Eye Calculation For Lifting
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsEye Calculation For Lifting
Uploaded by
ScribdTranslationsCliente Fill in
Project:
Transporter:
Calculated
Recommended M4
Material Handling Machines
LIFTING EYE
Petrobras Reference Standard N2683, according to Mr. Magno Xavier, posted on LinkedIn
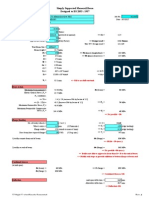
1 - Data
Load capacity to be applied C= 9.000 kgf
Numbers of Olhais N= 4
Angle of the tongue with the horizontal q= 60 degrees
Failure consequence factor of the eyelet fand= 1,3
Load deviation factor fdc= 1.25
Weight contingency factor fcp= 1,1
Uncertainty factor of the CG fCG= 1.05
Dynamic amplification FAD = 1.3
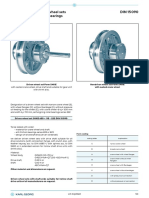
Dimensions of the EYELET
tlook
rpanel R R= 60 mm
tpanel rpanel= 40 mm
dpanel= 80 mm
dfuro dpine = 29 mm
def= 54 mm
g g= 19 degrees
def teye = 16 mm
X tpanel= 6.35 mm
base 150 mm
20.48 base Y
Material for the Eyelet ASTM A36
Yield limit of the material fy= 250 MPa
Flow limit of the electrode fthe= 413,685 MPa
2 - Strength in language - Flinga
Flinga= fe x fdc x fcp x fCGx (C / N) / sin(q) = Flinga = 4,876.3 kgf
3 - Force on the pin considering dynamic amplification - Fpine
Fpine= FAD x Flinga= Fpine = 6,339.1 kgf
62.165,8 N
4 - Diameter of the eyelet hole - dfuro
dfurrow= time off + dpine dfuro = 29.87 mm
relief = 0.03 x dpine break 0.87 mm
dpine≤ 33 mm - maximum clearance = 1 mm; for dpinegreater - maximum clearance = 6 mm
rfuro= dfuro/2 rfurrow= 14,935 mm
Eng. Luís A. MORGADO LIFTING EYE 1/5
Cliente Fill
Project:
Transporter:
Calculated
Recommended M4
Material Handling Machines
5 - Width of the eyelet for dimensioning b1, b2e b3(PETROBRAS criterion)
5.1 - Width b1e b2for the traction in the effective liquid area in the region of the hole
5.1.1 - b1real distance from the edge of the hole to the outer edge of the eyelet
It will be the lesser value between 4 x T and 0.8 x dfuro
Total thickness (eye + rings) - T = thello+ 2 x tpanel T= 28.70 mm
0.8 x dfuro = 23,896 mm
b1= 23,896 mm
5.1.1 - b2the "real" distance from the edge of the hole to the outer edge of the ring
It will be the lower value between (rpanel- rfuro) e b1 (rpanel- rfuro) = 25,065 mm
b1= 23,896 mm
b2= 23,896 mm
5.2 - Width b3for the raw section of the region below the reinforcement ring
It will be the lesser value between (2 x R) and (2 x b)1+ dfuro+ dpanel )
(2 x R) = 120 mm
(2 x b1+ dfuro+ dpanel)= 157,662 mm
b3 = 120 mm
6 - Tensions in the eyelet
6.1 - Contact pressure between the pin and the hole of the eyelet - Fp
Fp= Fpine/ (dpinex (tolhal+ 2 x tpanel) = Fp= 74,692 MPa
6.2 - Shear Stress of the effective area - Fv
Fv= Fpine/{2x[(R - rfuro) x teye+ (rpanel-bathe) x 2 x tpanel]} Fv= 29,906 MPa
6.3 - Tension of Traction in the effective liquid area in the hole region - Faf
Fof= Fpine/ [(2 x b1x twave) + (4 x b2x tpanel] Fof= 45,323 MPa
6.4 - Tensile Stress of the gross section in the region below the reinforcement ring - Fa
Fa= Fpine/ (b3x tlookFa)= 32,378 MPa
6.5 - Maximum tearing force of the ring and washer assembly - Fac
Fac(2 x R + rpanelx (gx2) x tsightx 0.6 x fy Fac= 351.670 N
35,860.3 kgf
If Fpine≤ FacOK 6,339.1 ≤ 35,860.3 OK
7 - Weld of the reinforcement ring
7.1 - Tension force in a reinforcement ring - Fpanel
Fpanel= Fpinex tpanel/ (twave+ 2 x tpanel ) Fpanel= 1,402.56 kgf
13.754,4 N
Mr. Luís A. MORGADO LIFTING EYE 2/5
Cliente Fill in
Project:
Carrier:
Calculated
Recommended M4
Material Handling Machines
7.2 - Allowable tension (base material and electrode) - Fw
7.2.1 - Allowable stress in the base metal -sam
s am= 0.4 x fyx (2)0.5 sam = 141.421 MPa
7.2.2 - Allowable voltage on the electrode -sE
translatedTextE= 0.3 x fthe sE= 124,106 MPa
The value to be considered is the smallest Fw= 124,106 MPa
7.3 - Minimum allowable throat thickness - gleft
gon the left= Fpanel/ (px ranelx FW) gon the=left 0.882 mm
7.4 - Minimum admissible fillet - andleft
eleft= 20.5x gon the left eon the =left 1,247 mm
Adopt the minimum value specified in Table 1
Thickness of the thickest plate of the fillet Minimum side of the welding bead (mm)
Up to 6.4 mm 3
From 6.4 mm to 12.5 mm, inclusive 5
Above 12.5 mm up to 19 mm, inclusive 6
Above 19 mm 8
NOTE: The thickness of the weld must not be greater than the thickness of the thinner sheet.
Table 1 -> 6 mm
Thinner sheets 6.35 mm 6
Adopted solder file esolda.ad = 6 mm
8 - Support base of the Support, according to AISC
8.1 - Geometric characteristic of the eye socket base
8.1.1 - Base area
2
Abase= base x thello Abase = 2.400 mm
8.1.2 - Resistance module on the X axis
3
Wxhellox base2/ 6 Wx = 60,000 mm
8.1.2 - Resistance module in the Y axis
3
Wy= thello2x base / 6 W y= 6,400 mm
8.2 - Acting stresses / Allowable stresses
8.2.1 - Axial tension
Fa= Fpinex sin(q) / Abase Fa= 22,432 MPa OK
Fadm≤ 0.6 x fy Fadm = 150,000 MPa
Eng. Luís A. MORGADO LIFTING EYE 3/5
Cliente Fill in
Project:
Carrier:
Calculated
Recommended M4
Material Handling Machines
8.2.2 - Bending stress in the X axis
Ffx= Fpinex cos(q) x def/ Wx Ffx= 27,976 MPa OK
Fadm≤ 0.6 x fy Fadm = 150,000 MPa
8.2.3 - Bending stress in the Y axis, adopting 5% lateral force on the eye
Ffx= 0.05 x Fpinex def/ Wy Ffx= 26,227 MPa OK
Fadm≤ 0.75 x fy Fadm = 187,500 MPa
8.2.4 - Combined stressessc≤ 1
sc= Fa/ (0,6 x fy) + Ffx/ (0,6 x fy) + Ffy/ (0.75 x fy) sc= 0.476 OK
8.2.5 - Shear stress
Fv= Fpinex cos(q) / (2/3 x Abase Fv= 19,427 MPa OK
Fv,adm≤ 0.4 x Fy Fv,adm = 100.00 MPa
Notes by Eng. Luís MORGADO
The attachment of a piece with more than three eyelets runs the risk of the other eyelets not securing the load.
This is why it is important to accurately calculate the lengths of the lifting cables.
Depending on the CG of the part, only two cables will be able to hold the entire load, leaving the others.
two in the load balance. BE CAREFUL with the length of the cables.
2 - This calculation is based on factors and criteria for determining the widths b1, b2e b3defined in
Petrobras standard, this criterion may be oversized or even undersized in
specific cases, therefore, the engineer, when applying this standard, must be aware of these
variables, and the risk is the responsibility of the consulting engineer, even if it is stated in the AISC standard.
3 - In Table 1, it was considered that the weld cannot be greater than the smallest thickness of the sheets.
from Eye and Strength.
4 - Verification of the base weld is different from the base itself, in which the base has lateral load and undergoes
various types of stresses, including shear stress. In the case of welding, only the
total load of traction in the welding. BE CAREFUL!, because the one holding the eyelet on the piece is this weld,
which should have precise calculations, since welding exhibits concerning stress concentrations,
even if it is recommended by the AISC.
5 - Conclusion, I recommend using calculation standards for lifting eye, instead of a standard.
of the company, which has no legal basis.
NOTES by Eng. Glauco R. (Marine Structures Engineer)
This standard was written based on calculations performed and the experience of the largest companies.
offshore lifting in the world. They are suitable for lifting large maritime structures and that the
care in manufacturing and assembly is much greater than in common steel constructions. About the
comments of the N-2683:
The load deviation factor of 1.25 is suitable with the manufacturing tolerances of the cables and the...
manufacturing and assembly tolerance of lifting eyes. It may even adopt values
greater or lesser than 1.25. The ISO 19901-6 standard mentioned in N-2683 clarifies the tolerances better
and the load deviation factor.
Eng. Luís A. MORGADO Lifting Eye 4/5
Cliente Fill
Project:
Carrier:
Calculated
Recommended M4
Material Handling Machines
The widths b1, b2, and b3 are patched according to AISC ASD9.
3- The Minimum Values of the welds presented in table 1 are recommended by the AISC and have the
function to prevent cracks and weakening of the weld due to rapid cooling of the weld by heat loss
accelerated by the base material.
4- The verification of the weld at the base of the eyelet is presented in the example of the standard and follows the
recommendations from the AISC.
5- The Standard is suitable for what it proposes, which is the lifting of offshore structures from 100
tons and whose lifts have already reached 12,000 tons, for weights less than 100 tons the factor
dynamic can increase significantly in relation to the 1.3 of the ISO. For lifting mechanical parts on
there are other standards. ASME has standards that deal with the lifting of mechanical parts, but
basically follow the same principles presented in N-2683 and also use the AISC for
sizing, and the values are compatible with N-2683.
The N-2683 serves as a guide for novice engineers in the area and unveils the lifting eyelets that
are usually not covered in structural engineering undergraduate courses.
seeks to alert to the most critical issues.