Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What You Need To Know About Tuberculosis: The Difference Between Inactive TB and Active TB Disease
Uploaded by
Descargar scribdOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What You Need To Know About Tuberculosis: The Difference Between Inactive TB and Active TB Disease
Uploaded by
Descargar scribdCopyright:
Available Formats
What You Need to Know About Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a disease caused by germs that are spread from
person to person through the air. TB usually affects the lungs, but it
can also affect other parts of the body, such as the brain, the kidneys,
or the spine.
Not everyone infected with TB germs becomes sick. As a result,
two TB-related conditions exist: latent TB infection (or inactive TB)
and TB disease. If not treated properly, TB disease can be fatal.
The Difference Between Inactive TB and Active TB Disease
A Person With Inactive TB A Person With Active TB Disease
• Has a small amount of TB germs in their • Has a large amount of active TB germs
body that are alive but inactive. in their body.
• Has no symptoms and does not feel sick. • Has symptoms and feels sick.
• Cannot spread TB germs to others. • May spread TB germs to others.
• Usually has a positive TB blood test or TB • Usually has a positive TB blood test or
skin test indicating TB infection. TB skin test indicating TB infection.
• Has a normal chest x-ray and a negative • May have an abnormal chest x-ray, or
sputum smear. positive sputum smear or culture.
• Needs treatment for inactive TB to prevent • Needs treatment for active TB disease.
active TB disease.
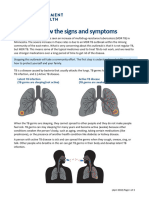
If your body cannot stop TB germs from growing, you develop
active TB disease. Symptoms of active TB disease include:
A cough that Coughing
Weakness
lasts 3 weeks up blood or
or fatigue
or longer sputum
Chest pain Fever Chills
Night sweats Loss of appetite Weight loss
U.S. Department of
Health and Human Services
Centers for Disease
Control and Prevention
301332 | October 2023
Testing for TB
Getting tested and treated for TB can protect yourself, your family and friends,
and your community. There are two types of tests for TB infection: the TB blood test
and the TB skin test.
+ A Positive Test For TB Infection - A Negative Test For TB Infection
You have TB germs in your body. Your A negative test means you likely do not have
doctor will do other tests to determine if you inactive TB or active TB disease.
have inactive TB or active TB disease. These
Your doctor may do more tests if:
tests may include a chest x-ray, and a test of
the sputum you cough up. • You have symptoms of active TB disease,
like coughing, chest pain, fever, weight
loss, or tiredness.
• You have HIV infection.
• Your exposure to TB germs was recent.
Tell Your Doctor if You Received a TB Vaccine
TB blood tests are the preferred test for people who have received the bacille
Calmette-Guérin (BCG) TB vaccine. Unlike the TB skin test, TB blood tests are not
affected by BCG vaccination.
Many people born outside of the United States have received the BCG TB vaccine.
BCG vaccination does not completely prevent people from getting TB. A positive reaction BCG
to a TB skin test may be due to the BCG vaccine itself or due to infection with TB germs.
TB Can Be Treated
TB germs can live in your body for years without
causing symptoms. If you have inactive TB,
treating it is the best way to protect you from
getting sick with active TB disease.
If you have been diagnosed with active TB disease,
you can be treated with medicine. You will need to
take and finish all of your TB medicine as directed
by your doctor or nurse. This is to help you feel
better and prevent other people from getting sick.
The best way to remember to take your medicines for active TB disease is by receiving directly observed
therapy (DOT). Through DOT, you will meet with a health care worker every day or several times a week
either in-person or virtually. The health care worker will make sure that the TB medicines are working as
they should.
You might also like
- Tuberculosis (TB) Presentation PDFDocument12 pagesTuberculosis (TB) Presentation PDFUday GuptaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) PresentationDocument13 pagesTuberculosis (TB) PresentationAbdullahi Mahmud LafiamiNo ratings yet
- TB Fact Sheet - EnglishDocument2 pagesTB Fact Sheet - EnglishDescargar scribdNo ratings yet
- IGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishDocument1 pageIGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishAdhimasRadityaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Get The-Facts PDFDocument2 pagesTuberculosis Get The-Facts PDFdjprh tbdotsNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA) : Minnesota Department of HealthDocument1 pageTuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA) : Minnesota Department of HealthYeon Ae NaritaNo ratings yet
- TB Fact Sheet - TB STOP EnglishDocument2 pagesTB Fact Sheet - TB STOP Englishmaria halogNo ratings yet
- TB Booklet - May 2015Document8 pagesTB Booklet - May 2015fatimaNo ratings yet
- TB-455I May Be Infected W TBGermDocument2 pagesTB-455I May Be Infected W TBGermRey-Anne Camille Sarmiento RodriguezNo ratings yet
- FRTHDocument21 pagesFRTHGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Taking ControlDocument9 pagesTuberculosis Taking Controlrkbhuvaneshwari32No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) Spreads Through The Air From One Person To AnotherDocument1 pageTuberculosis (TB) Spreads Through The Air From One Person To AnotherMark Philipp AbanNo ratings yet
- StopTB Poster 508Document1 pageStopTB Poster 508Nicole Sales DiazNo ratings yet
- What Is Tuberculosi: What Is The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and Active Disease?Document2 pagesWhat Is Tuberculosi: What Is The Difference Between Latent TB Infection and Active Disease?Koyel Sreyashi BasuNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis/General InformationDocument2 pagesTuberculosis/General InformationKatherine McNennyNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis / TBDocument11 pagesTuberculosis / TBSherree HayesNo ratings yet
- Basic TB FactsDocument75 pagesBasic TB FactsFebrian Ivan PePeNo ratings yet
- Get the Facts About Tuberculosis DiseaseDocument16 pagesGet the Facts About Tuberculosis Diseasedjprh tbdotsNo ratings yet
- FFTHDocument13 pagesFFTHGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument4 pagesTuberculosisKate SantosNo ratings yet
- What Are The Symptoms of TB?Document5 pagesWhat Are The Symptoms of TB?Reden Calubayan OblenaNo ratings yet
- What You Need To Know About Tuberculosis InfectionDocument16 pagesWhat You Need To Know About Tuberculosis Infectionayesha SNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Inflammatory Bowel Disease for Patients and their Supporters: Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's diseaseFrom EverandFast Facts: Inflammatory Bowel Disease for Patients and their Supporters: Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's diseaseNo ratings yet
- TB PamphletDocument2 pagesTB PamphletMuhammad Kamal0% (1)
- Nonhealthcare EmployersDocument2 pagesNonhealthcare EmployersJanani SundarNo ratings yet
- Biology Project: Made By:-Swasti Tyagi, Xii-A, 25Document18 pagesBiology Project: Made By:-Swasti Tyagi, Xii-A, 25Swasti TyagiNo ratings yet
- What you need to know about the TB skin testDocument8 pagesWhat you need to know about the TB skin testdjprh tbdotsNo ratings yet
- Staying Healthy with TB TreatmentDocument20 pagesStaying Healthy with TB Treatmentpingwei85No ratings yet
- What Is Tuberculosis?Document2 pagesWhat Is Tuberculosis?Shiela Fe PalenNo ratings yet
- TuberculosisDocument2 pagesTuberculosisamr amerNo ratings yet
- 1A Silvestre, Ped - Tuberculosis ModuleDocument8 pages1A Silvestre, Ped - Tuberculosis ModulePed SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (The Disease)Document24 pagesTuberculosis (The Disease)DiLahNo ratings yet
- FRSTDocument12 pagesFRSTGuezil Joy DelfinNo ratings yet
- What Is Tuberculosis (TB) ?: Patient EducationDocument2 pagesWhat Is Tuberculosis (TB) ?: Patient EducationBiniamNo ratings yet
- Testing For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Document2 pagesTesting For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Testing For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Document2 pagesTesting For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Aluh L DiniNo ratings yet
- PP4 Tuberculosis 1453878076Document43 pagesPP4 Tuberculosis 1453878076khijogpNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis TBDocument5 pagesTuberculosis TBHusna AmaliaNo ratings yet
- FAQ About Summit County TB InvestigationDocument5 pagesFAQ About Summit County TB InvestigationWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- Staying on Track with TB TreatmentDocument24 pagesStaying on Track with TB TreatmentbeartothebooNo ratings yet
- Leaflet 1Document2 pagesLeaflet 1nimasNo ratings yet
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Heal Your Gut Naturally in 90 Days!From EverandIrritable Bowel Syndrome: Heal Your Gut Naturally in 90 Days!No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Types & TreatmentDocument1 pageTuberculosis Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Types & Treatmentmark rosarioNo ratings yet
- TB DiagnosisDocument3 pagesTB Diagnosisمصطفى سهيلNo ratings yet
- TB PresentationDocument13 pagesTB PresentationHafid Iqbal MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA)Document4 pagesTuberculosis (TB) Blood Test (IGRA)Denada Florencia LeonaNo ratings yet
- Modul PMO TBDocument24 pagesModul PMO TBMuhammad RizkyNo ratings yet
- Brochure TuberkulosisDocument2 pagesBrochure TuberkulosisWulan SuwardiNo ratings yet
- Brochure 1Document4 pagesBrochure 1api-243214263No ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES ON TUBERCULOSIS (TBDocument6 pagesLECTURE NOTES ON TUBERCULOSIS (TBDENNIS N. MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- FAQs on TB Causes, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentDocument4 pagesFAQs on TB Causes, Symptoms, Tests & TreatmentMystery ShopperNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Tests and DiagnosisDocument3 pagesTuberculosis: Tests and DiagnosisArnie PengNo ratings yet
- MED 251 Block 9 PHL Brochure and TarpDocument6 pagesMED 251 Block 9 PHL Brochure and TarpFerdinand Sta Ana Jr.No ratings yet
- Understanding Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Causative Agent, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Causative Agent, Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDivya TiwariNo ratings yet
- TB Dots Treatment in The PhillippinesDocument8 pagesTB Dots Treatment in The Phillippinestmjrsvz84mNo ratings yet
- Viruses - Bacteria - Health 5th Sep, 2023Document27 pagesViruses - Bacteria - Health 5th Sep, 2023nazNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: What Is It and How Do We Keep Healthy?: A Presentation For Pacific Island Schools and CommunitiesDocument17 pagesTuberculosis: What Is It and How Do We Keep Healthy?: A Presentation For Pacific Island Schools and CommunitiesKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: by Rohma XI A2, Roll No.-2Document15 pagesTuberculosis: by Rohma XI A2, Roll No.-2fur ballNo ratings yet
- Case Study On TBDocument3 pagesCase Study On TBJamil Lorca75% (8)
- The Complete Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Symptoms, Risks, Prevention, Medicines & Home RemediesFrom EverandThe Complete Guide to Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Symptoms, Risks, Prevention, Medicines & Home RemediesNo ratings yet
- SignsDocument2 pagesSignsDescargar scribdNo ratings yet
- EngDocument68 pagesEngkannalijayaNo ratings yet
- Civ 609Document17 pagesCiv 609Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- MDR-RR TB Factsheet 2018 Apr2019Document2 pagesMDR-RR TB Factsheet 2018 Apr2019Farhan Rizqy RNo ratings yet
- Revenge 2Document1 pageRevenge 2Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Revenge 2Document1 pageRevenge 2Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document40 pagesModule 1Rohan RalliNo ratings yet
- Da Curated Archive 2021-11-02Document15 pagesDa Curated Archive 2021-11-02João Vitor Ferrari Campassi0% (1)
- Centronuclear Myopathy Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument2 pagesCentronuclear Myopathy Guide: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDescargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Goblin Kingdom Vol 3Document532 pagesGoblin Kingdom Vol 3Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- March 21 2018: Da Archive AnnexDocument65 pagesMarch 21 2018: Da Archive AnnexDescargar scribd0% (1)
- Catalog en 28-10-2022Document932 pagesCatalog en 28-10-2022Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Da Archive 2022-02-01Document115 pagesDa Archive 2022-02-01bob bisbetico bislacco100% (2)
- Zonal RegulationsDocument146 pagesZonal RegulationsBasavarajaCM50% (2)
- Measuring: TranslateDocument5 pagesMeasuring: Translatechelsea romaidaNo ratings yet
- Joycie 4-7Document2 pagesJoycie 4-7Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesDocument35 pagesUnit 1 The Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental StudiesNishant GawadNo ratings yet
- Runningrate Asiaking Juli'23Document32 pagesRunningrate Asiaking Juli'23cecilia ivadaaNo ratings yet
- Chennai Public School: CH 3 Coordinate Geometry Multiple AssessmentDocument3 pagesChennai Public School: CH 3 Coordinate Geometry Multiple Assessment11F10 RUCHITA MAARANNo ratings yet
- SR-21 SniperDocument6 pagesSR-21 SniperBaba HeadquaterNo ratings yet
- Realtime Physics: Active Learning Labs Transforming The Introductory LaboratoryDocument14 pagesRealtime Physics: Active Learning Labs Transforming The Introductory LaboratorysaleemNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Y9aDocument9 pagesComprehension Y9angwenping5No ratings yet
- Astm C1396 C1396M-17Document8 pagesAstm C1396 C1396M-17Stefano CamillucciNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document19 pagesLecture 10Sara AlwehrNo ratings yet
- The Macadamia Industry in MalawiDocument77 pagesThe Macadamia Industry in Malawiwarlord_ckNo ratings yet
- Filtro MFV 27Document2 pagesFiltro MFV 27Diana PinosNo ratings yet
- Using Coffee Grounds as FertilizerDocument18 pagesUsing Coffee Grounds as FertilizerKyle BARRIOSNo ratings yet
- Katalog Single Split Packaged AC 2015-2016 PanasonicDocument32 pagesKatalog Single Split Packaged AC 2015-2016 Panasonicdoris0% (1)
- ANALYSIS OF TRANSFORMER OIL TESTING USING GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY METHODDocument9 pagesANALYSIS OF TRANSFORMER OIL TESTING USING GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY METHODmuhammad yaminNo ratings yet
- (MT 6322 - MYCO VIRO LAB) Unit 7 Laboratory Diagnosis For Negative-Sense (-) ssRNA VirusesDocument15 pages(MT 6322 - MYCO VIRO LAB) Unit 7 Laboratory Diagnosis For Negative-Sense (-) ssRNA VirusesAbbas MaghazehiNo ratings yet
- Meng 2nd Year Death Anniversary MassDocument6 pagesMeng 2nd Year Death Anniversary Massjoy in the spirit of the lordNo ratings yet
- Is 1726 1991Document17 pagesIs 1726 1991RaykochiNo ratings yet
- Dolphin Facts For Kids Ilovepdf CompressedDocument1 pageDolphin Facts For Kids Ilovepdf CompressedtechboostmrktgNo ratings yet
- A 1000 Calorie Diet Plan For Weight Loss - DMooseDocument15 pagesA 1000 Calorie Diet Plan For Weight Loss - DMoosekwasnyciakristinaNo ratings yet
- India's Power Industry History and FutureDocument11 pagesIndia's Power Industry History and FutureMinesh Chand MeenaNo ratings yet
- Sizing PSV Broady Valvitalia-R4Document18 pagesSizing PSV Broady Valvitalia-R4Anggun RushNo ratings yet
- Fine ArtsDocument12 pagesFine Artsatul prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Tle 9 DLL Q3 W1 1Document3 pagesTle 9 DLL Q3 W1 1Joanne GodezanoNo ratings yet
- 18.national Forestry Act 1984Document92 pages18.national Forestry Act 1984Sudhir A K KumarenNo ratings yet
- Press 2017 Fagioli enDocument2 pagesPress 2017 Fagioli enÁlvaro Rodríguez BNo ratings yet
- Nike Run Club 5K Training PlanDocument25 pagesNike Run Club 5K Training PlanSalvador0% (1)
- F 25 Sensor Family Miniature Sensors for Precision DetectionDocument34 pagesF 25 Sensor Family Miniature Sensors for Precision DetectionAlex GarduñoNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995Document11 pagesThe Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995laith AtekNo ratings yet