Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Georgia Ragmac0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesThe document describes 11 different endocrine glands and their characteristics and functions. The hypothalamus controls many bodily processes including mood, hunger, and sleep patterns. The pituitary gland regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction through the hormones it produces. The pineal gland conveys information about light and dark cycles by producing melatonin.
Original Description:
Original Title
endocrine-system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes 11 different endocrine glands and their characteristics and functions. The hypothalamus controls many bodily processes including mood, hunger, and sleep patterns. The pituitary gland regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction through the hormones it produces. The pineal gland conveys information about light and dark cycles by producing melatonin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views3 pagesEndocrine System
Endocrine System
Uploaded by
Georgia RagmacThe document describes 11 different endocrine glands and their characteristics and functions. The hypothalamus controls many bodily processes including mood, hunger, and sleep patterns. The pituitary gland regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction through the hormones it produces. The pineal gland conveys information about light and dark cycles by producing melatonin.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Gland Characteristics Functions
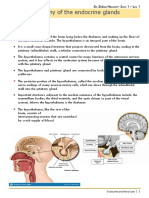
1.Hypothalamus -a bilateral collection of -controls many
nuclei divided into three processes in our body,
zones surrounding the including our mood,
third ventricle and the hunger and thirst, sleep
mammillary bodies. patterns and sexual
-about the size of an function.
almond, is located below
the thalamus and above
your pituitary gland. It
sits directly above the
brainstem at the base of
your brain.
2.Pituitary Gland -is a small, pea-sized -It regulates growth,
gland located at the base metabolism, and
of your brain below your reproduction through
hypothalamus. the hormones that it
-It’s located behind the produces.
nose at the base of the -The main function of
brain. your pituitary gland is to
produce and release
several hormones that
help carry out important
bodily functions.
3.Pineal Gland -it is solid, pine cone -to receive information
shaped, of red-grey color, about the state of the
approximately 5–9 mm in light-dark cycle from the
length and 1–5 mm in environment and convey
width. It weighs 100–180 this information by the
mg. production and
-attached to the secretion of the
posterior part of the 3rd hormone melatonin.
ventricle, between the
posterior commissure
and the dorsal habenular
commissure
4.Thyroid Gland -about 2-inches long and - control the speed of
lies in front of your your metabolism
throat below the (metabolic rate), which
prominence of thyroid is the process of how
cartilage sometimes your body transforms
called the Adam’s apple. the food you consume
-The thyroid gland is a into energy.
ductless endocrine gland
situated in the
anterior/front portion of
the neck. It roughly
resembles the shape of a
butterfly
5.Parathyroid -are two pairs of small, -plays a role in
oval-shaped glands. They regulating the body’s
are located next to the blood level of calcium
two thyroid gland lobes and phosphorus.
in the neck. Each gland is
usually about the size of
a pea.
6.Adrenal -also known as -produce hormones that
suprarenal glands, are help regulate your
small, triangular-shaped metabolism, immune
glands located on top of system, blood pressure,
both kidneys. response to stress and
-There are two adrenal other essential functions
glands, one on top of
each kidney. The outer
part of each gland is the
adrenal cortex and the
inner part is the adrenal
medulla.
7.Thymus - a soft gland with two -responsible for
lobes. producing and maturing
-the location of your lymphocytes, or immune
thymus gland is in your cells.
upper chest behind your
breastbone (sternum). It
sits between your lungs
in a part of your chest
called the mediastinum.
Your thymus is just in
front of and above your
heart.
8.Pancreas -is an abdominal organ -creates natural juices
located behind the called pancreatic
stomach and surrounded enzymes to break down
by spleen, liver and small foods.
intestine. - It is a vital part of the
-The pancreas is located digestive system and is
behind the stomach in responsible for
the upper left abdomen regulating blood sugar
-located across the back levels. The pancreas
of the belly, behind the secretes digestive
stomach. The right side enzymes such as
of the organ—called the amylase, proteases and
head—is the widest part lipase into the
of the organ and lies in duodenum.
the curve of the
duodenum, the first
division of the small
intestine.
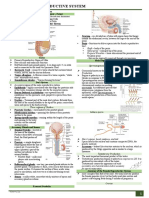
9.Ovary -solid, ovoid structure -These hormones play
about the size and shape an important role in
of an almond, about 3.5 female traits, such as
cm in length, 2 cm wide, breast development,
and 1 cm thick. body shape, and body
-The ovaries are located hair. They are also
in shallow depressions, involved in the
called ovarian fossae, menstrual cycle, fertility,
one on each side of the and pregnancy.
uterus, in the lateral
walls of the pelvic cavity.
10.Testes -are two oval-shaped -responsible for making
organs in the male sperm and are also
reproductive system. involved in producing a
-contain very fine-coiled hormone called
tubes, called testosterone.
seminiferous tubules and -to produce sperm and
are covered with tough to produce hormones,
membrane, tunica particularly
albuginea. testosterone.
11.Placenta(during -disklike in shape, 3 cm -provides oxygen and
pregnancy) thick, and about 20 cm in nutrients to a growing
diameter. A typical baby. It also removes
placenta weighs about waste products from the
500 g. The fetal side of baby’s blood.
the placenta is shiny -The placenta produces
because of the apposed oestrogen, which helps
amniotic membrane. The to soften tissues and
maternal side of the make them more
placenta is dull and is flexible.
subdivided into as many
as 35 lobes.
-The placenta attaches to
the wall of the uterus,
and the baby’s umbilical
cord arises from it.
You might also like
- A Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionFrom EverandA Simple Guide to The Pineal Gland (The Third Eye) And Its FunctionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyNeil Ceniza Saile100% (1)
- Cranial NervesDocument16 pagesCranial Nervesapi-302547403100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerNathaniel FerrerNo ratings yet
- How To Use Acupressure For FertilityDocument15 pagesHow To Use Acupressure For Fertilitysale18100% (1)
- Maternal/Ob NotesDocument38 pagesMaternal/Ob Notesraech_akel100% (1)
- FR5224 - Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology Workbook v4Document54 pagesFR5224 - Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology Workbook v4mark100% (4)
- Embryology of Respiratory System NotesDocument3 pagesEmbryology of Respiratory System NotesJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument35 pagesMonoclonal Antibodiespreetylyall100% (5)
- Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument152 pagesDysfunctional Uterine BleedingNavani Tharan100% (2)
- Ob Penta NotesDocument56 pagesOb Penta Notesstuffednurse100% (1)
- A Simple Guide To The Pineal Gland, And The All Seeing Third EyeFrom EverandA Simple Guide To The Pineal Gland, And The All Seeing Third EyeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Obstetrical NursingDocument36 pagesObstetrical NursingCzarina AsisNo ratings yet
- Maternal NewDocument30 pagesMaternal NewKhristine Rose Sanchez CaloNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland, Function, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandThyroid Gland, Function, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Maternal & Child Care Nursing ReviewDocument37 pagesMaternal & Child Care Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos98% (130)
- Maternity Nursing!Document138 pagesMaternity Nursing!cheenapberber100% (2)
- Pediatric Neurology - Lawson Peter N. (SRG)Document200 pagesPediatric Neurology - Lawson Peter N. (SRG)Hriday DeNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Maternal/Ob Notes: "Above Success There Is Excellence Beyond Impossible. " Skei Nursing Review & EnhancementDocument53 pagesMaternal/Ob Notes: "Above Success There Is Excellence Beyond Impossible. " Skei Nursing Review & EnhancementAbdullah, Atteya100% (1)
- Chapter Test in Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter Test in Circulatory SystemHrrym RamirezNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument42 pagesHead InjuryMohammad Husni Banisalman100% (3)
- Maternity Nursing 2Document133 pagesMaternity Nursing 2Rick100% (1)
- The Penis, Function, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandThe Penis, Function, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Modul F2 Science Chapter 1Document21 pagesModul F2 Science Chapter 1NorelyanaAli95% (21)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument68 pagesDengue Hemorrhagic FeverClaire Gentallan50% (2)
- Compilation of MCN NotesDocument48 pagesCompilation of MCN Notestempter_10100% (2)
- Thymus, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandThymus, Functions, Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemJharyd Gamayot JhayyNo ratings yet
- Group 5:endocrine Glands & Hormones ProducedDocument28 pagesGroup 5:endocrine Glands & Hormones Produceddanielsyafiq.officialNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Anatomy 1 Stage - College of PharmacyDocument6 pagesEndocrine System: Anatomy 1 Stage - College of PharmacyMarci MunirNo ratings yet
- Maternal/Ob NotesDocument38 pagesMaternal/Ob NotesJADE PATEGANo ratings yet
- Maternal/Ob Notes: A Person's Sexuality Encompasses The Complex Behaviors, Attitudes Emotions and Preferences That AreDocument37 pagesMaternal/Ob Notes: A Person's Sexuality Encompasses The Complex Behaviors, Attitudes Emotions and Preferences That Aresabao kizuiteNo ratings yet
- RUNNNDocument18 pagesRUNNNNathaniel FerrerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology FinalDocument20 pagesAnatomy and Physiology FinalShannelle SinciocoNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Community Engagement Solidarity and Citizenship CSC - Compendium of Appendices For DLPs - Class FDocument11 pages1.1 Community Engagement Solidarity and Citizenship CSC - Compendium of Appendices For DLPs - Class Fherlyn jueloNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisologi Kelenjar Endokrin ManusiaDocument45 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisologi Kelenjar Endokrin ManusiaFake HpNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument17 pagesScience ReviewerankaaNo ratings yet
- LEC 1 Ana & PhysioDocument10 pagesLEC 1 Ana & PhysioKrisRN01No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Endocrine Glands: HypothalamusDocument10 pagesAnatomy of The Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamusgashbin latifNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument10 pagesUntitledgroup 6No ratings yet
- 2.1 Male and Female Repro IntroductionDocument11 pages2.1 Male and Female Repro IntroductionTrisha Mae BalladNo ratings yet
- Obstetric Nursing Review NLEDocument48 pagesObstetric Nursing Review NLEDylan Angelo AndresNo ratings yet
- 1 TransDocument10 pages1 TranssenecabheNo ratings yet
- Reviewers 3rd Qrtr.Document33 pagesReviewers 3rd Qrtr.Kim Jay Ann HalongongNo ratings yet
- OB Prelim NotesDocument11 pagesOB Prelim NotesrizaustriaNo ratings yet
- Saq 2 EmbryologyDocument8 pagesSaq 2 EmbryologyShilpa DuttaNo ratings yet
- Simple Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesSimple Anatomy and PhysiologyPatrick ValerioNo ratings yet
- GENBIO REVIEWER - FinalsDocument6 pagesGENBIO REVIEWER - FinalsFiona CagolNo ratings yet
- Genbio 2Document39 pagesGenbio 2Pawn RookNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Definition & BackgroundDocument11 pagesEndocrine System: Definition & Backgroundعبدالرحمن عدي عبدالفتاحNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Ovum Fallopian Tube Uterus Sperm LatinDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System Ovum Fallopian Tube Uterus Sperm LatinMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother, Child, & Adolescent NOTES (Theory) : Domapias, Regene Katherine LDocument3 pagesCare of Mother, Child, & Adolescent NOTES (Theory) : Domapias, Regene Katherine LKisha BethelNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesThe Endocrine Glands and The Nervous SystemLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- (Week 17) Reproductive SystemDocument3 pages(Week 17) Reproductive SystemDiana Leen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer 3Rd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience Reviewer 3Rd Quartermikykyla08No ratings yet
- Ob Notes Normal 1Document41 pagesOb Notes Normal 1pinpindalgoNo ratings yet
- NP2 MCN Compiled NotesDocument23 pagesNP2 MCN Compiled NotesSadakoNo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Pharmacology & Cholinergic DrugsDocument80 pagesAutonomic Pharmacology & Cholinergic DrugsmajdNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Radio AnatomiDocument39 pagesKuliah Radio AnatomiKalemNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Function TestsDocument24 pagesThyroid Function Testspavani valluriNo ratings yet
- Quick Study Guide To The Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesQuick Study Guide To The Cardiovascular SystemMc Luis Glen AserdanoNo ratings yet
- The Postpartal Family Maybelle B. AnimasDocument43 pagesThe Postpartal Family Maybelle B. AnimasErika Anne Mercado CadawanNo ratings yet
- Patologi Endokrin 2016Document132 pagesPatologi Endokrin 2016agusNo ratings yet
- NamasteDocument34 pagesNamasteAsha LathaNo ratings yet
- Cushing ReflexDocument4 pagesCushing ReflexJoko SusesoNo ratings yet
- Oral MucosaDocument109 pagesOral Mucosashahzeb memonNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument102 pagesDigestive Systemkavya nandhiNo ratings yet
- Perspective of Facial Esthetics in Dental Treatment PlanningDocument13 pagesPerspective of Facial Esthetics in Dental Treatment PlanninganasbukhariNo ratings yet
- New Design Space Regainers JCDocument43 pagesNew Design Space Regainers JCsnehasthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document8 pagesChapter 9Bea SeloterioNo ratings yet
- A Case of Persistent Bloody DiarrhoeaDocument9 pagesA Case of Persistent Bloody DiarrhoeaRuhama ErmiasNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument69 pagesDigestive SystemDennis ValdezNo ratings yet
- Learning Task 1.4 Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesLearning Task 1.4 Reading ComprehensionAndrei Marie SamillanoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Follicular Phase?: Good To KnowDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Follicular Phase?: Good To KnowNancy SinghNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Immunology Adaptive Immunity 17dec2021Document37 pages7.2 Immunology Adaptive Immunity 17dec20212023406162No ratings yet
- Third Quarter ExamDocument5 pagesThird Quarter ExamTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet