100% found this document useful (1 vote)
3K views4 pagesEye Bolt Calculation
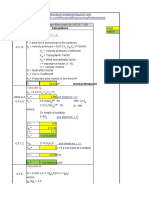
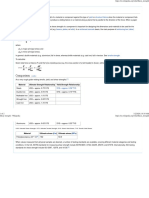
This document calculates the stress on lifting eye bolts used to lift a pump. It determines the smallest bolt area is at the thread root diameter. It then calculates the total pump weight, tensile load per bolt, and resultant shear force on each bolt. Based on these calculations, the stress on each bolt is 1792 psi, with a safety factor greater than 2.5. Therefore, the eye bolts and attachment method are sufficient to safely lift the pump.
Uploaded by
Alok KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
3K views4 pagesEye Bolt Calculation
This document calculates the stress on lifting eye bolts used to lift a pump. It determines the smallest bolt area is at the thread root diameter. It then calculates the total pump weight, tensile load per bolt, and resultant shear force on each bolt. Based on these calculations, the stress on each bolt is 1792 psi, with a safety factor greater than 2.5. Therefore, the eye bolts and attachment method are sufficient to safely lift the pump.
Uploaded by
Alok KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as XLS, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Overview: Provides a cover page with purchase order details, indicating origin and approval of the calculations documented herein.
- Lifting Lug Stress Calculations: Details the procedure and assumptions for calculating stress on the lifting lug using specific equations and material standards.
- Resultant Force Calculations: Calculates the resultant force applied to the eye bolt, defining parameters under specific load conditions.
- Conclusion: Summarizes findings about the safety and adequacy of the design, highlighting compliance with industry standards.
- Stress on Bolt due to Resultant Force: Describes how to determine the stress experienced by the bolt by applying the resultant force, with safety factors considered.