Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eukaryotes Brandon Isai Cruz Saracco 4A T:V
Eukaryotes Brandon Isai Cruz Saracco 4A T:V
Uploaded by
BRANDON ISAI CRUZ SARACCOOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eukaryotes Brandon Isai Cruz Saracco 4A T:V
Eukaryotes Brandon Isai Cruz Saracco 4A T:V
Uploaded by
BRANDON ISAI CRUZ SARACCOCopyright:
Available Formats
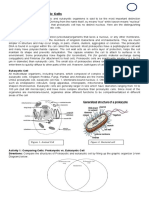
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as
well as most algae. Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular. Eukaryotes are
differentiated from another class of organisms called prokaryotes by way of the presence of internal
membranes that separate parts of the eukaryotic cell from the rest of the cytoplasm. These
membrane-bound structures are called organelles.
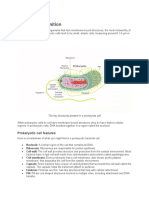
In eukaryotes, the cell's genetic material, or DNA, is contained within an organelle called the
nucleus, where it is organized in long molecules called chromosomes. Eukaryotic cells also contain
other organelles, including mitochondria, which generate energy; the endoplasmic reticulum, which
plays a role in the transport of proteins; and the Golgi apparatus, which sorts and packages proteins
and lipids for transport throughout the cell. Plant cells additionally contain organelles called
chloroplasts, which are used to collect energy from sunlight.
You might also like
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMark MagatNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellsBerch MelendezNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell PowerPoint PresentationDocument24 pagesEukaryotic Cell PowerPoint PresentationVARIGALA SAI CHARAN GUPTANo ratings yet
- Group 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsDocument4 pagesGroup 3 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells HandoutsClaire Angelie Ruaya100% (1)
- Cell OrganizationDocument6 pagesCell OrganizationKaarthigan RamaiahNo ratings yet
- The Cell/ All About CellsDocument35 pagesThe Cell/ All About CellsJandrew Gomez DimapasocNo ratings yet
- Eukaryote BiologyDocument9 pagesEukaryote BiologyKrizzy EstoceNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science 11Document23 pagesEarth and Life Science 11Red LopezNo ratings yet
- Notes For Cell Biology BT-I YearDocument16 pagesNotes For Cell Biology BT-I YearKRATIKA TYAGINo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument3 pagesAnimal CellReyna Chame GarcinezNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio w1 SummaryDocument5 pagesGen Bio w1 Summaryyxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Human CellDocument12 pagesHuman CellCrystal GarciaNo ratings yet
- L.3 - The CellDocument3 pagesL.3 - The CellJari JariNo ratings yet
- CellDocument79 pagesCellClemente Castañeda MontillaNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument15 pagesCell (Biology) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShabbir Hussain MaloobhaiNo ratings yet
- Human Cell, Feb. 2012.Document3 pagesHuman Cell, Feb. 2012.Nina UrakovićNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsSerena Adeline RiveraNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 1Document9 pagesBiology Section 1karim adelNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth & Life ScienceYhazmeen Lily LibrodoNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotes: The Basic Structure of A ProkaryoteDocument2 pagesEukaryotes: The Basic Structure of A ProkaryoteAnnie Jay BedeNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument19 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellReanne MeregildoNo ratings yet
- Nucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticDocument5 pagesNucleoid: The Irregularly-Shaped Region Within A Prokaryote Cell Where The GeneticHustler ZaydeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document65 pagesChapter 3Sintayehu Tsegaye100% (1)
- Rozy KhanDocument18 pagesRozy KhanBANTU RANANo ratings yet
- What Is A CellDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Celljose de jesus sanchezNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDocument13 pagesThe Cell: Eukaryotic Cells and Prokaryotic CellsDiane CastroNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleDocument14 pagesCell (Biology) : Cells in Different Phases of The Cell CycleroavNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic VsDocument1 pageProkaryotic VsAllison SprungerNo ratings yet
- General Biology The CellDocument14 pagesGeneral Biology The CellIraqiNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 4 EukaryotesDocument12 pagesLECTURE 4 EukaryotesNicole MandyNo ratings yet
- Bio SciDocument6 pagesBio ScilovemeluffyNo ratings yet
- UOI Science Journal 3Document2 pagesUOI Science Journal 3reemagotewala81No ratings yet
- Gen. Bio 1 Module 2Document6 pagesGen. Bio 1 Module 2Evelyn MagbarilNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument56 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellKENT GARCIA100% (1)
- Prokaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesDocument5 pagesProkaryote Definition: Prokaryotic Cell FeaturesAli ShanNo ratings yet
- Cell TypesDocument2 pagesCell TypesbuyaorubiNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument34 pagesThe Celljaco_ansaldiNo ratings yet
- Cell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallDocument5 pagesCell (Biology) : Structures Outside The Cell WallAsad MasoodNo ratings yet
- Microbes and Oral DiseasesDocument40 pagesMicrobes and Oral DiseasesRadwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Document26 pagesCell Biology Assignment Gr. 3Lamin N CeesayNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell DefinitionDocument7 pagesAnimal Cell DefinitionJoanne AlindayoNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument7 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsPrashant PatilNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument4 pagesCell BiologyasadzamanchathaNo ratings yet
- Biology Cell StructureDocument2 pagesBiology Cell StructureCut Rizka RahmiNo ratings yet
- All About CellsDocument49 pagesAll About CellsJeanine CristobalNo ratings yet
- Bio and PhysicsDocument25 pagesBio and Physicsyasser yousriNo ratings yet
- Structure of CellsDocument14 pagesStructure of CellsTimothy JonesNo ratings yet
- The Cell (Biology)Document13 pagesThe Cell (Biology)Fred MontNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument2 pagesCellsmalikaiman1015No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Reviewer in BiosciDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Reviewer in BiosciAngelica PaulinoNo ratings yet
- EukaryotesDocument4 pagesEukaryotesWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document2 pagesActivity 1Ryan Lee DelremedioNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cells: Main Article: ProkaryoteDocument6 pagesProkaryotic Cells: Main Article: ProkaryoteGian Carlo MagdalenoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsDocument41 pagesLESSON 3 - Prokaryotid Vs Eukaryotic CellsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Types of CellsDocument8 pagesThe Cell: Types of CellsushapvermaNo ratings yet
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Molbio Quiz1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesMolbio Quiz1 ReviewercheNo ratings yet
- Molbio Quiz1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesMolbio Quiz1 ReviewercheNo ratings yet
- ZH Core IV - Cell BiologyDocument95 pagesZH Core IV - Cell Biologysahib100% (1)