Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Emergency Childbirth Protocol
Uploaded by
Kenneth DizonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Emergency Childbirth Protocol
Uploaded by
Kenneth DizonCopyright:
Available Formats
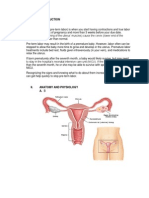
EMERGENCY CHILDBIRTH PROTOCOL
Objectives:
An early pregnancy complication usually occurs because the developing baby has not properly
attached or formed. This means the baby will not grow and a miscarriage occurs.
Sometimes, often for unknown reasons, a miscarriage may occur many weeks into a seemingly
healthy pregnancy.
Other obstetric emergencies can be caused by a number of factors, such as trauma or for
genetic reasons. Sometimes a woman’s experience in earlier pregnancies can help her doctor
identify possible complications and prepare for them.
1. At first signs of labor assign the most qualified person to take care of the mother.
2. Place mother in a secure well attended monitoring room possible
3. Keep an up-to-date contact list of anyone who may be able to come to help you with the birth
Guidelines to consider as Emergency Childbirth
1. Shoulder dystocia – where the baby's shoulders wedge in the birth canal after the
birth of the baby’s head. Depending on its position, the baby may start to lose oxygen.
2. Prolapsed umbilical cord – where the umbilical cord is pushed down into the cervix or
vagina before the baby is born. If the cord becomes compressed, the fetus does not
receive enough oxygen. The result may be brain damage or even death.
3. Rupture of the uterus – where a weak spot in the uterus tears
4. Inversion of the uterus – where a portion of the placenta remains attached to the
uterine wall, and pulls the uterus out
5. Amniotic fluid embolism – where fluid moves from the amniotic sac (bag of water)
and ends up in the mother’s blood. This very rare complication can happen during
pregnancy but usually occurs during strong contractions in labor and causes serious
complications including death of the mother.
6. Pregnancy Induced Hypertension-Preeclampsia is one high blood pressure
(hypertension) disorder that can occur during pregnancy. Other disorders can happen,
too: Gestational hypertension is high blood pressure that begins after 20 weeks without
problems in the kidneys or other organs
7. Diabetes during pregnancy—including type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes—can
negatively affect the health of women and their babies.
8. Oligohydramnios- is when you have too little amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is the fluid
that surrounds your baby while they're in your body before birth. Your baby needs
amniotic fluid to grow. This watery fluid is inside the amniotic sac (membrane). It's
sometimes called the bag of waters
9. Infection
What to look for – signs of an obstetric emergency
1. Any bleeding during pregnancy is not normal – be sure to call your doctor or midwife
a. Heavy bleeding with severe stomach pain in the first three months of pregnancy
– could be a sign of ectopic pregnancy
b. Heavy bleeding with cramping in the first three to four months of pregnancy –
could be a sign of miscarriage
c. Bleeding with abdominal pain in the last three months of pregnancy – could be a
sign of placental abruption.
2. Stomach cramps – could be a sign of ectopic pregnancy
3. Severe Dizziness – could be a sign of ectopic pregnancy or pre-eclampsia
4. Severe vomiting or sickness – could be a severe symptom of pregnancy, or could be due
to an infection
5. Severe stomach pain – could be a sign of pre-eclampsia
6. Lower back pain – could be a sign of pre-eclampsia
7. Rapid increase in blood pressure, possibly signalled by nose bleeds, headache or
dizziness – could be a sign of pre-eclampsia
8. Blurry vision and headaches – could be a sign of pre-eclampsia
9. Sudden and significant swelling of hands, face and feet – could be a sign of pre-
eclampsia
10. Fever – could be a sign of an infection
11. A decrease in your baby’s normal daily movements, or if you are worried about how
frequently your baby moves
12. Regular, increasingly intense contractions before 37 weeks of pregnancy – might be a
sign of premature labor
13. If your waters break before labor begins – you may feel a gush or continual trickle of
fluid that has a slightly sweet smell
14. Blackouts (loss of consciousness) or fits (convulsions) – must be taken seriously. anyone
who faints or blacks out and has not recovered in a few minutes.
FLOWCHART FOR EMERGENCY DELIVERY
You might also like
- Obstetrics EmergenciesDocument26 pagesObstetrics EmergenciesMaya TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Pre Term and Post Term Labor: Group: G1Document9 pagesPre Term and Post Term Labor: Group: G1Valantino RamosNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy in the First TrimesterDocument22 pagesPregnancy in the First TrimesterriskaczhrNo ratings yet
- Health 8 Quarter 2 Lesson 3Document38 pagesHealth 8 Quarter 2 Lesson 3GLISCY MAY TINGSONNo ratings yet
- Polyhydramnious and oligohydramnious: Causes, effects and managementDocument34 pagesPolyhydramnious and oligohydramnious: Causes, effects and managementEdward Munyaradzi KutsanziraNo ratings yet
- عرض تقديميDocument24 pagesعرض تقديميAlibeyatliNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument5 pagesCase StudyJui Perano100% (2)
- NCM 109 Resource UnitDocument51 pagesNCM 109 Resource UnitDaryl Adrian RecaidoNo ratings yet
- Promoting Fetal Maternal HealthDocument3 pagesPromoting Fetal Maternal HealthAngela DancelNo ratings yet
- 2nd 2ndlesson Health8Document25 pages2nd 2ndlesson Health8jurizNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion During PregnancyDocument9 pagesHealth Promotion During PregnancyJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Case Study OligoDocument7 pagesCase Study OligomutiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Self-Directed Learning on Clinical Areas of Pregnancy ComplicationsDocument4 pagesNursing Self-Directed Learning on Clinical Areas of Pregnancy ComplicationsMilagros FloritaNo ratings yet
- Delivery Room Write Up: Submitted To: Annie Mae Ugay Clinical InstructorDocument15 pagesDelivery Room Write Up: Submitted To: Annie Mae Ugay Clinical InstructorJhess RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 4 AbortionDocument14 pages4 AbortionMary Joy JugoNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Case Study 5 QuestionsDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Case Study 5 QuestionsChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Complications of PregnancyDocument2 pagesComplications of PregnancyPrincess Gwyneth MartinezNo ratings yet
- What Do You Want To Know About Pregnancy?Document6 pagesWhat Do You Want To Know About Pregnancy?BAYUFIJRIENo ratings yet
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 pagesPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs of PregnancyDocument1 pageDanger Signs of PregnancyOfelia Santillan100% (1)
- Emergencies ObsDocument7 pagesEmergencies ObsAshish GuptaNo ratings yet
- High Risk Neonates According to Gestational AgeDocument41 pagesHigh Risk Neonates According to Gestational Agesonava vichNo ratings yet
- Prenatal and Postnatal Care TipsDocument17 pagesPrenatal and Postnatal Care TipsMaria Oblea HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Maternal ConcernsDocument8 pagesMaternal ConcernsIzle TanNo ratings yet
- Portfolio On M104 Clinical Management and High Risk PregnanciesDocument31 pagesPortfolio On M104 Clinical Management and High Risk PregnanciesKIMBERLY JANE OTAGAN DALAGANNo ratings yet
- #12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesDocument4 pages#12 - NCM 109 (Rle) - TransesJaimie BanaagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The High - Risk Newborn To 2018Document325 pagesNursing Care of The High - Risk Newborn To 2018Keane Andal67% (3)
- Caesarean SectionDocument16 pagesCaesarean SectionA B Siddique RiponNo ratings yet
- Newborn and ComplicationDocument3 pagesNewborn and ComplicationPrincess Gwyneth MartinezNo ratings yet
- Psychological Changes, Danger Signs, DiscomfortsDocument21 pagesPsychological Changes, Danger Signs, DiscomfortsPasay Trisha Faye Y.No ratings yet
- Perubahan Tubuh Selama KehamilanDocument5 pagesPerubahan Tubuh Selama KehamilanAde NoviyantiNo ratings yet
- Postnatal Care (Puerperium) : Common Puerperal ProblemsDocument4 pagesPostnatal Care (Puerperium) : Common Puerperal ProblemsArumDesiPratiwiNo ratings yet
- Shree Siddaganga Institute of Nursing Sciences and Research CentreDocument8 pagesShree Siddaganga Institute of Nursing Sciences and Research CentreSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- 2 Psychological Changes, Danger Signs, Discomforts, TeratogensDocument53 pages2 Psychological Changes, Danger Signs, Discomforts, Teratogensmamsh KlangNo ratings yet
- MCN - Individual Activity 3Document26 pagesMCN - Individual Activity 3AngelicaJaneA.SuanNo ratings yet
- Fetal Distress Signs, Causes, and TreatmentDocument5 pagesFetal Distress Signs, Causes, and TreatmentJohn Lorenzo TabijeNo ratings yet
- Project in Competency AppraisalDocument52 pagesProject in Competency AppraisalGraxiia EvanzNo ratings yet
- Obstetrical Emergency & ManagementDocument38 pagesObstetrical Emergency & ManagementDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- B.INGG FERA NURJANAH 5b KEPERAWATANDocument3 pagesB.INGG FERA NURJANAH 5b KEPERAWATANFera NurjanahNo ratings yet
- Antenatal Care and HealthDocument17 pagesAntenatal Care and HealthInggrit WulansariNo ratings yet
- 8 Priorities of Care for High-Risk NeonatesDocument30 pages8 Priorities of Care for High-Risk NeonatesregNo ratings yet
- Herreria, Hannah U. BSN 2 N038Document2 pagesHerreria, Hannah U. BSN 2 N038Hannah Urmeneta HerreriaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrical EmergencyDocument41 pagesObstetrical EmergencyDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Conditions Affecting Pregnancy NewbornDocument10 pagesConditions Affecting Pregnancy NewbornMoon KillerNo ratings yet
- Cmca2 (Prelim) 1Document10 pagesCmca2 (Prelim) 1NOEL YRIGONNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan PNCDocument6 pagesLesson Plan PNCRafeza IsratNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument2 pagesFetal DistressReyniel Pablo ElumbaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Physiological Changes of PregnancyDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Physiological Changes of PregnancyNicole Sheen EnriquezNo ratings yet
- High Risk PregnancyDocument4 pagesHigh Risk PregnancyForky DorkyNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs of PregnancyDocument13 pagesDanger Signs of PregnancyDorothy Jane OrdinarioNo ratings yet
- EDU550 - CHILD BIRTH TYPESDocument16 pagesEDU550 - CHILD BIRTH TYPESसंजेश सुधेश शर्माNo ratings yet
- Midwifery AssingmentDocument10 pagesMidwifery AssingmentNena MineNo ratings yet
- 3 Trimester CompicationsDocument37 pages3 Trimester CompicationsAyesha MeloNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Document7098 PDFDocument26 pagesLESSON 2 Document7098 PDFKerberos DelabosNo ratings yet
- Nasterea Prematura Sarcina PrelungitaDocument34 pagesNasterea Prematura Sarcina PrelungitaelyssyNo ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn I StudentsDocument69 pagesHigh Risk Newborn I Studentsmichelle alvaradoNo ratings yet
- Hypertension in PregnancyDocument45 pagesHypertension in PregnancyMary Anne Cabalza ApinardoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Endocrine Glands in Maintaining HealthDocument26 pagesThe Role of Endocrine Glands in Maintaining HealthJayson Kier AquinoNo ratings yet
- Technical Notes Community Health NursingDocument8 pagesTechnical Notes Community Health NursingMary JoyNo ratings yet
- PSmarkup - ARTIKEL PRENATAL MASSAGE-LILIS SURYA WATIDocument9 pagesPSmarkup - ARTIKEL PRENATAL MASSAGE-LILIS SURYA WATIRiya WahyuniNo ratings yet
- (2019) Fetal Movement and Stillbirth EducationDocument9 pages(2019) Fetal Movement and Stillbirth EducationaninditaNo ratings yet
- Meet the ShortybullDocument2 pagesMeet the ShortybullJfiaoayeiwmavdkdsnbssmksaNo ratings yet
- DEBATEDocument2 pagesDEBATEKia LeighNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352552523000117 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2352552523000117 MainTahani MoncerNo ratings yet
- Science-F-1-Unit-3 - Cells and Human ReproductionDocument12 pagesScience-F-1-Unit-3 - Cells and Human ReproductionLong yiu ChanNo ratings yet
- Family Planning: Health EducationDocument10 pagesFamily Planning: Health EducationGerald BroceNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About the Menstrual CycleDocument16 pagesEverything You Need to Know About the Menstrual CycleCoxnxkNo ratings yet
- Guideline - Obs & GynDocument194 pagesGuideline - Obs & GynGood MaishaNo ratings yet
- Barangay Health Center Services and DOH ProgramsDocument7 pagesBarangay Health Center Services and DOH ProgramsKristil Chavez100% (1)
- Abortion Reversal Pill - August 15 2020Document2 pagesAbortion Reversal Pill - August 15 2020api-271968502No ratings yet
- Literature Review on Contraceptive ChallengesDocument10 pagesLiterature Review on Contraceptive ChallengesnaygelaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Offences Guide by Dr. Ganesh GovekarDocument73 pagesSexual Offences Guide by Dr. Ganesh GovekarSachin SinghNo ratings yet
- Hypotonic and Hypertonic Contractions and Precipitate LabourDocument3 pagesHypotonic and Hypertonic Contractions and Precipitate LabourRebecca ApeladoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 - Quiz 1 - Male ReproductiveDocument1 pageSCIENCE 10 - Quiz 1 - Male ReproductiveJessa Tirambulo0% (1)
- Understanding Male SubfertilityDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Male SubfertilityNicole Mendonis LunarNo ratings yet
- Biology G10 Unit PlanDocument70 pagesBiology G10 Unit PlanHoney Fe RestauroNo ratings yet
- Teenage Pregnancy - ExpositionDocument1 pageTeenage Pregnancy - ExpositionAyeshia MacamayNo ratings yet
- The Sexual Self-UtsDocument35 pagesThe Sexual Self-UtsAdmin111No ratings yet
- Nursing Care R/T Psychological & Physiologic Changes of PregnancyDocument3 pagesNursing Care R/T Psychological & Physiologic Changes of PregnancyLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceAlyssa Mae Gadingan Macasiljig100% (1)
- Lilac and Tan French Bulldog - Google SearchDocument1 pageLilac and Tan French Bulldog - Google SearchLyrics JuradoNo ratings yet
- TML - 4TH QuarterDocument12 pagesTML - 4TH QuarterVin MangulabnanNo ratings yet
- Pro-Choice Is Pro-LifeDocument4 pagesPro-Choice Is Pro-Lifeapi-551274228No ratings yet
- Role of HormonesDocument23 pagesRole of HormonesJhuvy C. TigbaoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument19 pagesPrenatal CareOlivia Teglia100% (1)
- A Sexual Adjustment Questionnaire For Use in Therapy andDocument10 pagesA Sexual Adjustment Questionnaire For Use in Therapy andVida Y SaludNo ratings yet