Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Future Tenses
Uploaded by
Laura Fernández AntequeraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Future Tenses
Uploaded by
Laura Fernández AntequeraCopyright:
Available Formats
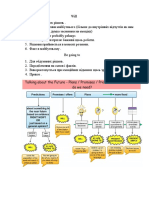
In English, the future tense is used to describe actions or events that will happen after the
present moment. There are several ways to express the future tense in English, including the
following:
1. Simple Future Tense: The simple future tense is formed by using the auxiliary verb "will"
or "shall" followed by the base form of the main verb. For example:
● "I will travel to Paris next week."
● "She shall call you tomorrow."
2. Going to Future: The "going to" future is used to talk about intentions, plans, or
predictions based on present evidence. It is formed by using the phrase "be going to"
followed by the base form of the main verb. For example:
● "They are going to buy a new car."
● "He is going to visit his grandparents this weekend."
3. Present Continuous: The present continuous tense can also be used to talk about future
events when there is a definite plan or arrangement. It is formed by using the present
tense of the verb "be" (am/is/are) followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the
main verb. For example:
● "We are having a party tomorrow."
● "She is leaving for the airport in an hour."
4. Future Continuous: The future continuous tense is used to describe ongoing actions or
events that will happen at a specific time in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary
verb "will" followed by "be" and the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb. For
example:
● "I will be studying for the exam all night."
● "They will be working on the project next month."
5. Future Perfect: The future perfect tense is used to describe actions or events that will be
completed before a specific time in the future. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb
"will" followed by "have" and the past participle of the main verb. For example:
● "By next year, I will have finished my degree."
● "They will have arrived by the time the party starts."
6. Future Perfect Continuous: The future perfect continuous tense is used to describe
ongoing actions or events that will continue until a certain point in the future. It is formed
by using the auxiliary verb "will" followed by "have been" and the present participle (-ing
form) of the main verb. For example:
● "I will have been working here for five years by the end of this month."
● "She will have been studying English for ten years when she graduates."
It's important to note that the choice of future tense depends on the context and the speaker's
intention. Different future tenses can convey different meanings and nuances.
You might also like
- تقرير الانجليزيDocument2 pagesتقرير الانجليزيbasel.khashashneh.44No ratings yet
- Perfect Future With ExamplesDocument1 pagePerfect Future With ExamplesShrikant GondhaliNo ratings yet
- Means of Expressing FuturityDocument10 pagesMeans of Expressing FuturityPereteanu ElenaNo ratings yet
- Master 16 Tenses EasilyDocument40 pagesMaster 16 Tenses Easilydhany1919No ratings yet
- FutureDocument30 pagesFutureStefanDribler998No ratings yet
- E1 - Module 1Document5 pagesE1 - Module 1Usep SupiadiNo ratings yet
- Means of Expressing FuturityDocument9 pagesMeans of Expressing FuturityEma Ghita50% (2)
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument6 pagesThe Present Continuous TenselepromNo ratings yet
- Simple Future TenseDocument5 pagesSimple Future TenseTia Rahma50% (2)
- Future Perfect Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesFuture Perfect Continuous TenseGeronimoNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument6 pagesFuture TensesSofía Simón RepettoNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Continuous TenseDocument5 pagesFuture Perfect Continuous TenseAditi ParmarNo ratings yet
- Micro LessonDocument31 pagesMicro LessonMarcela Borges PradoNo ratings yet
- The Future Perfect TenseDocument6 pagesThe Future Perfect TenseTia RahmaNo ratings yet
- Using The Correct TenseDocument5 pagesUsing The Correct TenseLula KotulovaNo ratings yet
- Expressing Future in EnglishDocument4 pagesExpressing Future in EnglishTamara PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Essay. Futurity in The English LanguageDocument2 pagesEssay. Futurity in The English LanguageColin YoungNo ratings yet
- Independent Learning 3Document3 pagesIndependent Learning 3novitaNo ratings yet
- I'll Have Finished This Book Soon. I'm Nearly at The EndDocument6 pagesI'll Have Finished This Book Soon. I'm Nearly at The EndValentin PatruNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses ExplainedDocument42 pagesFuture Tenses ExplainedMarcela Borges Prado100% (1)
- 3rd Ebook3Document3 pages3rd Ebook3Emma CarrilloNo ratings yet
- FUTURE TENSESDocument27 pagesFUTURE TENSESdaliaNo ratings yet
- Dyah Darma AndayaniDocument19 pagesDyah Darma AndayaniMuhammad FadlilNo ratings yet
- Future Forms: Intentions (Example: He's Going To Study Law)Document2 pagesFuture Forms: Intentions (Example: He's Going To Study Law)GreenLake36No ratings yet
- Future Tense and Future Continuous TenseDocument7 pagesFuture Tense and Future Continuous Tensedhinishagira12No ratings yet
- simple futureDocument1 pagesimple futureytomazeliNo ratings yet
- D360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 03 (Rodrigo A.) PDFDocument19 pagesD360 - Lingua Inglesa (M. Atena) - Material de Aula - 03 (Rodrigo A.) PDFrobson ferreiraNo ratings yet
- U3 Future TensesDocument18 pagesU3 Future Tenses2257010141No ratings yet
- Future PerfectDocument19 pagesFuture Perfectlizasolo305No ratings yet
- Future Perfect and Continuous FormsDocument7 pagesFuture Perfect and Continuous FormsIulia SzenteNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument20 pagesFutureAli AteeqNo ratings yet
- DoneDocument7 pagesDoneYasmin Putri MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12Document9 pagesLesson 12lorenafelipeclemNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect and Future Perfect ContinuousDocument1 pageFuture Perfect and Future Perfect Continuouscna.english.courseNo ratings yet
- Future Simple and Future ContinuousDocument9 pagesFuture Simple and Future ContinuousLeslie VazquezNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Microsoft WordDocument18 pagesEnglish Grammar Microsoft WordMarysia AndrunyszynNo ratings yet
- Engleski (Future Forms)Document12 pagesEngleski (Future Forms)Kozmetika Amina-Mirnesa SubašićNo ratings yet
- Present Progressive TenseDocument5 pagesPresent Progressive TenserameenNo ratings yet
- FUTURODocument16 pagesFUTUROrodrigoNo ratings yet
- Future TenseDocument2 pagesFuture Tensetestfortest1305No ratings yet
- The Expression of Future in Contemporary English: João Bittencourt de Oliveira (UERJ/UNESA)Document19 pagesThe Expression of Future in Contemporary English: João Bittencourt de Oliveira (UERJ/UNESA)degr8sidNo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Tense GuideDocument3 pagesFuture Perfect Tense GuideDost JanNo ratings yet
- The Future TensesDocument4 pagesThe Future TensesCélia ZENNOUCHENo ratings yet
- Future Perfect Tense: Created byDocument17 pagesFuture Perfect Tense: Created byRafi Sofian AliNo ratings yet
- 10.2 GrammarDocument8 pages10.2 GrammarGeorgiana GiusepiNo ratings yet
- M3 TensesDocument5 pagesM3 Tensesjessa caballeroNo ratings yet
- Sip DefenseDocument11 pagesSip DefensearnoxmamadorNo ratings yet
- Aspects of The Future TenseDocument2 pagesAspects of The Future TenseMilica MihajlovskiNo ratings yet
- Verb as the central part of speechDocument12 pagesVerb as the central part of speechАлина ГолубенкоNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses: Predictions/statements of Fact Intentions Arrangements Scheduled EventsDocument27 pagesFuture Tenses: Predictions/statements of Fact Intentions Arrangements Scheduled Eventsroxxi89No ratings yet
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 pagesFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense ExplainedDocument5 pagesFuture Perfect Continuous Tense Explainedshan1009No ratings yet
- FORM Future Perfect With "Will"Document3 pagesFORM Future Perfect With "Will"seetea95No ratings yet
- FutureDocument16 pagesFutureAnka A. PeNo ratings yet
- Simple Future TenseDocument1 pageSimple Future TenseAlina Cristina UțăNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7Document19 pagesPertemuan 7Dr. Dwi Fita HeriyawatiNo ratings yet
- FORM Future Perfect With "Will"Document3 pagesFORM Future Perfect With "Will"phillyfelipeNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument2 pagesConditionalsLaura Fernández AntequeraNo ratings yet
- Writing 1Document1 pageWriting 1Laura Fernández AntequeraNo ratings yet
- Movie ReviewDocument1 pageMovie ReviewLaura Fernández AntequeraNo ratings yet
- Aquí Hay Una Lista de 50 Phrasal Verbs Comunes en Inglés, Junto Con Sus Significados y Ejemplos de UsoDocument3 pagesAquí Hay Una Lista de 50 Phrasal Verbs Comunes en Inglés, Junto Con Sus Significados y Ejemplos de UsoLaura Fernández AntequeraNo ratings yet
- Atg Grambingo PresentperfectDocument2 pagesAtg Grambingo PresentperfectArturo Vasquez100% (1)
- Write The Verb To Be and Change To Short Form.: Re-Arrange The SentenceDocument4 pagesWrite The Verb To Be and Change To Short Form.: Re-Arrange The SentenceLeyner Osvaldo Calva Herrera100% (1)
- Simple Verb Tenses Explained in EnglishDocument7 pagesSimple Verb Tenses Explained in EnglishAhmad Agus SalimNo ratings yet
- A Complaint LetterDocument3 pagesA Complaint Letterprajwol lamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Present ProgressiveDocument9 pagesPresent ProgressiveIvan Gabriel montielNo ratings yet
- Compounding in English and ArabicDocument18 pagesCompounding in English and ArabicBajram HoxhaNo ratings yet
- LK 2 - Modul 2 - Ade Permata Sari - Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesLK 2 - Modul 2 - Ade Permata Sari - Bahasa InggrisAde Permata SariNo ratings yet
- Negative PrefixesDocument2 pagesNegative PrefixeskookaburraNo ratings yet
- Administrarea Disciplinei Limba EnglezăDocument12 pagesAdministrarea Disciplinei Limba EnglezăVica LunguNo ratings yet
- RecountDocument15 pagesRecountRatna D. AnjaniNo ratings yet
- Remember: Verb + Ing Verb+ Ing: Read-Reading Affirmative and Negative FormDocument1 pageRemember: Verb + Ing Verb+ Ing: Read-Reading Affirmative and Negative FormPawel PtakNo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu Ngu Phap Tieng Anh 2Document108 pagesTai Lieu Ngu Phap Tieng Anh 2Ka KenzoNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm Summative AssessmentDocument5 pagesAnimal Farm Summative AssessmentthpolanskyNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Third Person Singular WorksheetDocument3 pagesPresent Simple Third Person Singular WorksheetSofia PobladorNo ratings yet
- Explanations: All Roads To The North Have Been Blocked by SnowDocument3 pagesExplanations: All Roads To The North Have Been Blocked by Snowzarathusta_1234No ratings yet
- Analytical Scoring Rubrics For Telling A Story or A Personal AnecdoteDocument3 pagesAnalytical Scoring Rubrics For Telling A Story or A Personal AnecdoteRuzannaKniazchianNo ratings yet
- Silviana Rahayu Hersa - 8.3 - Remedial Pas PDFDocument14 pagesSilviana Rahayu Hersa - 8.3 - Remedial Pas PDFDesfi Nurrachma hersaNo ratings yet
- Test 8 - Module 8: VocabularyDocument4 pagesTest 8 - Module 8: VocabularyKollár GabriellaNo ratings yet
- Improving Sentence StructureDocument15 pagesImproving Sentence StructureNhật LinhNo ratings yet
- Quiz RubricsDocument2 pagesQuiz RubricsGherneil DalanonNo ratings yet
- Properties of A Well-Written TextDocument52 pagesProperties of A Well-Written TextBryan Callano100% (1)
- Team #2's Grammar Lesson on BE GOING TO and WOULD LIKE TODocument13 pagesTeam #2's Grammar Lesson on BE GOING TO and WOULD LIKE TOClaudia Rosalia Dzib MissNo ratings yet
- Cambridge ClausesDocument13 pagesCambridge ClausesRamon LopesNo ratings yet
- ID Kata Ganti Orang Bahasa Inggris Dan BahaDocument15 pagesID Kata Ganti Orang Bahasa Inggris Dan BahaKartika Dwi NurandaniNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect and Past SimpleDocument1 pagePresent Perfect and Past SimpleGabriela GarciaNo ratings yet
- Class - 3 English Grand TestDocument2 pagesClass - 3 English Grand TestSyed Asim Raza100% (1)
- Determiners and Quantifiers Part 1Document54 pagesDeterminers and Quantifiers Part 1Andrés MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs Sentence CompletionDocument2 pagesModal Verbs Sentence CompletionEveLina MatejkoNo ratings yet
- Tense ShiftsDocument3 pagesTense ShiftsSarah GomezNo ratings yet
- Comparatives and Superlatives: SuffixDocument4 pagesComparatives and Superlatives: SuffixAmalina HasbiNo ratings yet