Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Female Reproductive System Ovum Fallopian Tube Uterus Sperm Latin
Uploaded by
Micky Morante0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesThe document summarizes the key functions and features of several human organs and tissues. It describes the ovaries, liver, testes, skin, blood vessels, smooth muscle, spinal cord, sperm, bone, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, ureter, and pancreas. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, the liver filters blood and metabolizes drugs, and the testes produce and store sperm. Blood vessels transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body. Smooth muscle applies pressure to vessels and organs. The spinal cord transmits nerve signals between the brain and body.
Original Description:
Original Title
PART 1.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key functions and features of several human organs and tissues. It describes the ovaries, liver, testes, skin, blood vessels, smooth muscle, spinal cord, sperm, bone, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, ureter, and pancreas. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, the liver filters blood and metabolizes drugs, and the testes produce and store sperm. Blood vessels transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body. Smooth muscle applies pressure to vessels and organs. The spinal cord transmits nerve signals between the brain and body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views4 pagesFemale Reproductive System Ovum Fallopian Tube Uterus Sperm Latin
Uploaded by
Micky MoranteThe document summarizes the key functions and features of several human organs and tissues. It describes the ovaries, liver, testes, skin, blood vessels, smooth muscle, spinal cord, sperm, bone, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, ureter, and pancreas. The ovaries produce eggs and hormones, the liver filters blood and metabolizes drugs, and the testes produce and store sperm. Blood vessels transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen throughout the body. Smooth muscle applies pressure to vessels and organs. The spinal cord transmits nerve signals between the brain and body.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
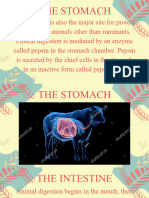
HUMAN OVARY
The ovary is an organ found in HUMAN LIVER
the female reproductive system that
produces an ovum.
The liver is a large, meaty organ that
When released, this travels down
sits on the right side of the belly.
the fallopian tube into the uterus,
Weighing about 3 pounds, the liver is
where it may become fertilized by
reddish-brown in color and feels
a sperm.
rubbery to the touch. Normally you
There is an ovary
can't feel the liver, because it's
(from Latin ovarium, meaning 'egg,
protected by the rib cage.
nut') found on the left and right sides
of the body.
The liver has two large sections,
The ovaries also
called the right and the left lobes.
secrete hormones that play a role in
The gallbladder sits under the liver,
the menstrual cycle and fertility.
along with parts of the pancreas and
The ovary progresses through many
intestines. The liver and these organs
stages beginning in the prenatal
work together to digest, absorb, and
period through menopause. It is also
process food.
an endocrine gland because of the
various hormones that it secretes.
The liver's main job is to filter the
HUMAN TESTIS blood coming from the digestive tract,
before passing it to the rest of the
Testicle or testis is the body. The liver also detoxifies
male reproductive gland or gonad in chemicals and metabolizes drugs.
all animals, including humans.
It is homologous to the female ovary. HUMAN JEJUNUM SMALL INTESTINE
The main function of the testes is
producing and storing sperm. They’re The jejunum is one of three sections
also crucial for creating testosterone that make up the small intestine. The
and other male hormones called small intestine is part of the digestive
androgens. system and is vital for breaking down
and absorbing nutrients.
HUMAN SKIN The jejunum makes up about two-
fifths of the small intestine. The main
Human skin, in human anatomy, the function of the jejunum is absorption
covering, or integument, of the of important nutrients such as
body’s surface that both provides sugars, fatty acids, and amino acids.
protection and receives sensory
stimuli from the HUMAN BLOOD VESSEL
external environment.
The human skin is the outer The blood vessels are the
covering of the body and is the components of the circulatory
largest organ of the integumentary system that
system. transport blood throughout
the human body.
These vessels transport blood cells, The spinal cord is composed
nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of neurons that send and receive
of the body. They also take waste signals along tracts towards and away
and carbon dioxide away from the from the brain.
tissues. Blood vessels are needed to The spinal cord functions primarily in
sustain life, because all of the body’s the transmission of nerve
tissues rely on their functionality. signals from the motor cortex to the
There are five types of blood vessels: body, and from the afferent fibers of
the arteries, which carry the blood the sensory neurons to the sensory
away from the heart; the arterioles; cortex.
the capillaries, where the exchange
of water and chemicals between the SPERM
blood and the tissues occurs;
the venules; and the veins, which Sperm is the male reproductive cell.
carry blood from the capillaries back In the types of sexual
towards the heart. reproduction known
as anisogamy and its
SMOOTH MUSCLE subtype oogamy, there is a marked
difference in the size of
Smooth muscle is a type of muscle the gametes with the smaller one
tissue which is used by various being termed the "male" or sperm
systems to apply pressure to vessels cell.
and organs. Smooth muscle is The human sperm cell is haploid, so
composed of sheets or strands of that its 23 chromosomes can join the
smooth muscle cells. These cells 23 chromosomes of the female egg
have fibers of actin and myosin to form a diploid cell. In mammals,
sperm develops in the testicles, is
which run through the cell and are
stored in the epididymis, and
supported by a framework of other
released from the penis.
proteins.
Sperm, also called spermatozoon,
Smooth muscle tissue, unlike skeletal
plural spermatozoa, male
or cardiac tissues, does not have reproductive cell, produced by most
clearly defined striations visible on animals., sperm are flagellated; that
the cells. is, they have a whiplike tail. In higher
the function of smooth muscle is to vertebrates, especially mammals,
contract. sperm are produced in the testes.
SPINAL CORD BONE
The spinal cord is a bundle of nerve A bone is a rigid organ that
fibers that extend from the brain constitutes part of
stem down the spinal column to the the vertebrate skeleton in animals.
lower back. Bones protect the various organs
The spinal cord is composed of the body, produce red and white
of nervous tissue. The interior of the blood cells, store minerals,
spinal cord consists of neurons, provide structure and support for
nervous system support cells the body, and enable mobility.
called glia, and blood vessels.
In the human body at birth, there Skeletal muscle is a specialized
are over 300 bones,[1] but many of contractile tissue found in animals
these fuse together during which functions to move
development, leaving a total of 212 an organism’s body.
separate bones in the adult Skeletal muscle is comprised from a
series of bundles of muscle fibers,
surrounded by protective
membranes.
URETER This arrangement allows skeletal
muscle to contract quickly and
The ureter is a tube that carries urine release quickly without subjecting the
from the kidney to the urinary individual fibers to too much friction.
bladder. There are two ureters, one Skeletal muscle tissue can be found
attached to each kidney. The upper across the animal kingdom, in most
half of the ureter is located in the multi-cellular forms of life.
abdomen and the lower half is Skeletal muscle is comprised of a
located in the pelvic area. series of muscle fibers made of
The ureter is about 10 to 12 inches muscle cells. These muscle cells are
long in the average adult. The tube long and multinucleated.
has thick walls composed of a
fibrous, a muscular, and a mucus CARDIAC MUSCLE
coat, which are able to contract.
Cardiac muscle tissue is only found
in your heart, where it performs
PANCREAS coordinated contractions that allow
your heart to pump blood through
The pancreas is an organ located in the your circulatory system.
abdomen. It plays an essential role in Cardiac muscle tissue works to keep
converting the food we eat into fuel for your heart pumping through
the body's cells. The pancreas has two involuntary movements.
main functions: an exocrine function
that helps in digestion and HUMAN BLOOD
an endocrine function that regulates
Blood is a constantly circulating fluid
blood sugar.
providing the body with nutrition,
The pancreas is located behind the
oxygen, and waste removal. Blood is
stomach in the upper left abdomen. It is mostly liquid, with numerous cells
surrounded by other organs including and proteins suspended in it, making
the small intestine, liver, and spleen. It is blood "thicker" than pure water. The
spongy, about six to ten inches long, and average person has about 5 liters
is shaped like a flat pear or a fish (more than a gallon) of blood.
extended horizontally across the It transports oxygen from the lungs to
abdomen. the body tissues, and carbon dioxide
from the tissues to the lungs. It
SKELETAL MUSCLE transports nutritive substances and
metabolites to the tissues and
removes waste products to the
kidneys and other organs of remaining waste material is stored
excretion. It has an essential role in as feces before being removed
the maintenance of fluid balance. by defecation.
which responsible for absorbing
water from indigestible food.
Measuring approximately six feet
long, the large intestine is made up of
four main parts: the cecum, the
STRIATED MUSCLE colon, the rectum, and the anus.
6*
Striated muscle tissue is a muscle
tissue that features repeating ADIPOSE TISSUE
functional units called sarcomeres.
Striated musculature is comprised Adipose tissue is a lipid-storing type of
of two types of tissues: skeletal loose connective tissue. Also called fat
muscle and cardiac muscle. tissue, adipose is composed primarily of
The main function of striated muscle adipose cells or adipocytes. While
tissue is to create force and contract. adipose tissue can be found in a number
These contractions will either pump of places in the body, it is found
blood throughout the body (cardiac primarily beneath the skin.
muscle) or powers breathing,
Adipose is also located
movement or posture (skeletal
between muscles and around internal
muscle).
organs, particularly those in the
HYALINE CARTILAGE abdominal cavity.
Adipose tissue helps to cushion and
Hyaline cartilage is a type of protect organs, as well as insulate the
connective tissue found in areas body from heat loss.
such as the nose, ears, and trachea
of the human body. The word hyaline
means “glass-like”, and hyaline
cartilage is a glossy, greyish-white
tissue with a uniform appearance.
Hyaline cartilage provides support
and flexibility to different parts of the
body.
Hyaline cartilage is the most
abundant type of cartilage in the
body.
LARGE INTESTINE
The large intestine, also known as
the large bowel, is the last part of
the gastrointestinal tract and of
the digestive system in vertebrates.
Water is absorbed here and the
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Organ Systems OverviewDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Organ Systems OverviewBea PrestoNo ratings yet
- Organ System 1Document15 pagesOrgan System 1LeoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologybobadillamarie156No ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphynaomimarielleNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument19 pagesAnaphy ReviewerGian Paolo P. CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- 3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodyDocument5 pages3-HANDOUT - Understanding The Human BodySabrina PorcoNo ratings yet
- SYSTEM STRUCTURES AND INTERACTIONSDocument1 pageSYSTEM STRUCTURES AND INTERACTIONSLianne LagromaNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Terms: Dr. SuwonoDocument6 pagesThe Human Body Terms: Dr. SuwonoRed DemonNo ratings yet
- Organizations of the Human BodyDocument9 pagesOrganizations of the Human BodyWilliam WongNo ratings yet
- CelllllDocument9 pagesCelllllbasman1212No ratings yet
- Body System Graphic Organizer With Answers 1pxx04bDocument3 pagesBody System Graphic Organizer With Answers 1pxx04bAthia ZamanNo ratings yet
- The Human AnatomyDocument6 pagesThe Human AnatomyChristian D. RamatNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveDocument3 pagesBody Systems Chart System Illustration Structures Function: DigestiveMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic 1Document3 pagesAssignment Topic 1Charlyn CasabalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Exploring The Human BodyDocument15 pagesAnatomy Exploring The Human BodyZack Aarton100% (1)
- SCIENCE KeypointsDocument5 pagesSCIENCE KeypointsSadidah MalawiNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 5 - Animal Organ SystemsDocument34 pagesBiology Module 5 - Animal Organ SystemsfloNo ratings yet
- Intro To Anaphy - ReviewerDocument5 pagesIntro To Anaphy - ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Document9 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology (Transes)Kathleen BalauagNo ratings yet
- These Tasks:: General Biology 2Document8 pagesThese Tasks:: General Biology 2Mary Rose MaribaoNo ratings yet
- Six levels of human body organizationDocument4 pagesSix levels of human body organizationMicaella ValdezNo ratings yet
- Ch. 13 Human Body Final 1Document16 pagesCh. 13 Human Body Final 1RANJAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Human BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Bodyjavier andres martinez100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyAnonymous 2k0o6az6lNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems OverviewDocument5 pagesHuman Body Systems OverviewJohn Niño CasuelaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesHimiko JacksonNo ratings yet
- Handout # 6 Cells, Tissues, OrgansDocument5 pagesHandout # 6 Cells, Tissues, OrgansRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument4 pagesOrgan SystemChristian PatingaNo ratings yet
- About Human BodyDocument16 pagesAbout Human BodyApril Lavenia BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJared LozadaNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyShem DelolaNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document27 pagesPart 3Rion BaiganNo ratings yet
- Science ProgeDocument7 pagesScience ProgePrince AngeloNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument13 pagesBody SystemsDarshema isduriNo ratings yet
- 10 Major System of Responsible For Body FunctionDocument27 pages10 Major System of Responsible For Body Functionقى قىNo ratings yet
- St. Sebastian School Grade 11 Body SystemsDocument5 pagesSt. Sebastian School Grade 11 Body Systemsmirriam mag-asoNo ratings yet
- Physiology 1 IntroductionDocument101 pagesPhysiology 1 IntroductionBrian KipchumbaNo ratings yet
- Differentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsDocument13 pagesDifferentiation: Similar in Structure Different Tissues Different Organs Different SystemsShivani HiteshNo ratings yet
- Vince Ford N. Marquez Grade 6 - RutherfordDocument15 pagesVince Ford N. Marquez Grade 6 - RutherfordfordmayNo ratings yet
- List of Human Body Parts With DiagramDocument13 pagesList of Human Body Parts With DiagramPankaj Pandya100% (1)
- Organ SystemDocument16 pagesOrgan SystemStephany RaveloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJan Andrew BuduanNo ratings yet
- Anatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Document10 pagesAnatomical, Physiological and Mechanical Bases of Movements: Body Really Made Of? "Jay Carlo BagayasNo ratings yet
- Performance Task For Science 7Document5 pagesPerformance Task For Science 7Abdullah MundasNo ratings yet
- Six Levels of Biological OrganisationDocument35 pagesSix Levels of Biological OrganisationPianomanSuperman100% (2)
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnaphy ReviewerRuby Jane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Hbs Unite 1 Summary FinalDocument45 pagesHbs Unite 1 Summary Finalapi-277775953No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - AnaphyDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - AnaphyCinderilla De AngelNo ratings yet
- Human Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Document9 pagesHuman Body: How Is The Human Body Similar To A Well-Tuned Machine?Montse GilNo ratings yet
- Male ReproductiveDocument1 pageMale ReproductiveMARI AN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Unit 12: - Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesUnit 12: - Reproductive SystemgilissaNo ratings yet
- L1 - Human Body PDFDocument10 pagesL1 - Human Body PDFNatsumi HarumiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemJharyd Gamayot JhayyNo ratings yet
- Á Léqééã Péaéuéiéã Uééxéñsãuééré Kéluéliéuréã Aqé×Iémüsévé Wûxiééré Xéuééïqéré Ìuéléévélééré Éæsééãyrélééjééré Éï Qéwûéìuéwhéuéã LéqéèDocument51 pagesÁ Léqééã Péaéuéiéã Uééxéñsãuééré Kéluéliéuréã Aqé×Iémüsévé Wûxiééré Xéuééïqéré Ìuéléévélééré Éæsééãyrélééjééré Éï Qéwûéìuéwhéuéã LéqéèAlapati Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment 1,2Document8 pagesBiology Assignment 1,2prasathindika312No ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document44 pagesGen Bio 2Reymark Dao-anNo ratings yet
- Human Biology IntroductionDocument22 pagesHuman Biology IntroductionAli HarthNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Module 1 - Development and Function of Reproductive SystemDocument55 pagesHuman Reproduction Module 1 - Development and Function of Reproductive SystemAdc ClamorNo ratings yet
- Certification ULD Management Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification ULD Management Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certification Security Awareness Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Security Awareness Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certification Safety Management System Awareness Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Safety Management System Awareness Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Student Module 1: Course Orientation: Ma. Zendria D. Catacutan, RN, MSNDocument11 pagesStudent Module 1: Course Orientation: Ma. Zendria D. Catacutan, RN, MSNMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Weekly nursing student scheduleDocument1 pageWeekly nursing student scheduleMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Weekly nursing student scheduleDocument1 pageWeekly nursing student scheduleMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Parallel Structure & The Example Essay: 3 of A KindDocument1 pageParallel Structure & The Example Essay: 3 of A KindMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certification Basic Safety Training Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Basic Safety Training Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certification Human Factor Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Human Factor Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Request Letter RefereeDocument1 pageRequest Letter RefereeMicky Morante67% (3)
- Certification Cargohaus Familiarization Course Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Cargohaus Familiarization Course Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certification Dangerous Goods Category 8 Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Dangerous Goods Category 8 Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Office of The Sangguniang Kabataan: Republic of The Philippines City of Puerto Princesa Barangay ManingningDocument1 pageOffice of The Sangguniang Kabataan: Republic of The Philippines City of Puerto Princesa Barangay ManingningMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certification Basic Cargo Handling Michael - Morante PDFDocument1 pageCertification Basic Cargo Handling Michael - Morante PDFMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE. BDC ConstitutionDocument2 pagesTEMPLATE. BDC ConstitutionMicky Morante100% (8)
- Barangay Maningning Development PlanDocument2 pagesBarangay Maningning Development PlanMicky Morante75% (8)
- Enhanced BDP, Investment & BudgetingDocument24 pagesEnhanced BDP, Investment & BudgetingMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Magtanong CompoundDocument3 pagesMagtanong CompoundMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- List of SK Officials 2018-2022: Full Name PositionDocument1 pageList of SK Officials 2018-2022: Full Name PositionMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Ovum Fallopian Tube Uterus Sperm LatinDocument4 pagesFemale Reproductive System Ovum Fallopian Tube Uterus Sperm LatinMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Certificate For ML LeagueDocument5 pagesCertificate For ML LeagueMicky Morante100% (2)
- Certificate of Participation: Republic of The Philippines City of Puerto Princesa, Palawan Barangay ManingningDocument1 pageCertificate of Participation: Republic of The Philippines City of Puerto Princesa, Palawan Barangay ManingningMicky Morante100% (6)
- Workshop 1 - VISIONING - BDPDocument20 pagesWorkshop 1 - VISIONING - BDPMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- II. Plan of Activities: I.Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesII. Plan of Activities: I.Learning ObjectivesMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Office of The Punong Barangay Barangay Bagong SikatDocument2 pagesOffice of The Punong Barangay Barangay Bagong SikatMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Office of The Punong Barangay Barangay Bagong SikatDocument2 pagesOffice of The Punong Barangay Barangay Bagong SikatMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Special Activity Attendance: No. Name SignatureDocument2 pagesSpecial Activity Attendance: No. Name SignatureMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Sangguniang KabataanDocument13 pagesSangguniang KabataanMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists and Their ConceptsDocument10 pagesNursing Theorists and Their ConceptsMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- III. Activities Undertaken: II. Plan of ActivitiesDocument2 pagesIII. Activities Undertaken: II. Plan of ActivitiesMicky MoranteNo ratings yet
- The Interactions of Intensity, Frequency and Duration of Training in Altering Cardiorespiratory FitnessDocument2 pagesThe Interactions of Intensity, Frequency and Duration of Training in Altering Cardiorespiratory FitnessRioHero0% (1)
- Gambaran Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Hipertensi Dengan Gangguan Kebutuhan Rasa Nyaman NyeriDocument8 pagesGambaran Asuhan Keperawatan Pada Pasien Hipertensi Dengan Gangguan Kebutuhan Rasa Nyaman NyeriGhaniNo ratings yet
- Ang Tunay Na Excretory SystemDocument17 pagesAng Tunay Na Excretory SystemcjNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas Exchange PDFDocument74 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchange PDFrachitNo ratings yet
- En Kl-730-Introduction 10708Document4 pagesEn Kl-730-Introduction 10708mennaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AlkalosisDocument17 pagesRespiratory AlkalosisGhen CanosaNo ratings yet
- Hasil Lab An. CDocument2 pagesHasil Lab An. CDENNYNo ratings yet
- Chronic Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia (Lopera)Document5 pagesChronic Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia (Lopera)Raymond BernardusNo ratings yet
- A Study of Hydrotherapy and Its Health Benefits ISSNDocument12 pagesA Study of Hydrotherapy and Its Health Benefits ISSNPhocachinnoNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology 502 Winter 13 Lectures 1 and 2 HandoutDocument111 pagesHuman Physiology 502 Winter 13 Lectures 1 and 2 Handoutvgn_fz150ENo ratings yet
- SodaPDF Merged Merging ResultDocument648 pagesSodaPDF Merged Merging ResultFaith madayagNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock NclexDocument81 pagesCardiogenic Shock NclexKrishna SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolyte PediatricsDocument41 pagesFluids and Electrolyte PediatricsYusron BishryNo ratings yet
- Virchow TriadDocument6 pagesVirchow Triadarif 2006No ratings yet
- FT Desfibrilador-Monitor Comen S8Document6 pagesFT Desfibrilador-Monitor Comen S8Dayani GomezNo ratings yet
- Abg Quiz in Class With Answers 1Document3 pagesAbg Quiz in Class With Answers 1Janae TaylorNo ratings yet
- Stress Brain PlasticityDocument15 pagesStress Brain PlasticityLilian Cerri MazzaNo ratings yet
- Tan, Jolwin Laugo 2361052561Document6 pagesTan, Jolwin Laugo 2361052561JolwinTanNo ratings yet
- Cells Tissues Organs and Systems Power PointDocument11 pagesCells Tissues Organs and Systems Power PointNidonama E. KabmatNo ratings yet
- 18 ExcretionDocument70 pages18 ExcretionqingxuguNo ratings yet
- Hospitalized 67-Year-Old Black Woman MIDocument2 pagesHospitalized 67-Year-Old Black Woman MIMaria Jessica DumdumNo ratings yet
- Association of Abo and RH Blood Groups With Hypertension: Original ArticleDocument4 pagesAssociation of Abo and RH Blood Groups With Hypertension: Original ArticleAprilia IlaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System FunctionsDocument25 pagesAutonomic Nervous System FunctionsLisa KangNo ratings yet
- Vasopressors For ShockDocument21 pagesVasopressors For ShocknugrahaNo ratings yet
- PE:2 Running For Fitness HandoutDocument2 pagesPE:2 Running For Fitness HandoutJoseph IcaonapoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Sleep 10281 MRWQRVBDocument10 pagesBiochemistry of Sleep 10281 MRWQRVBMinh Tri TranNo ratings yet
- Bahan BrainDocument7 pagesBahan BrainArwina Syazwani Binti GhazaliNo ratings yet
- ABG Tic Tac Toe Part 1Document2 pagesABG Tic Tac Toe Part 1Shala Miller100% (1)
- 1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood VesselsDocument9 pages1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood Vessels13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Physiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelDocument40 pagesPhysiology Course: Dr. Velu M. RachelKunda JosephNo ratings yet