Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meiosis
Uploaded by
Aishatu Adamu GadoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Meiosis
Uploaded by
Aishatu Adamu GadoCopyright:
Available Formats
Meiosis
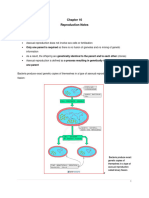
In the sexually reproducing organism two sex cell or gametes containing
haploid number of chromosomes (n) fuse and form a zygote. The zygote
possesses a nucleus which contains double number of chromosomes. Such
cells are commonly symbolized as diploid or 2n cells. If mitosis is the only
method of nuclear division the number of chromosomes would be doubled in
succeeding generations. But, the chromosomes number for a particular animal
or plant species is fixed. It is, therefore, necessary that the gametes must be
provided with haploid chromosomes number in order to keep the number of
chromosomes of a given species constant in each generation. The number of
chromosomes of a gamete is symbolized by ‘n’ (haploid or gametic
chromosomes number). The mechanism which reduces the double (diploid or
2n) complements of chromosomes to haploid set (n) in each sexual generation
is called meiosis.
Weismann (1887) was the first to point out the reduction of chromosomes
number in the reproductive cells. Later Farmer and Moor (1905) proposed the
term meiosis for the special type of cell division that reduces the chromosomes
number by half from diploid to haploid condition. The products of meiosis have
half as many chromosomes as the parental cell possesses.
During meiosis, homologous chromosomes of a diploid nucleus pair, replicate
only once producing 4n and undergo assortment so that each of the four
daughter cells resulting from two successive divisions of the meiosis cell or
meiocyte receives one representative of each chromosomes set. Thus, the
diploid chromosomes number is meiotically reduced to haploid number (n),
characteristics for the gametes of haploid phase of the life cycle.
Types of Meiosis
The reduction of chromosomes number takes place either before or after
reduction. In animals, the reduction division occurs during germ cell formation,
but in higher plants it occurs generally in the spore mother cells during
sporogenesis (spore formation). On the basis of time at which meiosis takes
place three different types of meiosis have been recognized:
1. Terminal or gametic meiosis. It is found in animal and a few lover plant,
this type of Meiosis occurs just before the formation of gametes or
gametes genesis.
2. Initial or zygotic meiosis. This type of meiosis is seen in plants with
haplontic life cycle and it occurs in zygote just after fertilization.
3. Intermediary meiosis or sporic meiosis. It is a characteristic of species
with diplo – haplontic life cycle. This type of meiosis takes place at some
time intermediate between fertilization and formation of gametes. It is
involved in the production of spores or sporogenesis.
MEIOCYTES. The cells which divide by meiosis are called meiocytes. In animals
the primary oocytes and primary spermocytes are meiocytes. In most of higher
plants the meiocytes are sporocytes (spore mother cells) giving rise to
microspores or pollen grains (male sex) and megaspores (female sex). In
haploid plants, the zygotes act as meiocytes.
Important materials for the study of this process in plant are young anther of
tradescantia, Datura, maize, vicia and onion.
Process of meiosis
Meiosis completes in two successive divisions:
1. Meiosis I or reduction division or heterotypic division.
2. Meiosis II or homotypic division.
Both these divisions involve two steps:
a. Division of nucleus or karyokinesis
b. Division of cytoplasm or cytokinesis
1. Meiosis first
It is very important division in which chromosomes number of a cell is
reduced to half in daughter cells. It is also called heterotypic division or
reduction division.
You might also like
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNo ratings yet
- Meiosis & MitosisDocument8 pagesMeiosis & MitosisAna Melisa DorueloNo ratings yet
- SEX AND GENDER EXAM REVIEWDocument4 pagesSEX AND GENDER EXAM REVIEWMaritoni Medalla100% (3)
- Science10 Q3 Mod5 MutationDocument25 pagesScience10 Q3 Mod5 Mutationjane mamon100% (1)
- Mitosis vs Meiosis: Cell Division Processes ExplainedDocument7 pagesMitosis vs Meiosis: Cell Division Processes ExplainedJD DX100% (1)
- Disha SQP BioDocument148 pagesDisha SQP BioJeevya Ani SIngh100% (1)
- Cellular Reproduction and GeneticsDocument31 pagesCellular Reproduction and GeneticsMary Grace LemonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology MCQs - Set 6 PDFDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology MCQs - Set 6 PDFsarimfayyazNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis NotesDocument6 pagesMitosis & Meiosis NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Meiosis - The Process of Cell Division That Produces Gametes in Biology Form 4Document4 pagesMeiosis - The Process of Cell Division That Produces Gametes in Biology Form 4Umi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Meiosis Is A Special Type of Cell Division Necessary For Sexual Reproduction in Eukaryotes, Such AsDocument1 pageMeiosis: Meiosis Is A Special Type of Cell Division Necessary For Sexual Reproduction in Eukaryotes, Such AsTechies123456No ratings yet
- Meiosis: Week 4 DiscussionDocument9 pagesMeiosis: Week 4 DiscussionJacob CarlNo ratings yet
- ReproB21Document33 pagesReproB21SeptiNo ratings yet
- BIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5Notes[1]Document43 pagesBIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5Notes[1]nasonfreeman63No ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To GeneticsDocument3 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Geneticsrizza reyesNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocument11 pagesWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNo ratings yet
- Meiosis (: ListenDocument13 pagesMeiosis (: ListenmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- TB20003 Lab Manual GeneticsDocument18 pagesTB20003 Lab Manual Geneticsluver_lynz903814No ratings yet
- Sci 123Document1 pageSci 123John ferdinand TamayoNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4)Document25 pagesBiology (Form 4)Aloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5Document5 pagesChapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5ctazimaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisjeline raniNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument89 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Worksheet OpenstaxDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Worksheet Openstaxapi-255334265No ratings yet
- Cytological Bases of HeredityDocument42 pagesCytological Bases of Heredity'tephanie Salcedo100% (1)
- AP Biology Lab 3 QuestionsDocument3 pagesAP Biology Lab 3 Questionsedwarddame100% (1)
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosisaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesAsexual and Sexual ReproductionPrecious MapehNo ratings yet
- MegaDocument10 pagesMegaolivia pangaribuanNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyDocument52 pagesCell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyZuha HarithNo ratings yet
- Botany Notes Part 3Document13 pagesBotany Notes Part 3Rochenick MagoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and MitosisDocument6 pagesMeiosis and MitosisSummer LoveNo ratings yet
- BLG143- Final Exam Cheat Sheet (1) (1)Document2 pagesBLG143- Final Exam Cheat Sheet (1) (1)Indraragini AnpalakanNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument6 pagesVirusMarc Lawrence LagascaNo ratings yet
- 203RZDocument13 pages203RZSohan PkNo ratings yet
- CELLULAR REPRODUCTION AND THE CELL CYCLEDocument3 pagesCELLULAR REPRODUCTION AND THE CELL CYCLEDarwin Competente LagranNo ratings yet
- Mitosis vs. MeiosisDocument59 pagesMitosis vs. MeiosisJohn Paul NarvasNo ratings yet
- J5-6 Lesson 10 - Meiosis StudentDocument3 pagesJ5-6 Lesson 10 - Meiosis Studentkristhel ann caringal reyes0% (1)
- Brownfield 2011 JXB Unreduced Gamete Formation in Plants Mechanisms and ProspectsDocument10 pagesBrownfield 2011 JXB Unreduced Gamete Formation in Plants Mechanisms and ProspectsAJMRNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument4 pagesCH 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycleswil7verNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis: Cell Division Gametes Biological Life Cycle Organism Meiotic Gametocytes Mitotic PlantsDocument8 pagesGametogenesis: Cell Division Gametes Biological Life Cycle Organism Meiotic Gametocytes Mitotic PlantsHerne BalberdeNo ratings yet
- The Significance of MeiosisDocument24 pagesThe Significance of MeiosisDiosa BakingNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Lab 211Document8 pagesMeiosis Lab 211Tracy LykaNo ratings yet
- CellBio Sitzung9 MeiosisDocument20 pagesCellBio Sitzung9 MeiosisVeronika TataruNo ratings yet
- Skema Siklus Sel Mitosis-MeiosisDocument58 pagesSkema Siklus Sel Mitosis-MeiosisAniss MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Guided Reading AP BioDocument4 pagesCH 13 Guided Reading AP BioKyle Schmidt50% (2)
- Sexual Reproduction and Genetics: Meiosis, Gametes, and InheritanceDocument53 pagesSexual Reproduction and Genetics: Meiosis, Gametes, and InheritanceNellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle&MitosisDocument43 pagesCell Cycle&MitosisPrecy Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument25 pagesMeiosisAnjelica BucasasNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ReportDocument6 pagesMeiosis ReportDaizLee Ahmad71% (7)
- Cell Structure and DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics 3 Week Lecture SEPTEMBER 11, 2021: 2.3 MeiosisDocument50 pagesCytogenetics 3 Week Lecture SEPTEMBER 11, 2021: 2.3 MeiosisRC SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- Continuity and Variation: Section C of The CSEC Biology SyllabusDocument40 pagesContinuity and Variation: Section C of The CSEC Biology SyllabusYanique JonesNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation NotesDocument19 pagesHeredity and Variation NotesAmelia DavisNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 2010 SeratasDocument28 pagesBiology Module 2010 SeratasNurul AzuwinNo ratings yet
- Vic Sample Notes BiologyDocument20 pagesVic Sample Notes BiologyEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsLakkiNo ratings yet
- Polyploidy AssignmentDocument13 pagesPolyploidy AssignmentMuqadas NaeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - MeiosisDocument29 pagesChapter 10 - Meiosisnancie8No ratings yet
- Meiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesMeiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionDocument38 pagesCA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionNKANo ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument31 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaMustapha AbdullateefNo ratings yet
- A2 Edexcel Biology Session 4 7 TranscripDocument25 pagesA2 Edexcel Biology Session 4 7 TranscripRick WuNo ratings yet
- Human Life Cycle in Holy QuranDocument34 pagesHuman Life Cycle in Holy QurankabdelmaeboudNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division-1Document35 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division-1shaikh mohammadNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Reproduction TypesDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Reproduction TypesRalph EspejoNo ratings yet
- 4BBA1010 - Building A Human - 2022Document31 pages4BBA1010 - Building A Human - 2022Ritika ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Transcriptionally Active HERV-H Retrotransposons Demarcate Topologically Associating Domains in Human Pluripotent Stem CellsDocument20 pagesTranscriptionally Active HERV-H Retrotransposons Demarcate Topologically Associating Domains in Human Pluripotent Stem CellsBrachy ZhaoNo ratings yet
- How Does IPTG Induced Gene Expression Work at A Molecular Level - QuoraDocument3 pagesHow Does IPTG Induced Gene Expression Work at A Molecular Level - QuoraDiksha GahlotNo ratings yet
- 16 - Development of Organisms and Continuity of Life: Candidates Should Be Able ToDocument3 pages16 - Development of Organisms and Continuity of Life: Candidates Should Be Able ToWeb BooksNo ratings yet
- 16 Reproduction Notes Igcse BiologyDocument29 pages16 Reproduction Notes Igcse Biologyasmatullahmohammed2No ratings yet
- Enhancer-Promoter Contact Formation Requires RNAPII and Antagonizes Loop ExtrusionDocument19 pagesEnhancer-Promoter Contact Formation Requires RNAPII and Antagonizes Loop ExtrusionHemangaNo ratings yet
- Mutation: - Today? Mutation Refers To Changes That Occur Within GenesDocument18 pagesMutation: - Today? Mutation Refers To Changes That Occur Within Genesapplemango93No ratings yet
- BrazdanjeDocument27 pagesBrazdanjezgood0% (1)
- CH 3 PDFDocument4 pagesCH 3 PDFAbhishek BarmanNo ratings yet
- Modeling Mitosis ActivityDocument4 pagesModeling Mitosis ActivityJobanie AmadhayNo ratings yet
- Copy Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesCopy Lesson PlanCarla Rose CruzNo ratings yet
- Summary of Metabolism LectureDocument20 pagesSummary of Metabolism Lectureaquasrk250No ratings yet
- BIOLOGY CLASSWORKDocument5 pagesBIOLOGY CLASSWORKInsiya TalwariNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesPlant and Animal Reproductive Systemrei08No ratings yet
- Early DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEarly DevelopmentyelloweverglowNo ratings yet
- Bzyct-133 Jun 2022Document6 pagesBzyct-133 Jun 2022Akram HusainNo ratings yet
- Quiz ReproductionDocument16 pagesQuiz Reproductionelenacatiggay83No ratings yet
- Vertebrate Embryology - Randel PDFDocument399 pagesVertebrate Embryology - Randel PDFrandelNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Chapter 4Document10 pagesBiology Form 5 Chapter 4Caryn YeapNo ratings yet
- Fungus-Like ProtistsDocument21 pagesFungus-Like ProtistsMia IbayNo ratings yet
- Notes of HeredityDocument2 pagesNotes of Hereditygayathris111No ratings yet
- MemoryDocument8 pagesMemoryShams JhugrooNo ratings yet














![BIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5Notes[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/720246673/149x198/ab3b18bb39/1712302138?v=1)