Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Static Member Function Code
Uploaded by
amolia20040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThe code defines a Book class with member variables to store a book ID, price, and a static count variable. It includes member functions to set the book data, display the book data, and display the count of Book objects. Main creates 3 Book objects, sets their data, and calls the static count display function twice to show the incrementing number of objects.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe code defines a Book class with member variables to store a book ID, price, and a static count variable. It includes member functions to set the book data, display the book data, and display the count of Book objects. Main creates 3 Book objects, sets their data, and calls the static count display function twice to show the incrementing number of objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesStatic Member Function Code
Uploaded by
amolia2004The code defines a Book class with member variables to store a book ID, price, and a static count variable. It includes member functions to set the book data, display the book data, and display the count of Book objects. Main creates 3 Book objects, sets their data, and calls the static count display function twice to show the incrementing number of objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
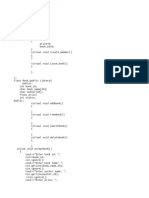
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Book{
int bookid;
float price;
static int count; //static data member
public:
void getdata(int i,float j)
{
bookid=i;
price=j;
++count; //count the number of objects
}
void showdata()
{
cout<<"Book ID: "<<bookid<<"\t";
cout<<"Price: "<<price<<"\n";
}
static void showcount() //Static member function
{
cout<<"Count of objects of class Book: "<<count<<"\n";
}
};
int Book::count=0; // initializing the static data member to 0
int main()
{
Book B1, B2;
B1.getdata(198, 2550.3);
B2.getdata(174, 3756.89);
Book::showcount(); //calling static member function
B1.showdata();
B2.showdata();
Book B3; //another object of the class is created
B3.getdata(345,5432.4);
Book::showcount(); //calling static member function again
B1.showdata();
B2.showdata();
B3.showdata();
return 0;
}
You might also like
- Library Management System For Computer Science Project Class 12Document31 pagesLibrary Management System For Computer Science Project Class 12Jyotirmoy Bandyopadhayaya70% (10)
- Class Item (Int Code Float Price Public: Void Getdata (Int A, Float B) (Code A Price B ) Void Show (Cout Code Price ) )Document7 pagesClass Item (Int Code Float Price Public: Void Getdata (Int A, Float B) (Code A Price B ) Void Show (Cout Code Price ) )Er Ashish BahetiNo ratings yet
- Class Item (Int Code Float Price Public: Void Getdata (Int A, Float B) (Code A Price B ) Void Show (Cout Code Price ) )Document7 pagesClass Item (Int Code Float Price Public: Void Getdata (Int A, Float B) (Code A Price B ) Void Show (Cout Code Price ) )Er Ashish BahetiNo ratings yet
- 19112A AaryanJoshi Lab-PointersDocument5 pages19112A AaryanJoshi Lab-PointersPrajwal JadhavNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument14 pagesInheritanceSyed HaiderNo ratings yet
- Practical No 14Document8 pagesPractical No 14Mick YT100% (2)
- Sahabpreet C++Document36 pagesSahabpreet C++Sanjay PalNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledRaluca IordacheNo ratings yet
- Gopal C++Document36 pagesGopal C++Sanjay PalNo ratings yet
- CDocument69 pagesCSoumya Prakash SahooNo ratings yet
- String Author (4) : // Begin Function Getters/AccessorsDocument6 pagesString Author (4) : // Begin Function Getters/AccessorsJuahir BkNo ratings yet
- Array of ObjectsDocument16 pagesArray of ObjectsHarshada JadhavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document6 pagesAssignment 3Swaraj FarakateNo ratings yet
- ZaryabDocument13 pagesZaryabsaad khanNo ratings yet
- OODP - Week 3Document23 pagesOODP - Week 3vinith gomezNo ratings yet
- OOP Lab 3 DT-45Document12 pagesOOP Lab 3 DT-45EBAADUREHMAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Using Namespace Class Private Char Float Int Public New Char New Char New Char New Float New Int Void Void Void Int Char Char VoidDocument7 pagesUsing Namespace Class Private Char Float Int Public New Char New Char New Char New Float New Int Void Void Void Int Char Char VoidNkNo ratings yet
- Program To Show Addition of Two ObjectsDocument25 pagesProgram To Show Addition of Two ObjectsAnkit ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 1) Write A C++ Program To Declare A Class "Book" Having Data Members Book - Name, Author andDocument4 pages1) Write A C++ Program To Declare A Class "Book" Having Data Members Book - Name, Author and1213 Vaibhav Kothare100% (1)
- Assignment 2: Object Orientated ProgramingDocument14 pagesAssignment 2: Object Orientated ProgramingZeeshan MughalNo ratings yet
- Oops ExperimentDocument13 pagesOops Experimentayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- Book CPPDocument6 pagesBook CPPabhi GaikwadNo ratings yet
- C++ HarleenDocument23 pagesC++ HarleenTwinkle SadanaNo ratings yet
- Lab FileDocument55 pagesLab FileSKOD SKODNo ratings yet
- Practice Examples: CodeDocument5 pagesPractice Examples: Codebandi nagavindhyaNo ratings yet
- Abstract ClassDocument16 pagesAbstract ClasskumararguruNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming Project ReportDocument23 pagesObject Oriented Programming Project ReportJohn WickNo ratings yet
- C++ Functions 1-1Document33 pagesC++ Functions 1-1Lameck MosetiNo ratings yet
- CSDocument30 pagesCSmitalinagar2113No ratings yet
- Polymarphism ShahDocument6 pagesPolymarphism ShahMuhammed AliNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Investigatory ProjectDocument22 pagesComputer Science Investigatory Projectyou tubeNo ratings yet
- Oop QuizDocument5 pagesOop QuizAmina RiazNo ratings yet
- BCSL 032 Solved Assignment 2023Document8 pagesBCSL 032 Solved Assignment 2023learnerlexiNo ratings yet
- 21CAP-654 Worksheet 02.03 21MCA2144Document10 pages21CAP-654 Worksheet 02.03 21MCA2144Humanshi JangraNo ratings yet
- CDocument74 pagesCxblueknightNo ratings yet
- Oop Assignmnet 2Document15 pagesOop Assignmnet 2mozalfaNo ratings yet
- Syed Shams Haider 203 Lab Report 07Document24 pagesSyed Shams Haider 203 Lab Report 07Syed ShamsNo ratings yet
- Poly Mar Phi SimDocument6 pagesPoly Mar Phi SimMuhammed AliNo ratings yet
- Document 5Document23 pagesDocument 5honey.qazi33No ratings yet
- Polymarphisim 1 2Document4 pagesPolymarphisim 1 2Muhammed AliNo ratings yet
- Virtual Function: #Include #IncludeDocument17 pagesVirtual Function: #Include #IncludeByg BasherNo ratings yet
- OOP Lab Report-6Document14 pagesOOP Lab Report-6Talha TufailNo ratings yet
- Classes and ObjectsDocument8 pagesClasses and Objectsamolia2004No ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming - 6Document18 pagesObject Oriented Programming - 6rakesh dasNo ratings yet
- BCSL 032 Solved AssignmentDocument8 pagesBCSL 032 Solved AssignmentlearnerlexiNo ratings yet
- Library Management System in JavaDocument59 pagesLibrary Management System in JavaSachin ShikarwarNo ratings yet
- Oop PR6Document5 pagesOop PR6AshwathNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Theory Assignment 2 Library Management System CodeDocument9 pagesSoftware Engineering Theory Assignment 2 Library Management System CodeGowtham SaiNo ratings yet
- Ilist and Arraylist Program: Using Using Using Using Namespace Class Static Void String New New New NewDocument6 pagesIlist and Arraylist Program: Using Using Using Using Namespace Class Static Void String New New New NewRachit HarlalkaNo ratings yet
- OopsDocument61 pagesOopsAshlee Nishanth LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Static Members of A C++ ClassDocument3 pagesStatic Members of A C++ ClassAbhilash KNo ratings yet
- Assignment 03 (Oop TH)Document8 pagesAssignment 03 (Oop TH)Usama Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledgetivaNo ratings yet
- 2.abstract Data Type and C++ Classes PDFDocument40 pages2.abstract Data Type and C++ Classes PDFSaimo MghaseNo ratings yet
- Library Managment Project by Tushar (C++)Document22 pagesLibrary Managment Project by Tushar (C++)General weedNo ratings yet
- Objects and ClassesDocument6 pagesObjects and ClassessanbioinfoNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Creating ObjectsDocument7 pages3.3 Creating ObjectsRAMI RAMINo ratings yet
- C ++ ProjectsDocument45 pagesC ++ ProjectsDeepakRohal100% (1)
- SushilcppDocument66 pagesSushilcppSushil GurjarNo ratings yet
- Simple ProgramDocument1 pageSimple Programamolia2004No ratings yet
- Functions in C++Document2 pagesFunctions in C++amolia2004No ratings yet
- Inheritance ProgramDocument18 pagesInheritance Programamolia2004No ratings yet
- Array of ObjectsDocument1 pageArray of Objectsamolia2004No ratings yet
- Access SpecifierDocument1 pageAccess Specifieramolia2004No ratings yet
- Constructor and DestructorDocument16 pagesConstructor and Destructoramolia2004No ratings yet
- Classes and ObjectsDocument8 pagesClasses and Objectsamolia2004No ratings yet
- Exception HandlingDocument1 pageException Handlingamolia2004No ratings yet
- Introduction of Oops and C++Document13 pagesIntroduction of Oops and C++amolia2004No ratings yet
- C++ ProgramsDocument8 pagesC++ Programsamolia2004No ratings yet