Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TB Fact Sheet - TB STOP English
Uploaded by
maria halogOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TB Fact Sheet - TB STOP English
Uploaded by
maria halogCopyright:
Available Formats
Tuberculosis - TB
Rev. October 2017
Definition
TB is an infectious disease caused by TB germs. TB usually attacks the lungs and can affect any
part of the body. TB has been around for centuries.
Transmission
TB is spread from person to person through the air. TB is spread when someone sick with TB in
the lungs, coughs or sneezes. It is not highly contagious. Close, prolonged or regular contact with
someone who is sick with TB disease is needed to spread this disease.
Signs and Symptoms
TB infection:
Most people who breathe in TB germs are able to stop them from growing. Their immune system
traps the TB germs and keeps them inactive. This is called TB infection.
People with TB infection:
Cannot spread TB germs to others
Do not feel sick or have TB symptoms
Have a positive skin test (people with weak immune systems may have a negative skin test
even though they are infected with TB - speak with your doctor or nurse)
May develop active TB disease later in life
TB disease:
TB germs become active when the body's immune system cannot stop the germs from growing.
The active TB germs begin to grow and cause damage to the body. This is called TB disease. TB
disease of the lungs and throat can be spread to others.
People with TB disease can feel sick with:
Fever / chills / night sweats
Coughing (more than 3 weeks)
Tiredness
Loss of appetite / unexplained weight loss
If the TB disease is in another part of the body, the symptoms will depend on where the TB is
growing, for example swollen lymph node or joint pain.
Tests
Screening for TB infection is done by a skin test. A positive skin test means a person has the TB
germ in their body. A physical examination, chest x-ray and sputum (mucous coughed up from the
lungs) are done to check for TB disease.
Treatment
People with TB infection may benefit from medicine to prevent TB disease. The medicine will
keep the germ inactive and will stop the bacteria from growing in your body.
People with TB disease must take medicine to cure the disease. The doctor will decide how long
the person needs to take the medicine. All TB medicine is free.
TB is preventable, treatable and curable.
Stop TB
TB is preventable, treatable and curable!
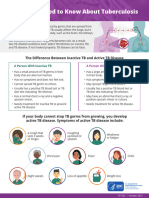
Tuberculosis (TB) is spread when a person who is sick with TB disease
coughs or sneezes the germs into the air. Anyone can get TB.
If you breathe in the TB germs, the germs go to your lungs.
Sometimes the germs go to other parts of your body.
TB Infection TB Disease
If your body is strong it can stop the TB germs from If your body is weak, it may not stop the TB germs
growing. from growing. Your body can be weak if you are sick
with another disease, under stress or just getting older.
The germs are in your body, but do not grow and do The germs keep growing and make you sick. This is
not make you sick. This is called TB infection. called TB disease. You can spread TB to others.
• You cannot spread TB to others. You can feel sick with:
• You will not feel sick. • Fever
• You can have a positive skin test. • Cough (more than 3 weeks)
• Your chest x-ray might look normal. • Feel tired
• Loss of appetite
• Weight loss
• Night sweats
• Chest pain
You can take medicine so that the germs in your body You must take medicine to treat the TB. Your doctor
do not grow and make you sick with TB disease. will decide how long you need to take the medicine.
TB medicine is free! TB medicine is free!
PH0903GB083 (English) (Rev. Oct. 2013)
You might also like
- Tuberculosis (TB) Presentation PDFDocument12 pagesTuberculosis (TB) Presentation PDFUday GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) PresentationDocument13 pagesTuberculosis (TB) PresentationAbdullahi Mahmud LafiamiNo ratings yet
- TB Fact Sheet - EnglishDocument2 pagesTB Fact Sheet - EnglishDescargar scribdNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know About Tuberculosis: The Difference Between Inactive TB and Active TB DiseaseDocument2 pagesWhat You Need To Know About Tuberculosis: The Difference Between Inactive TB and Active TB DiseaseDescargar scribdNo ratings yet
- FRTHDocument21 pagesFRTHGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- Basic TB FactsDocument75 pagesBasic TB FactsFebrian Ivan PePeNo ratings yet
- What Is Tuberculosi: What Is The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and Active Disease?Document2 pagesWhat Is Tuberculosi: What Is The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and Active Disease?Koyel Sreyashi BasuNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument4 pagesTuberculosisKate SantosNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (The Disease)Document24 pagesTuberculosis (The Disease)DiLahNo ratings yet
- Get the Facts About Tuberculosis DiseaseDocument16 pagesGet the Facts About Tuberculosis Diseasedjprh tbdotsNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Taking ControlDocument9 pagesTuberculosis Taking Controlrkbhuvaneshwari32No ratings yet
- TB PresentationDocument13 pagesTB PresentationHafid Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis in The Community Flipbook ENGLISHDocument70 pagesTuberculosis in The Community Flipbook ENGLISHDANICA BONBONNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Get The-Facts PDFDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Get The-Facts PDFdjprh tbdotsNo ratings yet
- Clinical Aspects of TBDocument2 pagesClinical Aspects of TBRaja EllysyaNo ratings yet
- Stop TBDocument1 pageStop TBAnonymous nbU88FeNo ratings yet
- TB-455I May Be Infected W TBGermDocument2 pagesTB-455I May Be Infected W TBGermRey-Anne Camille Sarmiento RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Brochure 1Document4 pagesBrochure 1api-243214263No ratings yet
- MedSurg 063510Document10 pagesMedSurg 063510Saviana TiekuNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis / TBDocument11 pagesTuberculosis / TBSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know About Tuberculosis (TB)Document17 pagesWhat You Need To Know About Tuberculosis (TB)feby_valNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: What Is It and How Do We Keep Healthy?: A Presentation For Pacific Island Schools and CommunitiesDocument17 pagesTuberculosis: What Is It and How Do We Keep Healthy?: A Presentation For Pacific Island Schools and CommunitiesKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About TuberculosisDocument1 pageEverything You Need to Know About TuberculosisMariaClarizaNo ratings yet
- Staying Healthy with TB TreatmentDocument20 pagesStaying Healthy with TB Treatmentpingwei85No ratings yet
- IGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishDocument1 pageIGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishAdhimasRadityaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis TBDocument5 pagesTuberculosis TBHusna AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Brochure TuberkulosisDocument2 pagesBrochure TuberkulosisWulan SuwardiNo ratings yet
- TB Booklet - May 2015Document8 pagesTB Booklet - May 2015fatimaNo ratings yet
- Group Case Study - Pulmonary TBDocument8 pagesGroup Case Study - Pulmonary TBCj NiñalNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA) : Minnesota Department of HealthDocument1 pageTuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA) : Minnesota Department of HealthYeon Ae NaritaNo ratings yet
- StopTB Poster 508Document1 pageStopTB Poster 508Nicole Sales DiazNo ratings yet
- Tuber Clos IsDocument9 pagesTuber Clos IsAmit kumarNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) Spreads Through The Air From One Person To AnotherDocument1 pageTuberculosis (TB) Spreads Through The Air From One Person To AnotherMark Philipp AbanNo ratings yet
- TBDocument19 pagesTBJohn Kevin De VeraNo ratings yet
- 1A Silvestre, Ped - Tuberculosis ModuleDocument8 pages1A Silvestre, Ped - Tuberculosis ModulePed SilvestreNo ratings yet
- TB Prevention: What Is It and How to Stay HealthyDocument17 pagesTB Prevention: What Is It and How to Stay HealthyKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About TBDocument18 pagesEverything You Need to Know About TBmedeviNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Types & TreatmentDocument1 pageTuberculosis Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Types & Treatmentmark rosarioNo ratings yet
- MED 251 Block 9 PHL Brochure and TarpDocument6 pagesMED 251 Block 9 PHL Brochure and TarpFerdinand Sta Ana Jr.No ratings yet
- Staying on Track with TB TreatmentDocument24 pagesStaying on Track with TB TreatmentbeartothebooNo ratings yet
- Modul PMO TBDocument24 pagesModul PMO TBMuhammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Inflammatory Bowel Disease for Patients and their Supporters: Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's diseaseFrom EverandFast Facts: Inflammatory Bowel Disease for Patients and their Supporters: Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's diseaseNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know About Tuberculosis InfectionDocument16 pagesWhat You Need To Know About Tuberculosis Infectionayesha SNo ratings yet
- FRSTDocument12 pagesFRSTGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- Cours tuberculosediabetEBOAHIVDocument18 pagesCours tuberculosediabetEBOAHIVhamedpourlesmeufsNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis/General InformationDocument2 pagesTuberculosis/General InformationKatherine McNennyNo ratings yet
- FAQs on TB Causes, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDocument4 pagesFAQs on TB Causes, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentMystery ShopperNo ratings yet
- PP4 Tuberculosis 1453878076Document43 pagesPP4 Tuberculosis 1453878076khijogpNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Health Education Quarter 3 Disease Prevention and ControlDocument25 pagesGrade 8 Health Education Quarter 3 Disease Prevention and ControlRandom GuyNo ratings yet
- Viruses - Bacteria - Health 5th Sep, 2023Document27 pagesViruses - Bacteria - Health 5th Sep, 2023nazNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument2 pagesTuberculosisamr amerNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis Health TeachingDocument3 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis Health Teachinggenellemaarte100% (1)
- Case Study On TBDocument3 pagesCase Study On TBJamil Lorca75% (8)
- TUBERCULOSISDocument4 pagesTUBERCULOSISamirNo ratings yet
- Power Point 11Document15 pagesPower Point 11zekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Fact SheetDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Fact SheetDavid A. GilesNo ratings yet
- 10 Harmful Myths That Prevent Us From Being Healthy & Fully Alive!From Everand10 Harmful Myths That Prevent Us From Being Healthy & Fully Alive!No ratings yet
- Silent Thyroiditis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSilent Thyroiditis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Vaccines Explained (Somali-English): Language Lizard Bilingual Explore SeriesFrom EverandVaccines Explained (Somali-English): Language Lizard Bilingual Explore SeriesNo ratings yet
- What Is Bronchitis: Understanding The Bronchitis Symptoms And Curing ItFrom EverandWhat Is Bronchitis: Understanding The Bronchitis Symptoms And Curing ItNo ratings yet
- OBSTETRIC FORMDocument4 pagesOBSTETRIC FORMKhylamarie VillalunaNo ratings yet
- (Leon Gordis) Epidemiology (4th Edition)Document26 pages(Leon Gordis) Epidemiology (4th Edition)Anna Dixon100% (1)
- Parkinsonism (巴金森氏症) and other movement disordersDocument29 pagesParkinsonism (巴金森氏症) and other movement disordersShing Ming TangNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway For Family Wellness Promotion in Elderly: Junayyah A. Sarip Jaeron Den D. TopinioDocument36 pagesClinical Pathway For Family Wellness Promotion in Elderly: Junayyah A. Sarip Jaeron Den D. TopinioJunayyah Abdullah SaripNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Overview of Health Information SystemsDocument21 pagesModule 5: Overview of Health Information SystemsCookie MonsterNo ratings yet
- Mental Health 1CC3 Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesMental Health 1CC3 Discussion QuestionsSim100% (1)
- Femina July 2020 DDocument26 pagesFemina July 2020 DOlivia Limson DiasNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Disease and ReikiDocument5 pagesParkinson's Disease and ReikiSteve FlahertyNo ratings yet
- TM1-Environmental EpidemiologyDocument17 pagesTM1-Environmental EpidemiologyFarahAzzahraAnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Proceeding Book 28th Jakarta Diabates Meeting 2019Document19 pagesProceeding Book 28th Jakarta Diabates Meeting 2019David DwiputeraNo ratings yet
- Maigp 16 BroDocument16 pagesMaigp 16 Broapi-249304998No ratings yet
- Sam's Letter from HolidayDocument15 pagesSam's Letter from HolidaykamtoNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide to Data VisualizationDocument119 pagesPractical Guide to Data VisualizationAnonymous qeolzNIFdf100% (1)
- Running Head: AGING RESEARCH 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: AGING RESEARCH 1david omondiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Community and Environmental HealthDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Community and Environmental HealthSunday MochicanaNo ratings yet
- Vision, Mission and Planning CycleDocument215 pagesVision, Mission and Planning CyclePalwasha Khan100% (4)
- BotnyDocument62 pagesBotnyRangu Dodmane RamNo ratings yet
- The Family Illness TrajectoryDocument3 pagesThe Family Illness TrajectoryAlya Putri Khairani80% (5)
- Schizotypal Personality DisorderDocument5 pagesSchizotypal Personality DisorderFeraNovianti100% (1)
- An Essay On The Shaking Palsy by Parkinson, JamesDocument27 pagesAn Essay On The Shaking Palsy by Parkinson, JamesGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- Use of Herbal Medicines and Aphrodisiac Substances Among Women in Kano State, NigeriaDocument10 pagesUse of Herbal Medicines and Aphrodisiac Substances Among Women in Kano State, NigeriaIOSRjournal100% (1)
- Unit 1 (Introduction To Health Assessment Concepts) - ConverteDocument28 pagesUnit 1 (Introduction To Health Assessment Concepts) - ConverteUmme HabibaNo ratings yet
- Herd Health ManagmentDocument10 pagesHerd Health ManagmentAjasrNo ratings yet
- Ey Making Quality Cancer Care More Accessible and Affordable in IndiaDocument160 pagesEy Making Quality Cancer Care More Accessible and Affordable in Indiaabhiyan0008494No ratings yet
- English Text DiseasesDocument1 pageEnglish Text DiseasesJoao Pedro MendesNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Complications of HypoparathyroidismDocument12 pagesEpidemiology and Complications of HypoparathyroidismErika AvilaNo ratings yet
- TAX - SSS BenefitsDocument10 pagesTAX - SSS BenefitsGinaNo ratings yet
- THC 123 - Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and SanitationDocument94 pagesTHC 123 - Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Security, and SanitationJanry Bantiles90% (10)
- Adolescent Health UpdatedDocument18 pagesAdolescent Health Updatedanon_588049728No ratings yet
- Psychosomatic 1Document15 pagesPsychosomatic 1Jaiprakash AgrawalNo ratings yet