Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Megaloblastic Anemia
Uploaded by
Mary Kaye Yvonne Otilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesOriginal Title
MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesMegaloblastic Anemia
Uploaded by
Mary Kaye Yvonne OtillaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
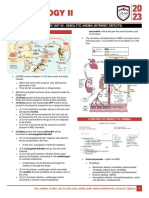
ANEMIAS CAUSED BY DEFECTS OF DNA ▪ Inherited errors in
METABOLISM absorption or transport
– Imerslund-grasbeck
• Most but not all macrocytic anemias are
syndrome,
caused by impairment of DNA
transcobalamin
metabolism
deficiency
• There are macrocytic anemias that are ▪ Competition for the
not caused by DNA metabolism vitamin – D. latum, Blind
MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIA loop syndrome (there is
a part of the intestine
• Macrocytic red cells is caused by that is cyanotic due to
impairment of DNA metabolism inflammation or
• Macrocytic RBC, Hyper segmented surgery)
neutrophils (5 and up) ▪ SYMPTOMS – Jaundice,
• Hallmark of the diseases affecting DNA Weakness, Glossitis,
metabolism (abnormality) Gastrointestinal
• Impaired DNA synthesis – very large disorder, Numbness,
bone marrow cells that develops Other CNS problems (3-
distinctive morphology 6 years development)
• Defective DNA synthesis causes o FOLATE DEFICIENCY
abnormal nuclear maturation; RNA (pteroylglutamic acid)
synthesis is normal, so the cytoplasm is ▪ Inadequate intake
not affected. The nucleus matures ▪ Increased need
slower than the cytoplasm. ▪ Impaired absorption
(asynchronism) ▪ Impaired use due to
• VITAMIN B12 DEFICIENCY drugs (antiepileptic
(COBALAMIN) and FOLATE DEFICIENCY drug, antineoplastic
• Megaloblastic erythropoiesis – slow drug/ chemotherapy)
maturation of cell (8 -12 um) ▪ Excessive loss with renal
• CAUSES: dialysis
o VB12 DEFICIENCY ▪ Body has a reserve for 3
▪ Inadequate intake months – if no intake
▪ Increased need – megaloblastic anemia
bleeding, pregnancy, may be developed
growth spurt, lactation ▪ Overcooking may
▪ Impaired absorption – diminish folic acid in
failure to split from food – heat labile
food, failure to split substance
from haptocorrin, lack ▪ SYMPTOMS: Poor diet,
of intrinsic factor pregnancy,
(pernicious anemia, chemotherapeutic anti-
achlorhydria) folic acid drugs
▪ General Malabsorption (Methotrexate)
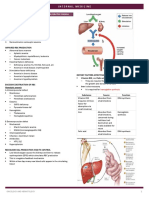
• OTHER CAUSES OF MEGALOBLASTOSIS: COBALAMIN METABIOLISM
o Myelodysplastic syndromes
• VB12 – liver, fish, poultry products, meat,
o Acute erythroid leukemia
and dairy products
o Congenital dyserythropoietic
o Formed by microorganisms and
anemia
fungi
o Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
o 5 ug per day
(HIV meds)
o Unlike iron, it can be excreted in
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF MEGALOBLASTIC the urine or feces
ANEMIA o 1-5 mg is stored in liver
• Enters alimentary tract
• SCREENING TESTS
o R binders transports VB12 into
o CBC: slight macrocytosis is the
duodenum (saliva, food, peptic
earliest sign of megaloblastic
secretions)
anemia (oval macrocytes,
o Intrinsic Factor binds VB12 for
hypersegmented neutrophils
absorption in the ileum (parietal
with 6 or more lobes)
cells – produces HCl to maintain
o RETICULOCYTE COUNT: low
acidity)
absolute reticulocyte count
o Amnionless & Cubilin receptors
o WBC DIFFERENTIAL COUNT:
for VB12-IF complex (Epithelial
hypersegmentation of
cells of terminal Ileum)
neutrophils (right shift WBC
▪ If no IF – no binder for
histogram, hypo is left shift) is
VB12 and no absorption
pathognomonic for
will happen in the ileum
megaloblastic anemia
▪ If not absorbed or upon
o SERUM BILIRUBIN: elevated
absorption the VB12 will
total and indirect bilirubin
enter the storage. If not
o LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE:
stored it will go to liver
elevated values
or general circulation for
o SCHILLING’S TEST
other part of the body
▪ Test for cobalamin
▪ Impaired absorption TRANSPORT IN PLASMA
could indicate IF
o Methyl cobalamin is a transport
deficiency
form of cobalamin (VB12)
▪ Radioactive cobalamin
▪ Transcobalamin II +
is given orally
VB12
▪ 2 hrs after, a non-
▪ Haptocorrins
labelled “flushing” dose
(cobalophilin)
is given
▪ 24 hr urine is examined
for radioactive
cobalamin
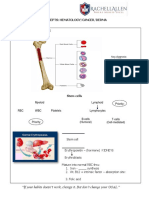
SEQUENCE OF DEVELOPMENT OF
MEGALOBLASTIC ANEMIAS
• Decrease in vitamin levels
• Hypersegmentation of neutrophils in
peripheral blood
• Oval macrocytes in peripheral blood
• Megaloblastosis in bone marrow
• Anemia
TREATMENT
• Better nutrition
• Treatment for D. latum
• High dose orat VB12/ Folic acid
• Iron supplements
NON-MEGALOBLASTIC MACROCYTIC ANEMIA
• Alcoholism
• Liver disease
• Bone marrow disorder/ failure
You might also like
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument23 pagesMegaloblastic Anemiamameekasim75No ratings yet
- 1.3 Macrocytic Anaemia, Megaloblastic and Nonmegaloblastic AnaemiaDocument43 pages1.3 Macrocytic Anaemia, Megaloblastic and Nonmegaloblastic AnaemiaAlex KamougerosNo ratings yet
- Anemia, Ida 1Document131 pagesAnemia, Ida 1zaha shamseerNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2Document42 pagesAnemia 2AbdulKhaleq AlkadimiNo ratings yet
- Chapters 33 and 33: Hematological System Iron Deficiency Anemia Etiology (Cause)Document14 pagesChapters 33 and 33: Hematological System Iron Deficiency Anemia Etiology (Cause)Celena LorenaNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument15 pagesAnemiaManali JainNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGYDocument17 pagesHEMATOLOGYMA. ANDREA NICOLE BITOINNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic Anemias: Dept of Medicine AcmsDocument71 pagesMegaloblastic Anemias: Dept of Medicine Acmskunal ghosh100% (1)
- AnaemiaDocument25 pagesAnaemiaIshali NuwanjiniNo ratings yet
- September - 6 - 2021-For - Students (HEMA)Document24 pagesSeptember - 6 - 2021-For - Students (HEMA)Christian John V. CamorahanNo ratings yet
- CH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument6 pagesCH 044 Megaloblastic AnemiaGshshNo ratings yet
- הרצאה- אנמיה וטרומבוציטופניהDocument87 pagesהרצאה- אנמיה וטרומבוציטופניהliatfurmanNo ratings yet
- Hema 311 Lecture Guide Notes No. 8 - Anemia (Part 3)Document6 pagesHema 311 Lecture Guide Notes No. 8 - Anemia (Part 3)Nel TinduganiNo ratings yet
- Pernicious Anemia - ECEDocument46 pagesPernicious Anemia - ECEaparna reddyNo ratings yet
- ANEMIADocument3 pagesANEMIAjessa tabanginNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiasDocument37 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiasL3mi DNo ratings yet
- Haemolytic Anaemia: DR Nurul Fahmiza Tumiran P109273Document55 pagesHaemolytic Anaemia: DR Nurul Fahmiza Tumiran P109273Nurul FahmizaNo ratings yet
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument8 pagesAnemia in Pregnancycurry yumeNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2024Document50 pagesAnemia 2024b9p6vmfnc4No ratings yet
- Hemafinals 01Document19 pagesHemafinals 01Clarence SantosNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnemiaDocument36 pagesMegaloblastic AnemiaMandyam Monica SaiNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic Anaemia: Moderator - Dr.G.Prem Kumar Presenter - DR - Dinesh VarmaDocument24 pagesMegaloblastic Anaemia: Moderator - Dr.G.Prem Kumar Presenter - DR - Dinesh VarmaAbhinav ReddyNo ratings yet
- MSN I 12.6.2020 FN Unit V Megaloblastic Anemia & Aplastic AnemiaDocument44 pagesMSN I 12.6.2020 FN Unit V Megaloblastic Anemia & Aplastic AnemiaHariniNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic and Hypoproliferative DisordersDocument34 pagesMacrocytic and Hypoproliferative Disordersjahahn.t.sullivanNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument20 pagesHematologyJunaid SabirNo ratings yet
- Anemia of Bone Marrow FailureDocument6 pagesAnemia of Bone Marrow FailureKim Alyssa GoNo ratings yet
- Anemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionDocument5 pagesAnemias Caused by Decreased Erythrocyte ProductionJette Charmae OlboNo ratings yet
- Anemia 2011 Student Dental FDocument64 pagesAnemia 2011 Student Dental Fkays30002403No ratings yet
- MED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaDocument5 pagesMED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaFlora XuNo ratings yet
- 7anemia Caused by Defects of DNA MetabolismDocument30 pages7anemia Caused by Defects of DNA MetabolismanonacadsNo ratings yet
- Oral Hypoglycemics AgentsDocument39 pagesOral Hypoglycemics Agentsmukdad9No ratings yet
- Macrocytic AnemiaDocument49 pagesMacrocytic AnemiaANo ratings yet
- 4 - Hematology 3Document15 pages4 - Hematology 3Kristen NateNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pale ChildDocument37 pagesApproach To Pale ChildsangheetaNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic AnemiasDocument28 pagesMacrocytic AnemiasDeepankar SrigyanNo ratings yet
- Megaloblastic and Other Macrocytic Anaemia: Dr. Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistDocument58 pagesMegaloblastic and Other Macrocytic Anaemia: Dr. Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistThaveeshaLindsayWhiteNo ratings yet
- Share Megaloblastic-Wps OfficeDocument13 pagesShare Megaloblastic-Wps OfficeShivam SehgalNo ratings yet
- 31.chronic Diarrhea and MalabsorbtionDocument14 pages31.chronic Diarrhea and MalabsorbtionSajjal AliNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Prof. Dr. Djoni Djunaedi, DR., SP - PD., KptiDocument48 pagesAnemia: Prof. Dr. Djoni Djunaedi, DR., SP - PD., KptiHarmas Novryan FarezaNo ratings yet
- Types of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesTypes of AnaemiaSuhaila NaemaNo ratings yet
- Type Inheritance Pathogenesis Features Treatment: Iron Deficiency AnaemiaDocument4 pagesType Inheritance Pathogenesis Features Treatment: Iron Deficiency AnaemiaNa NiNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia IntrinsicDocument14 pagesHemolytic Anemia IntrinsicSophia Gail ChingNo ratings yet
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument10 pagesNephritic SyndromeRam AryalNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic Anemias: Defective DNA SynthesisDocument17 pagesMacrocytic Anemias: Defective DNA SynthesispallavberiNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument40 pagesAnemiaGreenNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Diseases of Platelets/Vessel Wall or of Coagulation FactorsDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Diseases of Platelets/Vessel Wall or of Coagulation FactorsIlyasHasanNo ratings yet
- Congenital AnemiaDocument5 pagesCongenital AnemiaharideepNo ratings yet
- Macrocytic Anemias: NotesDocument10 pagesMacrocytic Anemias: NotesRaja SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microcytic AnemiaDocument6 pagesMicrocytic AnemiaharideepNo ratings yet
- PediatricDocument192 pagesPediatricbolt boltNo ratings yet
- Hematology SBIM Part 1Document7 pagesHematology SBIM Part 1Gousay AlkhazmariNo ratings yet
- Haematinics & ErythropoietinDocument30 pagesHaematinics & ErythropoietinManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet
- Pharm Anemia TSDocument37 pagesPharm Anemia TSNahome YebassewNo ratings yet
- UW (Step 1) GIT - Educational Objectives PDFDocument69 pagesUW (Step 1) GIT - Educational Objectives PDFDrbee10No ratings yet
- Megaloblastic AnaemiaDocument11 pagesMegaloblastic AnaemiaJesmin_36No ratings yet
- Hematology SummaryDocument9 pagesHematology SummaryJovielle Hayden100% (1)
- Anemia 07oct FINALDocument77 pagesAnemia 07oct FINALDr pragya joshiNo ratings yet
- Lec Quantitative Platelet DisordersDocument3 pagesLec Quantitative Platelet DisordersVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- (PPT) IM (Onco and Hema)Document78 pages(PPT) IM (Onco and Hema)ricaannpanugalinogNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Management of QualityDocument19 pagesTopic 10 Management of QualityMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9 - Location Planning and AnalysisDocument10 pagesTopic 9 - Location Planning and AnalysisMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Topic 12 - Occupational Safety and Health StandardsDocument9 pagesTopic 12 - Occupational Safety and Health StandardsMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 and 2 Introduction To Pathology Cellular Injury Death Adaptation Inflammation and RepairDocument96 pagesLecture1 and 2 Introduction To Pathology Cellular Injury Death Adaptation Inflammation and RepairMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory MathDocument13 pagesLaboratory MathMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- VILLALONDocument1 pageVILLALONMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Villalon ApplicationDocument1 pageVillalon ApplicationMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- HPCTDocument1 pageHPCTMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Biopsy and Autopsy: Lecture#4Document44 pagesBiopsy and Autopsy: Lecture#4Mary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- ImseDocument18 pagesImseMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- OTILLADocument2 pagesOTILLAMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument4 pagesEndocrineMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Group SystemDocument56 pagesABO Blood Group SystemMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- MONOLOGUEDocument1 pageMONOLOGUEMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 LabDocument2 pagesWeek 7 LabMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- LIVERDocument8 pagesLIVERMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- WBC Morphologic DefectDocument10 pagesWBC Morphologic DefectMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- EnteroDocument10 pagesEnteroMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- NORMOCYTICDocument2 pagesNORMOCYTICMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Forms of HemoglobinDocument4 pagesForms of HemoglobinMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsDocument11 pagesLEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Filipino Chicken Cordon BleuDocument7 pagesFilipino Chicken Cordon BleuHazel Castro Valentin-VillamorNo ratings yet
- 2011 06 13-DI-PER8-Acoustic Insulation Catalogue-Rev 01Document12 pages2011 06 13-DI-PER8-Acoustic Insulation Catalogue-Rev 01Tien PhamNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Marketing Arithmetic For Business AnalysisDocument12 pages5.4 Marketing Arithmetic For Business AnalysisashNo ratings yet
- Signal&Systems - Lab Manual - 2021-1Document121 pagesSignal&Systems - Lab Manual - 2021-1telecom_numl8233No ratings yet
- G.R. No. 186450Document6 pagesG.R. No. 186450Jose Gonzalo SaldajenoNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Service Requirements of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises in The PhilippinesDocument10 pagesAccountancy Service Requirements of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises in The PhilippinesJEROME ORILLOSANo ratings yet
- FACT SHEET KidZaniaDocument4 pagesFACT SHEET KidZaniaKiara MpNo ratings yet
- Sportex 2017Document108 pagesSportex 2017AleksaE77100% (1)
- CA39BDocument2 pagesCA39BWaheed Uddin Mohammed100% (2)
- Google Chrome OSDocument47 pagesGoogle Chrome OSnitin07sharmaNo ratings yet
- Social Networking ProjectDocument11 pagesSocial Networking Projectapi-463256826No ratings yet
- Does Social Media Influence Consumer Buying Behavior An Investigation of Recommendations and PurchasesDocument7 pagesDoes Social Media Influence Consumer Buying Behavior An Investigation of Recommendations and Purchasesyash_28No ratings yet
- Laws and Policies of Fertilizers SectorDocument12 pagesLaws and Policies of Fertilizers Sectorqry01327No ratings yet
- Neolms Week 1-2,2Document21 pagesNeolms Week 1-2,2Kimberly Quin CanasNo ratings yet
- EMP Step 2 6 Week CalendarDocument3 pagesEMP Step 2 6 Week CalendarN VNo ratings yet
- Construction Agreement SimpleDocument3 pagesConstruction Agreement Simpleben_23100% (4)
- WIKADocument10 pagesWIKAPatnubay B TiamsonNo ratings yet
- Propht William Marrion Branham Vist IndiaDocument68 pagesPropht William Marrion Branham Vist IndiaJoshuva Daniel86% (7)
- Snowflake Core Certification Guide Dec 2022Document204 pagesSnowflake Core Certification Guide Dec 2022LalitNo ratings yet
- Visual Acuity: Opthalmology CEX StepsDocument5 pagesVisual Acuity: Opthalmology CEX StepsVanessa HermioneNo ratings yet
- Anglicisms in TranslationDocument63 pagesAnglicisms in TranslationZhuka GumbaridzeNo ratings yet
- Grammar: English - Form 3Document39 pagesGrammar: English - Form 3bellbeh1988No ratings yet
- Kangaroo High Build Zinc Phosphate PrimerDocument2 pagesKangaroo High Build Zinc Phosphate PrimerChoice OrganoNo ratings yet
- New Count The DotsDocument1 pageNew Count The Dotslin ee100% (1)
- Deep MethodDocument13 pagesDeep Methoddarkelfist7No ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument48 pagesPeptic Ulcerscribd225No ratings yet
- Quizo Yupanqui StoryDocument8 pagesQuizo Yupanqui StoryrickfrombrooklynNo ratings yet
- College PrepDocument2 pagesCollege Prepapi-322377992No ratings yet
- Apush Leq Rubric (Long Essay Question) Contextualization (1 Point)Document1 pageApush Leq Rubric (Long Essay Question) Contextualization (1 Point)Priscilla RayonNo ratings yet
- Solution Document For Link LoadBalancerDocument10 pagesSolution Document For Link LoadBalanceraralNo ratings yet