Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitosis and Meiosis
Uploaded by
aanonymousbros.0Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis and Meiosis
Uploaded by
aanonymousbros.0Copyright:
Available Formats
Describe mitosis and meiosis and explain the crucial roles each play.
Minimum: 5
paragraphs, each at least 2 sentences long.
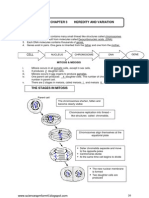
Meiosis and mitosis are both essential cellular processes that play crucial roles in the growth,
development, and reproduction of living organisms. While they share some similarities, such as
involving the division of cells, they also have distinct differences in terms of their purpose and
outcomes.
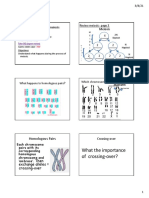
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells,
each containing the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process is essential for
growth, repair, and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Mitosis consists of several stages,
including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes
condense and become visible. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up along the center of the
cell. Anaphase involves the separation of sister chromatids to opposite poles of the cell. Finally,
telophase marks the formation of two daughter cells with identical genetic material. Mitosis
ensures genetic stability by producing cells with a complete set of chromosomes.
On the other hand, meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells
to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes as the parent
cell. This reduction in chromosome number is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic
diversity. Meiosis consists of two rounds of cell division (meiosis I and meiosis II), each with
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase stages. During meiosis I, homologous
chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through crossing over, leading to genetic
variation among offspring. In meiosis II, sister chromatids separate to form haploid gametes.
One key difference between meiosis and mitosis is the number of daughter cells produced.
Mitosis results in two diploid daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent
cell, whereas meiosis produces four haploid daughter cells with half the number of
chromosomes. Additionally, meiosis involves genetic recombination through crossing over
during prophase I, which contributes to genetic diversity.
In conclusion, mitosis is essential for growth and tissue repair in multicellular organisms, while
meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and generating genetic variation among offspring. Both
processes are tightly regulated and ensure the proper distribution of genetic material to daughter
cells. Understanding the differences between mitosis and meiosis is fundamental to
comprehending how organisms grow, develop, and reproduce.
You might also like
- Dawes Hoang, Rachel - Heston, Katherine - Meneely, Philip Mark - Okeke, Iruka N - Genetics - Genes, Genomes, and Evolution-Oxford University Press (2017)Document775 pagesDawes Hoang, Rachel - Heston, Katherine - Meneely, Philip Mark - Okeke, Iruka N - Genetics - Genes, Genomes, and Evolution-Oxford University Press (2017)Wahyu W'cas Pamungkas100% (4)
- M3 Writing AnalysisDocument4 pagesM3 Writing AnalysisGood ChannelNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Test Yourself 16.1 (Page 298)Document2 pagesCell Division: Test Yourself 16.1 (Page 298)lee100% (2)
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division.Document1 pageCell Cycle and Cell Division.ag8211729No ratings yet
- Scitech 2Document2 pagesScitech 2remeceldo dagamacNo ratings yet
- Biology - Mitosis & Meiosis SummaryDocument2 pagesBiology - Mitosis & Meiosis SummaryWei HouNo ratings yet
- Meiosis NotesDocument2 pagesMeiosis Noteslevyan.alakesan9736No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsuckamaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDocument7 pagesMitosis Vs MeiosisJD DX100% (1)
- Meiosis: Week 4 DiscussionDocument9 pagesMeiosis: Week 4 DiscussionJacob CarlNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument38 pagesCell DivisionJane Marry IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument21 pagesMitosis and MeiosisJuLie Ann DeGuzman GeslaniNo ratings yet
- Science8 Q4 M2Document6 pagesScience8 Q4 M2Arabella BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions On Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesMisconceptions On Mitosis and MeiosisEdcademiaNo ratings yet
- (Biology Form 4) MeiosisDocument4 pages(Biology Form 4) MeiosisUmi Zaheera AzharNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell Divisionhm khanNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesModule 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionBalolot RalphNo ratings yet
- SZL B206 Principles of GeneticsDocument28 pagesSZL B206 Principles of Geneticsawuors249No ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ReviewDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis Reviewwilz.zliw773No ratings yet
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocument11 pagesWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNo ratings yet
- Meoises NoteDocument1 pageMeoises NoteRIVALS〆toxicNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell DivisionNusrat ShoshiNo ratings yet
- Meiosis & MitosisDocument8 pagesMeiosis & MitosisAna Melisa DorueloNo ratings yet
- Prelim Task 4Document1 pagePrelim Task 4Kagami TaigaNo ratings yet
- Bio 001 Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesBio 001 Cell DivisionKnick KnackNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell DivisionedukahonNo ratings yet
- Meiosis - WikipediaDocument89 pagesMeiosis - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionDocument38 pagesCA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionNKANo ratings yet
- Bio Discussion 3Document2 pagesBio Discussion 3api-241205310No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument25 pagesMeiosisAnjelica BucasasNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis NotesDocument6 pagesMitosis & Meiosis NotesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Mitosis DefinitionDocument19 pagesMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Function of MeiosisDocument7 pagesFunction of MeiosisPhilip AtmaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of CellsDocument1 pageReproduction of CellsruivaacobreadaNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument3 pagesMeiosisJaja Jr. Evasco EmbarqueNo ratings yet
- Activity 4.2Document2 pagesActivity 4.2Jam TabucalNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument1 pageCell DivisionManas AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Vic Sample Notes BiologyDocument20 pagesVic Sample Notes BiologyEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Tri-Fold Template-1Document2 pagesTri-Fold Template-1api-260947636No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell DivisionAlbert Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesCell DivisionLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesDocument11 pagesCytogenetics Mitosis & Meiosis and Their DiferrencesGeemilReyNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell DivisionDocument70 pagesCell Structure and Cell DivisionAMALIA INDAH ALLIZA ALLIZANo ratings yet
- Meiosis (: ListenDocument13 pagesMeiosis (: ListenmuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- mitosis-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesmitosis-WPS OfficeSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis I & 2Document17 pagesMeiosis I & 2Mar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gametogenisis (Course)Document19 pagesGametogenisis (Course)achraf rabadiNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyDocument52 pagesCell Division: Dr. P. Pokorski University of Michigan - Dearborn Department of BiologyZuha HarithNo ratings yet
- Heredity and Variation NotesDocument19 pagesHeredity and Variation NotesAmelia DavisNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To GeneticsDocument3 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Geneticsrizza reyesNo ratings yet
- Subhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentDocument8 pagesSubhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentHero PratikNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis and Meiosis EssayDocument2 pagesBiology Mitosis and Meiosis Essayhammad133No ratings yet
- Charbel Matar BIO RESEARCHDocument5 pagesCharbel Matar BIO RESEARCH2eemmee eeccoolleeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsDocument3 pagesClass 10 Biology Chapter 2 Revision Notes GeneticsLakkiNo ratings yet
- Biology, Mitosis & MeiosisDocument2 pagesBiology, Mitosis & MeiosisfluffNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis and MeiosisShiela BelandresNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4)Document25 pagesBiology (Form 4)Aloysius RajNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesMeiosis: Dr. Shayma'a J. Ahmed Prof. Genetic Engineerin& BiotechnologyMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptDocument2 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: TranscriptKareem AghaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis NotesDocument2 pagesMitosis Noteslevyan.alakesan9736No ratings yet
- The Story From FlowersDocument5 pagesThe Story From Flowersaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- The Life of LilyDocument5 pagesThe Life of Lilyaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- The Dance of LiliesDocument5 pagesThe Dance of Liliesaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- As The Time FliesDocument5 pagesAs The Time Fliesaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Fahrenheit 451Document8 pagesFahrenheit 451aanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Why It Is Important To Be A CitizenDocument5 pagesWhy It Is Important To Be A Citizenaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Series of Metabolic Reactions That Take Place Within The Cells ofDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Series of Metabolic Reactions That Take Place Within The Cells ofaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- ACL Season IDocument5 pagesACL Season Iaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- The Impact of Mendelian Genetics and Its LawsDocument1 pageThe Impact of Mendelian Genetics and Its Lawsaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Writing Assignment, Storytelling 101Document1 pageWriting Assignment, Storytelling 101aanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Season OneDocument4 pagesSeason Oneaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- Summary of Short Story Read in Class TodayDocument1 pageSummary of Short Story Read in Class Todayaanonymousbros.0No ratings yet
- June 2009 QP - Unit 2 Edexcel BiologyDocument24 pagesJune 2009 QP - Unit 2 Edexcel BiologyKhaled TurkNo ratings yet
- CXC Human and Social Biology CSEC Notes PDFDocument12 pagesCXC Human and Social Biology CSEC Notes PDFMickalia MadourieNo ratings yet
- BiopracticalDocument51 pagesBiopracticalSourav joshiNo ratings yet
- Gamete FormationDocument26 pagesGamete FormationIslahNo ratings yet
- Day 6 More Meiosis-1Document4 pagesDay 6 More Meiosis-1Saad FraitekhNo ratings yet
- Biology-Lab Manual Sep2022Document32 pagesBiology-Lab Manual Sep2022Trân TuyếtNo ratings yet
- Subject: Science and Technology Grade Level: Grade 8 Teachers: Strand(s)Document9 pagesSubject: Science and Technology Grade Level: Grade 8 Teachers: Strand(s)richardsamranoNo ratings yet
- BBC1-K11-13 Cell ReplicationDocument81 pagesBBC1-K11-13 Cell Replicationirvan tpNo ratings yet
- Soalan Objektif Bio KSSM F4Document43 pagesSoalan Objektif Bio KSSM F4Hamirah Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionLim Wai Wai100% (1)
- Flashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSEDocument75 pagesFlashcards - Topic 17 Inheritance - CAIE Biology IGCSERinen ParacadNo ratings yet
- Evolution NotesDocument19 pagesEvolution Notesmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: MeiosisDocument6 pagesThis Study Resource Was: MeiosisMark Jerome CifraNo ratings yet
- SPERMATOGENESIS Spermatocytes Schimenti and Singh 2018Document6 pagesSPERMATOGENESIS Spermatocytes Schimenti and Singh 2018LudimilaNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 3 Study GuideDocument4 pagesAP Bio Unit 3 Study GuideKaycia HenryNo ratings yet
- Kips FLP 7 MdcatDocument15 pagesKips FLP 7 MdcatIsmail HamzaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Biology With Concept Coach 3.4Document98 pagesConcepts of Biology With Concept Coach 3.4Jasdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 2020 F4 Science Notes KSSM Chapter 4 6Document15 pages2020 F4 Science Notes KSSM Chapter 4 6紫菱No ratings yet
- Lab 5Document13 pagesLab 5Chikaodinaka Okoro0% (4)
- Mcat Full Lenth Practice PaperDocument15 pagesMcat Full Lenth Practice PaperFatima qaiserNo ratings yet
- Biology Unitwise MCQ - S (MCAT)Document41 pagesBiology Unitwise MCQ - S (MCAT)M Noaman Akbar100% (1)
- LSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseDocument11 pagesLSPU BSBIO - ZOO1 - SLM4 ExerciseJohn ValenciaNo ratings yet
- เลคเชอร์รวมพันธุศาสตร์Document16 pagesเลคเชอร์รวมพันธุศาสตร์ณัฐภัทร วิศิษฎ์วรณัฐNo ratings yet
- The Hologram As A Teaching Medium For The Acquisition of STEM ContentsDocument15 pagesThe Hologram As A Teaching Medium For The Acquisition of STEM ContentsAndi KaharuddinNo ratings yet
- Human Embryo' - : A Biological DefinitionDocument46 pagesHuman Embryo' - : A Biological DefinitionFernando Castro EchavezNo ratings yet
- MCQ 2010Document13 pagesMCQ 2010Nam NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Key Term Link: Unit 3 - Life ScienceDocument4 pagesKey Term Link: Unit 3 - Life Scienceapi-380948601No ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointJared CoyagboNo ratings yet