harnica - Sea of Ivae v2Justin BechenNo ratings yet
- Flooding ReportDocument3 pagesFlooding Reportapi-355774141No ratings yet
- 001 Reservoir PlanDocument12 pages001 Reservoir PlanilavarasantNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document6 pagesResearch 1Angel Cabrido100% (1)
- ESS Revision Session 2 - Topics 5-8 & P1 - 2Document54 pagesESS Revision Session 2 - Topics 5-8 & P1 - 2jinLNo ratings yet
- NCSC 2022 OrientationDocument73 pagesNCSC 2022 OrientationDYNATY DRANGENo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Questions AnswersDocument5 pagesEngineering Hydrology Questions AnswersBashairu WaseemNo ratings yet
- Asselin Payette Ecoscience 06Document8 pagesAsselin Payette Ecoscience 06Margo SmithNo ratings yet
- Ecology Test For CSEC StudentsDocument3 pagesEcology Test For CSEC Studentsnehru09No ratings yet
- Agnihotra Timings - Cerro Azul, PanamaDocument3 pagesAgnihotra Timings - Cerro Azul, PanamaJoao PrezNo ratings yet
- Climate ClassificationDocument16 pagesClimate ClassificationA S VermaNo ratings yet
- 170519N - Assignment 03 - Design of Rural Water Supply SystemDocument20 pages170519N - Assignment 03 - Design of Rural Water Supply SystemUthpala LokugeNo ratings yet