Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CEP HISTO - Lab Exercise 3 - Musculoskeletal Tissues
Uploaded by
Pia CincoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CEP HISTO - Lab Exercise 3 - Musculoskeletal Tissues
Uploaded by
Pia CincoCopyright:
Available Formats
宿务亚典耀圣心学校
SACRED HEART SCHOOL – ATENEO de CEBU
H. Abellana Street, Canduman, Mandaue City
Senior High School Department
SY 2022 – 2023
CURRICULUM ENRICHMENT PROGRAM FOR STEM
(CEP-MEDICAL)
PREPARED BY:
MR. NATHANIEL C. NIAR
MS. PIA ANGELICA CINCO
2
TABLE OF CONTENTS
NO. TITLE OF LABORATORY EXERCISE
1 EPITHELIUM AND ADIPOSE TISSUES
1.1 EPITHELIAL TISSUES
1.2 ADIPOSE TISSUES
2 NERVOUS TISSUES
2.1 NEURONS AND GLIAL CELLS
2.2 CENTRAL AND PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
3 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
3.1 MUSCULAR TISSUES
3.2 SKELETAL TISSUES
4 CIRCULATORY TISSUES
4.1 HEART AND VASCULATURE
4.2 COMPONENTS OF BLOOD
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS
1) Online laboratory exercises will be done every Independent Learning day (i.e.,
Wednesdays) during the period. Deadlines for the Histology Laboratory Journal will
be on predetermined Mondays. Students will have to submit their journals to their
beadles which will be submitted to the teacher to the faculty room anytime within the
day.
2) Students will be drawing different structures from histological specimens archived in
the internet. Drawn structures will be labeled accordingly based on the description of
this manual.
3) All drawings must be placed in a drawing book (i.e., Histology Laboratory Journal)
that each student must provide for themselves. All drawings must be done using
colored pencils to depict a precise and accurate representation of the specimen
discussed. Labels (i.e., parts or structures seen in the slides) must be placed at the
right and written using a BLUE pen.
4) General rubrics will be attached in every exercise to guide the students on how they
are graded.
7Cs: CHRIST-CENTEREDNESS ∙ COMPETENCE ∙ CONSCIENCE ∙ CHARACTER ∙ COMMUNITY ∙ COMPASSION ∙ CULTURE
3
LABORATORY EXERCISE NO. 3
MUSCULOSKELETAL TISSUES
Learning Competencies:
Through this laboratory exercise, I can…
1) Characterize and differentiate different kinds of muscle tissues according to their
shape, size, and function; and,
2) Characterize and differentiate different bone cells according to their size, shape,
structure, and function.
Introduction
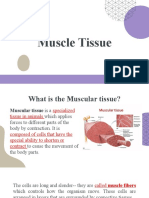
Muscular tissue is the fourth basic tissue type, along with epithelia, connective tissues,
and nervous tissues. It is composed of a group of cells that optimize one of the cell’s
property, contractility. It is composed of elongated cells (muscle fibers or myocytes)
that utilizes ATP to generate force. Moreover, this generated force will result to different
body movements, posture maintenance, and heat generation. Muscle tissues also
provide protection to different organs. Generally, they are classified according to their
structural and functional features as skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles.
Skeletal muscles are typically attached to the bones of the skeleton. They are specialized
to execute rapid voluntary movements of different organs of the body in response to the
signals transmitted by the CNS. On the other hand, cardiac muscle is specialized for
repetitive, rhythmic contractions over a long period of time without ceasing. Its contraction
is involuntary and regulated by the autonomic nervous system and hormones and
neurotransmitters in the blood. In contrast, smooth muscle Is diverse in its characteristics
and is found in many organs of the body, such as the gastrointestinal, vascular,
respiratory, reproductive, and urinary system.
The bone of the skeletal system is a specialized type of supporting connective tissue
which is different from cartilage. One of the main differences of bones from cartilages is
that the bone is calcified which makes it harder and stronger than the cartilage. They
protect internal organs (e.g., brain, heart), provide an environment for the production of
blood cells (e.g., bone marrow), detoxifies chemicals in the body, and support body
movements.
MUSCULAR TISSUES
A. Skeletal muscle
The whole muscle is surrounded by a thin sheet of dense irregular connective tissue
(epimysium). The whole skeletal muscle is composed of numerous muscle fiber bundles
(fascicles). Each fascicle is surrounded by a sheet of moderately dense irregular
connective tissues (perimysium), while each muscle fiber in the fascicle is surrounded
7Cs: CHRIST-CENTEREDNESS ∙ COMPETENCE ∙ CONSCIENCE ∙ CHARACTER ∙ COMMUNITY ∙ COMPASSION ∙ CULTURE
4
by endomysium, a delicate collagen network. Locate these connective tissues in slide
no. 1 at low power magnification.
Moreover, skeletal muscle tissues are characterized by a striped or striated
appearance when viewed at higher objectives under the microscope. The striations
reflect a repeating pattern of contractile elements (sarcomeres) while each sarcomere is
composed of actin and myosin myofilaments orderly arranged. Muscle fibers are
considered as the cellular units of the skeletal muscle. They are characterized a long,
roughly cylindrical cell bounded by a plasma membrane (sarcolemma). Note that a single
muscle cell may have several nuclei because each skeletal muscle fiber arises during
embryonic development from the fusion of numerous mesodermal cells (myoblasts). A
distinctive feature of skeletal muscles, visible in the longitudinal section, is a repeating
pattern of dark and light bands oriented at right angles to the length of the fiber. Find
these bands in the specimens.
Use these slides for your output:
#1, Larynx, Frontal section, H&E
(https://vmicro.iusm.iu.edu/virtual_h_nw/nw_hist_1_92.html)
#2, Skeletal muscle, Longitudinal section, H&E
(https://histologyslides.med.umich.edu/Histology/Basic%20Tissues/Muscle/058L_HIST
O_20X.htm)
For Box #1 – Use slide no. 1 to label the structures described in the 1st paragraph
For Box #2 – Use slide no. 2 to label the structures described in the 2nd paragraph.
B. Cardiac muscle
Examine the cardiac muscle tissue in gross view. Note that the cardiac muscle tissue has
an endomysium and perimysium but lacks an epimysium. Like the skeletal muscle,
cardiac muscle tissues are also striated. Actin and myosin filaments are arranged into
sarcomeres. They are much shorter than skeletal muscle fibers with a single, centrally
located nucleus. They typically split into two or more branches that are joined by
intercalated discs and form a meshwork of muscle fibers. These microscopic structures
are irregular transverse thickenings of the sarcolemma, and contain desmosomes, which
hold the fibers together, and gap junctions, which allow muscle action potentials to spread
from one cardiac muscle fiber to another.
In longitudinal sections, examine the slide for the intercalated discs and the centrally
located nucleus of each muscle fiber. Longitudinal striping or striations due to myofibrils
can sometimes be seen.
Use this slide for your output:
#3, Heart with mitral valve, Monkey, Mallory azan stain
(https://histologylab.ctl.columbia.edu/slides/slide17/)
7Cs: CHRIST-CENTEREDNESS ∙ COMPETENCE ∙ CONSCIENCE ∙ CHARACTER ∙ COMMUNITY ∙ COMPASSION ∙ CULTURE
5
For Box #3 – Use slide no. 3 to label the structures described above.
C. Smooth muscle
Smooth muscle fibers are short, and spindle shaped. They have one, centrally placed
nuclei. The sarcoplasm of smooth muscle fibers contains thick myosin filaments, thin actin
filaments, and intermediate filaments. Because the various filaments have no regular
pattern of overlap, smooth muscle fibers do not exhibit striations, causing a smooth
appearance. The actin and myosin filaments are organized as a lattice-like network that
is connected to the sarcolemma via adhesion complexes called dense bodies. This
organization allows the cells to twist as they contract, sometimes giving them a distinctive
corkscrew appearance in specimens.
Examine slides 4 to 6 below. Remember that the muscularis of the gastrointestinal tract
is frequently organized as inner circular and outer longitudinal layers of smooth muscle
with a nerve plexus located in between the layers. In hollow organs in which the overall
size of the organ is reduced by smooth muscle contraction, such as the uterus, the
fascicles are intertwined and run in all different directions. In this specimen, some
fascicles are cut in a longitudinal plane, some in a tangential plane, and others are cut
diagonally. Smooth muscle lines the walls of the bronchioles in the respiratory system.
Bronchioles can be identified in the specimen by having a ciliated cuboidal or columnar
epithelium with intensely basophilic nuclei. This smooth muscle aids in expelling air from
the lungs during breathing. It is also important in the cough reflex, which helps to expel
foreign matter such as dust, smoke, and excess mucus from the lungs.
Use these slides for your output:
#4, Endometrium, Pre-menstrual, H&E
(http://medsci.indiana.edu/junqueira/virtual/81_bl_5.html)
#5, Lung, Human, H&E (http://medsci.indiana.edu/junqueira/virtual/97_bl_5.html)
#6, Jejunum, Human. H&E (http://medsci.indiana.edu/junqueira/virtual/158_bl_5.html)
For Box #4 – Use slide no. 4, 5, or 6 to label the structures described above.
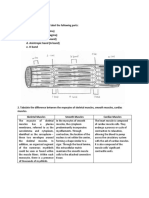
SKELETAL TISSUES
Examine the dried bone specimen which shows the compact bone. The osteon, also
called a Haversian system, is the basic unit of the compact bone structure. It has
concentrically arranged lamellae surrounding a centrally located Haversian canal. The
Haversian system consists of (1) a Haversian canal through which blood vessels pass,
(2) concentric lamellae, (3) lacunae, each one of which contains an osteocyte, (4)
canaliculi, which are small narrow spaces containing osteocyte processes, and (5) a
cement line, the thin dense, external bony layer that surrounds each osteon. Volkmann
canals run perpendicularly to and connect Haversian canals with each other. Interstitial
lamellae lie between the more distinct Haversian systems; these are the remnants of
earlier Haversian systems that have been partially resorbed during bone remodeling.
7Cs: CHRIST-CENTEREDNESS ∙ COMPETENCE ∙ CONSCIENCE ∙ CHARACTER ∙ COMMUNITY ∙ COMPASSION ∙ CULTURE
6
Use this slide for your output:
#9, Dried bone, Shaft of tibia, Human, Unstained
(https://histologylab.ctl.columbia.edu/slides/slide09/)
For Box #5 – Use slide no. 9 to label the structures described above.
REFERENCES
Braun DM. 2016. Human structure virtual microscopy. [accessed 2023 Feb 2].
https://vmicro.iusm.iu.edu/hs_vm/toc.htm.
Spitalnik PF. N.d. Histology laboratory manual. [accessed 2023 Feb 2].
https://histologylab.ctl.columbia.edu/HistologyLabManual.pdf
Braun DM. A560 Histology Slides. [accessed 2023 Feb 2].
http://medsci.indiana.edu/junqueira/virtual/junqueira.htm.
GUIDE QUESTIONS
Analyze the following guide questions and answer them after your labeled screenshots
of the specimen.
1) (LC1) Justify the reason why muscular tissue needs a rich source of blood. What
will happen if muscular tissues are avascular?
2) (LC2) Justify the importance of having enough supply of calcium and vitamin D in
your diet and how it can affect general bone health. What happens to the bones if
they don’t have enough sources of these
7Cs: CHRIST-CENTEREDNESS ∙ COMPETENCE ∙ CONSCIENCE ∙ CHARACTER ∙ COMMUNITY ∙ COMPASSION ∙ CULTURE
7
RUBRICS
Intervention
Advanced Proficient Developing
Competencies Required
Student demonstrates STRONG, IN- Student demonstrates SUFFICIENT and Student demonstrates LIMITED Student demonstrates LACK or
DEPTH, and CLEAR mastery CLEAR mastery evidenced by … mastery evidenced by… NO mastery evidenced by…
evidenced by…
Characterize and Drawings clearly depict Drawings depict MOST Drawings depict FEW Drawings DO NOT
differentiate ALL the structures the structures of the structures depict the structures
different kinds of described. described. described. described.
muscle tissues
according to their ALL structures found in MOST structures found FEW structures found
NO structure found
shape, size, and the tissues are labeled in the tissues are in the tissues are
in the tissues are
function CORRECTLY (i.e., NO labeled CORRECTLY labeled CORRECTLY
labeled
mistakes). (i.e., FEW [1-3] (i.e., MANY [4-6]
CORRECTLY (i.e.,
mistakes). mistakes).
ALL are mistakes).
Characteristics of Characteristics of Characteristics of
Characteristics of
histological specimens histological specimens histological
histological
are clearly are generally specimens are
specimens are not
incorporated and incorporated and partially incorporated
incorporated and
explained excellently. explained sufficiently. and explained.
explained
incompletely.
Characterize and Drawings clearly depict Drawings depict MOST Drawings depict FEW Drawings DO NOT
differentiate ALL the structures the structures of the structures depict the structures
different bone cells described. described. described. described.
according to their
size, shape, ALL structures found in MOST structures found FEW structures found NO structure found
structure, and the tissues are labeled in the tissues are in the tissues are in the tissues are
function CORRECTLY (i.e., NO labeled CORRECTLY labeled CORRECTLY labeled
mistakes). (i.e., FEW [1-3] (i.e., MANY [4-6] CORRECTLY (i.e.,
mistakes). mistakes). ALL are mistakes).
Characteristics of Characteristics of Characteristics of Characteristics of
histological specimens histological specimens histological histological
are clearly are generally specimens are specimens are not
incorporated and incorporated and partially incorporated incorporated and
explained excellently. explained sufficiently. and explained. explained
incompletely.
7Cs: CHRIST-CENTEREDNESS ∙ COMPETENCE ∙ CONSCIENCE ∙ CHARACTER ∙ COMMUNITY ∙ COMPASSION ∙ CULTURE
You might also like
- Lab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesPia CincoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On TissuesDocument5 pagesWorksheet On TissuesBryan AmoresNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Muscle Tissue17Document7 pagesModule 5. Muscle Tissue17Mark Jay PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Cuizon Lab Act 3Document18 pagesCuizon Lab Act 3Clarizza Joy J. CuizonNo ratings yet
- (Muscle Tissue) SHREYASI PDFDocument5 pages(Muscle Tissue) SHREYASI PDFShreyasi DongreNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 6 Muscle TissueDocument10 pagesExercise No. 6 Muscle TissueRyan Aaron Cruz ParNo ratings yet
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument29 pagesMuscular SystemJoanna Alecxa PagunsanNo ratings yet
- MAHANDocument9 pagesMAHANKANT JAMES D. MAHANNo ratings yet
- Answers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsDocument7 pagesAnswers UNIT 2 Lesson 2.2 Structures of Animal CellsKatznjammrNo ratings yet
- Pines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualDocument9 pagesPines City Colleges Medical Laboratory Science Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory ManualLynch Devin Kirtug-SalengNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec NotesDocument14 pagesAnaphy Lec NotesJohn Rick OrineNo ratings yet
- PCAT ChartsDocument9 pagesPCAT Chartsbrandonh131No ratings yet
- The Muscular TissueDocument23 pagesThe Muscular TissueMuhammad Salisu IliyasuNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Tissue Answers PDFDocument9 pagesLab 6 Tissue Answers PDFJameson Ephisson Ferguson Forson100% (3)
- The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]From EverandThe Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- The Tissue Level of Organization General ObjectivesDocument5 pagesThe Tissue Level of Organization General ObjectivesRjosheNo ratings yet
- ANS001 AnatomyDocument141 pagesANS001 AnatomyChristian Paul Palma BasigNo ratings yet
- MODUL Praktikum Anatomi Dan HistologiDocument20 pagesMODUL Praktikum Anatomi Dan HistologiandikaNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfDocument30 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TISSUE NOTESpdfYego EdwinNo ratings yet
- Class IX Practicals TISSUESDocument6 pagesClass IX Practicals TISSUESDhruv BhagatNo ratings yet
- Histology: The Study of TissuesDocument39 pagesHistology: The Study of TissuesEla Santos100% (1)
- CELL TISSUES AND INTEGUMEMNTARY SYS (September 30)Document14 pagesCELL TISSUES AND INTEGUMEMNTARY SYS (September 30)xuxi dul100% (1)
- NCLEX PNChartsDocument9 pagesNCLEX PNChartsTara Buantello60% (5)
- UNIT 3 (Muscular System)Document7 pagesUNIT 3 (Muscular System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Muscular and Nervous Tissue Handout 1Document17 pagesMuscular and Nervous Tissue Handout 1Wheteng YormaNo ratings yet
- Class9, Plant and Animal TissuesDocument4 pagesClass9, Plant and Animal Tissuessachdevashaurya08No ratings yet
- Bio 2100 Lab 3Document19 pagesBio 2100 Lab 3Kayseri PersaudNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4. AnswersDocument5 pagesExperiment 4. AnswersChristian Roy CNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Muscular SystemDocument5 pagesAssignment For Muscular SystemIrene Grace Z. RagasNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: Laboratory Exercise No. 6Document3 pagesMuscular System: Laboratory Exercise No. 6Joy borlagdanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Homeostasis, Feedback Mechanism, and TissuesDocument27 pages1 - Homeostasis, Feedback Mechanism, and TissuesrenatoamarNo ratings yet
- CCCC C CDocument16 pagesCCCC C CLennon Mars LamsinNo ratings yet
- Course 4Document9 pagesCourse 4bordinessrineNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lab.2Document8 pagesAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Electron Microscopic Cell StructureDocument26 pagesElectron Microscopic Cell StructureMaria ArshadNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedDocument5 pages09 Science Notes ch06 Tissues-UnlockedShekhar UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument5 pagesTissuesDarshilNo ratings yet
- JihijiojhiDocument5 pagesJihijiojhiGaurav Kumar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Hadba University CollegeتقريرDocument11 pagesHadba University Collegeتقريرtaha1995irqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: "Tissues"Document5 pagesChapter 6: "Tissues"Anil TripathiNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument6 pagesMuscular TissueChezkaMayC.OliverosNo ratings yet
- 1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissueDocument8 pages1-Epithelial Tissue 2-Connective Tissue 3-Muscle Tissue 4-Nervous Tissues Epithelial TissuekawiNo ratings yet
- PDF 20221214 190246 0000Document11 pagesPDF 20221214 190246 0000Hiba ZiziNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle TissueFady FadyNo ratings yet
- Histology Muscle and Nervous TissueDocument8 pagesHistology Muscle and Nervous Tissuejosh100% (1)
- Smooth Muscle Tissue Lines The Inside of Hollow Organs Like The Stomach, IntestinesDocument2 pagesSmooth Muscle Tissue Lines The Inside of Hollow Organs Like The Stomach, IntestinesMeanie ManszNo ratings yet
- MusclesssDocument4 pagesMusclesssLiam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 TissuesDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Tissuesh8631259No ratings yet
- Muscle and Nerve HistoPHysioDocument91 pagesMuscle and Nerve HistoPHysioashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Types of Tissues Muscular and Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesTypes of Tissues Muscular and Nervous TissueJonathan HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Document 11Document5 pagesDocument 11ARRWEN DOMINIQUE YZABELLE TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Ncert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter6Document5 pagesNcert Notes Class 9 Science Chapter6Mohammed AadilNo ratings yet
- Section SurnameFirstname Worksheet Week 4 Muscle PhysiologyDocument9 pagesSection SurnameFirstname Worksheet Week 4 Muscle PhysiologyZoe FormosoNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument12 pagesMuscular SystemChrisjohn Aster OsioNo ratings yet
- FRANCHESKA ALAINE DILLUPAC - Assignment 2Document2 pagesFRANCHESKA ALAINE DILLUPAC - Assignment 2Cheska DillupacNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - 6 - TG - Q2.docx Filename - UTF-8''SCIENCE 6 TG Q2Document103 pagesSCIENCE - 6 - TG - Q2.docx Filename - UTF-8''SCIENCE 6 TG Q2אנג' ליקהNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1Document26 pagesالمحاضرة الثانية تشريح اسنان م 1mfhrluvxxxNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument9 pagesMuscle Tissuesangelo beldaNo ratings yet
- Gene FlowDocument7 pagesGene FlowManikantan KNo ratings yet
- Dams Video Based TestDocument30 pagesDams Video Based TestPandey AyushNo ratings yet
- JNTUH MTech Biotech Syllabus (For Affiliated Colleges) 2010-2012Document40 pagesJNTUH MTech Biotech Syllabus (For Affiliated Colleges) 2010-2012Zahoorullah Shaik MohammedNo ratings yet
- Cavalli-Sforza - EugenicsDocument17 pagesCavalli-Sforza - EugenicsRace-RealistNo ratings yet
- Identification of Malassezia SpeciesDocument3 pagesIdentification of Malassezia SpeciesSJ IraaNo ratings yet
- BIO007.2 Lab Act 5 Answer SheetDocument3 pagesBIO007.2 Lab Act 5 Answer SheetSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- WBCS Optional Paper Syllabus 2020Document51 pagesWBCS Optional Paper Syllabus 2020FirozNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Study of C. (Morphocarabus) Zawadzkii SeriatissimusDocument1 pagePreliminary Study of C. (Morphocarabus) Zawadzkii SeriatissimusPrunar FlorinNo ratings yet
- Plant - Pathogen Interaction & Disease Development - ppt-2003Document91 pagesPlant - Pathogen Interaction & Disease Development - ppt-2003lordniklaus100% (6)
- Info On Blood DonationDocument5 pagesInfo On Blood DonationsuhaibqaisarNo ratings yet
- 13 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.3 Cell Specialization PowerPointDocument45 pages13 - IB Biology 2023 New Syllabus B2.3 Cell Specialization PowerPointmike bevnNo ratings yet
- Genetics & Genomics in Pediatric Primary CareDocument55 pagesGenetics & Genomics in Pediatric Primary CareAda AzotamNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer'S Disease: A Review PaperDocument7 pagesAlzheimer'S Disease: A Review PaperShruti MalaniNo ratings yet
- March Rqs COMPILED BY DR. STRANGEDocument89 pagesMarch Rqs COMPILED BY DR. STRANGEghassan100% (1)
- Premature Rupture of MembranesDocument3 pagesPremature Rupture of MembranesSheena Kunkel100% (2)
- Freebirth LeseprobeDocument37 pagesFreebirth LeseprobedidibutterflyNo ratings yet
- Exam18 ICSE Sample Paper Biology PDFDocument10 pagesExam18 ICSE Sample Paper Biology PDFShristi SinghNo ratings yet
- Tissue Engineering: Dr. Siti SunarintyasDocument33 pagesTissue Engineering: Dr. Siti SunarintyasNoni Tuhlifi Miadani100% (1)
- Fragile X Syndrome Case FileDocument3 pagesFragile X Syndrome Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- Biofeild TuningDocument3 pagesBiofeild TuningvastuNo ratings yet
- Nabl 102 PDFDocument74 pagesNabl 102 PDFRajat JainNo ratings yet
- TCS Book RevisedDocument40 pagesTCS Book RevisedkkNo ratings yet
- Absans, MiklonikDocument11 pagesAbsans, MiklonikrendyNo ratings yet
- Measurment of Health Edited PDFDocument347 pagesMeasurment of Health Edited PDFBekele AberaNo ratings yet
- Pathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersDocument5 pagesPathology Biochemical and Molecular Basis of Some Mendelian DisordersAmna Baig0% (1)
- AbstractDocument4 pagesAbstractDinindu SiriwardeneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Achalasia: Wai-Kit Lo and Hiroshi MashimoDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Achalasia: Wai-Kit Lo and Hiroshi MashimoInomy ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- AcneDocument13 pagesAcneapi-254664546No ratings yet
















![The Practical Guide to Drawing Anatomy: [Artist's Workbook]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/238627287/149x198/b1987107b7/1617237212?v=1)