Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SOCIOLOGY
Uploaded by
Siddhant Shameena0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views8 pagesSociology pdf for UPSC CSE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSociology pdf for UPSC CSE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views8 pagesSOCIOLOGY
Uploaded by
Siddhant ShameenaSociology pdf for UPSC CSE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
UPSC IAS
Mains
S CI LOGY
F undation Batch
01:00 PM to 04:00 PM
By- Divakar Bothra
Batch Starting On 18th October’22
The More You
Sweat in the Training
The less You bleed In the war
Norman Schwarzkopf
It is said that Optional determines the destiny of UPSC journey. It is the
most important weapon to conquer this exam. To get into the final list
one must ace the optionals.
Features of the Course
400+ hours of live lectures Previous Year Questions
discussions
Comprehensive coverage through Current affairs to keep the aspirant
high quality lecture notes updated
Hand written notes and Doubt clearing sessions by the
hand written model answers faculty
Live answer writing program under Mains Mentorship Sessions to
the guidance of faculty enhance the marks
• PEDAGOGY- First 20 mins every day we will discuss the previous
years questions in the class on the topics covered in the previous
class.
• The classes will start from Chapter 1 of Paper 1 and will follow the
sequence given in the syllabus of UPSC Mains Sociology.
• MATERIAL- All the material will be provided in two formats i.e Hand
written and Typed .
• CURRENT AFFAIRS- The current aspects of every topic will be incul-
cated in the classes. The sources of current affairs which will be
covered are-EPW, THE HINDU, INDIAN EXPRESS.
• Current compilations and list of thinkers (topic wise) will also be
provided.
Timetable
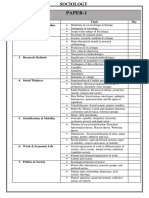
Paper Chapter Sub Topic Status
PAPER - 1 Introduction • Basic theories and 18 Oct - 20 Oct
approaches in Sociology
1) Sociology - The • Modernity and Social 27 Oct - 31 Oct
Discipline change in Europe 07 Nov - 10 Nov
• Scope of the subject and
comparison
• Sociology and common
sense
2) Sociology as • Science, scientific 11 Nov - 18 Nov
Science method and critique
• Major theoretical strands
of research methodology
• Positivism and its
critique
• Fact value and
objectivity
• Non- positivist
• methodologies
3) Research Methods and • Qualitative and 21 Nov - 25 Nov
Analysis quantitative methods
• Techniques of data
collection
• Variables, Sampling,
Hypothesis, Reliability
and Validity
4) Sociological Thinkers • Karl Marx-Historical 26 Nov - 20 Dec
materialism, MOP, Class
and class conflict,
Alienation
• Emile Durkheim-DOL,
Social fact, Suicide,
Religion
• Max Weber-Social action,
Ideal types, Authority,
Bureaucracy, PE&SC
• Talcolt Parsons-Social
syatem, Pattern variables
• Robert Merton- Latent &
Manifest, Conformity and
Deviance, Reference
Group
• Mead- Self and Identity
Paper Chapter Sub Topic Status
PAPER - 1 5) Stratification and • Concepts-Equality, 21 Dec - 27 Dec
Mobility Inequality, Hierarchy,
Exclusion, Poverty and
Deprivation
• Theories of Stratification
-Structural functionalist
theory, Marxist theory,
Weberian theory
• Dimension - Social
stratification of class,
Status groups, Gender,
Ethnicity and Race
• Social Mobility - Open
and Closed system,
Types of social mobility,
Sources and causes of
mobility
6) Work and Economic • Social organization of 28 Dec - 30 Dec
Life work in different types of
societyslave society,
feudal society, industrial
/ capitalist society.
• Formal and informal
organization of work.
• Labour and society
7) Politics and Society • Sociological theories of 2 Jan - 10 Jan
Power
• Power elite, bureaucracy,
pressure groups, and
political parties.
• Nation, state, citizenship,
democracy, civil society,
ideology.
• Protest, agitation, social
movements, collective
action,revolution.
8) Religion and • Sociological theories of 11 Jan - 17 Jan
Society Religion
• Types of religious
practices: animism,
monism, pluralism,
sects, cults.
• Religion in modern
society: religion and
science, secularization,
religious revivalism,
fundamentalism.
Paper Chapter Sub Topic Status
9) System of Kinship . • Family, Household, 18 Jan - 25 Jan
Marriage
• Types and forms of
family.
• Lineage and descent
• Patriarchy and sexual
division of labour.
• Contemporary trends.
10) Social change in • Sociological theories of 26 Jan - 31 Jan
Modern society social change
• Development and
dependency.
• Agents of social change.
• Education and social
change.
• Science, technology and
social change.
1) Perspectives on the • Indology ( Ghurye ) 1 Feb - 3 Feb
PAPER - 2 study of Indian society: • Structural Functionalism
• ( Srinivas )
• Marist Sociology (Desai)
• Social background of 6 Feb - 8 Feb
2) Impact of Colonial Rule Indian nationalism
• Modernisation of Indian
tradition
• Protestand movements
during colonial period
• Social reforms
3) Village • The idea of Indian Village 9 Feb - 10 Feb
• Evolution of Land tenure
system, Land reforms.
4) Caste System • Perspectives on the 11 Feb - 15 Feb
study of caste systems:
GS Ghurye, M N Srinivas,
Louis Dumont, Andre
• Beteille.
• Features of caste
system.
• Untouchability - forms
and perspectives.
Paper Chapter Sub Topic Status
PAPER - 2 5) Tribe • Definitional Problems 16 Feb - 18 Feb
• Geographical Spread
• Colonial policies and
tribes
• Issues of integration and
autonomy
6) Social classes in • Agrarian class structure 20 Feb - 22 Feb
India • Industrial class structure
• Middle class structure
7) System of Kinship • Lineage and Descent COVERED WITH
in India • Types of kinship PAPER 1
systems.
• Family and marriage in
India.
• Household dimensions
of the family.
• Patriarchy, entitlements
and sexual division of
labour
8) Religion and Society • Religious communities COVERED WITH
in India PAPER 1
• Problems of religious
minorities
9) Social Change in • Idea of development COVERED WITH
India planning and mixed PAPER 1
economy.
• Constitution, law and
social change.
• Education and social
change.
10) Rural and Agrarian • Programmes of rural 23 Feb - 26Feb
Transformation in development,
India Community Development
Programme,
cooperatives, poverty
alleviation schemes.
• Green revolution and
social change.
• Changing modes of
production in Indian
agriculture .
• Problems of rural labour,
• bondage,migratio
Paper Chapter Sub Topic Status
PAPER - 2 11) Industrialisation • Evolution of modern 27 Feb - 1 March
and Urbanisation in industry in India.
India • Growth of urban
settlements in India.
• Working class: structure,
growth, class
mobilization.
• Informal sector, child
labour.
• Slums and deprivation in
urban areas.
12) Politics and • Nation, democracy and COVERED WITH
Society citizenship. PAPER 1
• Political parties,
pressure groups , social
and political elite.
• Regionalism and
decentralization of
power.
• Secularization
13) Social • Peasants and farmers 2 March - 4March
Movements in India movements.
• Women’s movement.
• Backward classes & Dalit
movement.
• Environmental
movements.
• Ethnicity and Identity
movements.
14) Population Dynamics • Population size, growth, 6 March - 8 March
composition and
distribution.
• Components of
population growth: birth,
death, migration.
• Population policy and
family planning.
• Emerging issues:
ageing, sex ratios, child
and infant mortality,
reproductive health.
Paper Chapter Sub Topic Status
PAPER - 2 15) Challenges of Social • Crisis of development: 9 March - 12 March
Transformations displacement,
environmental problems
and sustainability.
• Poverty, deprivation and
inequalities.
• Violence against women.
• Caste conflicts.
• Ethnic conflicts,
communalism, religious
revivalism.
• Illiteracy and disparities
in education.
Price: 17,999
₹13,999
m 080-6897-3353 k contact@studyiq.com
You might also like
- UPSC Mains Sociology Test SeriesDocument6 pagesUPSC Mains Sociology Test Seriesamol maliNo ratings yet
- Paper-1: Topic Day 1. Sociology: The DisciplineDocument4 pagesPaper-1: Topic Day 1. Sociology: The Disciplinesujeet100% (1)
- ISC Sociology SyllabusDocument13 pagesISC Sociology SyllabusBIPAS_DHARNo ratings yet
- ISC Sociology PDFDocument13 pagesISC Sociology PDFAdrija SenNo ratings yet
- Upsc Ias: Socio OgyDocument6 pagesUpsc Ias: Socio OgyKadwa Sach0% (2)
- AERS Theoretical Framework and DesignDocument34 pagesAERS Theoretical Framework and DesignJubel Jetro PontuyaNo ratings yet
- ISC Sociology XI RevisedDocument5 pagesISC Sociology XI RevisedMeenakshi DasNo ratings yet
- A. Distinguishing The Nature, Goals and Perspectives of Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceDocument2 pagesA. Distinguishing The Nature, Goals and Perspectives of Anthropology, Sociology and Political ScienceGabriella OrdizNo ratings yet
- Sociology Syllabus Grade IX 2021-22Document9 pagesSociology Syllabus Grade IX 2021-22Aisha MuneerNo ratings yet
- Sociology: Perspective, Theory, and MethodDocument25 pagesSociology: Perspective, Theory, and MethodKushNo ratings yet
- Qualitative & Quantitative ApproachDocument21 pagesQualitative & Quantitative Approachsunit dasNo ratings yet
- Sociology For Competitive Exams: Sarfraz Hussain Ansari (Pa&As) CSP BCS, MPA, FPFA, SAP-FI Consultant 0321-4912664Document41 pagesSociology For Competitive Exams: Sarfraz Hussain Ansari (Pa&As) CSP BCS, MPA, FPFA, SAP-FI Consultant 0321-4912664Mehvish Akbar ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Social ResearchDocument7 pagesSocial ResearchLavanya BinduNo ratings yet
- Session 4Document18 pagesSession 4sunit dasNo ratings yet
- Howe's Taxonomy of Social Work ParadigmsDocument79 pagesHowe's Taxonomy of Social Work ParadigmsSamantha292000No ratings yet
- Kopio - Learning PortfolioDocument14 pagesKopio - Learning PortfolioTrương Quốc HuyNo ratings yet
- DIASS MODULE 1 Social Sciences and Applied Social Sciences PDFDocument4 pagesDIASS MODULE 1 Social Sciences and Applied Social Sciences PDFBeltran, Andrea Nicole E.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Sociology (APSO-111) PDFDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Sociology (APSO-111) PDFIsrar BalochNo ratings yet
- ClassifyingtheworldDocument4 pagesClassifyingtheworldapi-337646087No ratings yet
- Nature Scope Defintion of SociologyDocument29 pagesNature Scope Defintion of SociologyVikram BijNo ratings yet
- Emmanuel S. Caliwan: 1 Can Be Either Oral, Written or BothDocument7 pagesEmmanuel S. Caliwan: 1 Can Be Either Oral, Written or BothDevika KhanNo ratings yet
- Materi Strategi Penelitian KualiDocument49 pagesMateri Strategi Penelitian KualiDiyah Ayu Amalia AvinaNo ratings yet
- ISC SociologyDocument13 pagesISC Sociologysamadrita dasNo ratings yet
- Uses and Gratifications Theory 1 Uses An PDFDocument13 pagesUses and Gratifications Theory 1 Uses An PDFAliAwaisNo ratings yet
- 75 Days Mains Revision Plan Time TableDocument22 pages75 Days Mains Revision Plan Time TableGourav BooraNo ratings yet
- Research ParadigmsDocument17 pagesResearch ParadigmsSyed Ahmed100% (1)
- Unit 1: Inquisitive World of Research Main Idea: Research Manifests in Everyday Life Essential Question: What Is Research All About? Research Paradigm Approaches To Qualitative ResearchDocument2 pagesUnit 1: Inquisitive World of Research Main Idea: Research Manifests in Everyday Life Essential Question: What Is Research All About? Research Paradigm Approaches To Qualitative Researchanna mae orcioNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lecture 1: Introduction To MethodologyDocument36 pagesWeek 2 Lecture 1: Introduction To MethodologyPrincehopeNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1: Andreve John L. RebuciasDocument43 pagesPractical Research 1: Andreve John L. RebuciasAndreve john RebuciasNo ratings yet
- Modern Theory 2014 20140122Document3 pagesModern Theory 2014 20140122Umair MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Role of Theories in ResearchDocument18 pagesLecture 2 Role of Theories in ResearchwinnieNo ratings yet
- Introduction B 01032023 094734am 03102023 022910pmDocument25 pagesIntroduction B 01032023 094734am 03102023 022910pmhuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Lec 2, Intro To IRDocument43 pagesLec 2, Intro To IRAli DostNo ratings yet
- Week 5Document39 pagesWeek 5narsapufukNo ratings yet
- Natureandfunctionsofthesocialsciences 220904111504 De89ce82 PDFDocument50 pagesNatureandfunctionsofthesocialsciences 220904111504 De89ce82 PDFShē FæëlnärNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document25 pagesUnit 1Chandan DasNo ratings yet
- Xiii Xiv XV Xvi Xvii Xviii Xix XX Xxi Xxii: IdentityDocument3 pagesXiii Xiv XV Xvi Xvii Xviii Xix XX Xxi Xxii: IdentityJuan Pablo Bermudez VargasNo ratings yet
- Sma4801 Lu1 Introduction To ResearchDocument10 pagesSma4801 Lu1 Introduction To ResearchMolepa Isaac SeabelaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Theory in Research: Theoretical and Conceptual FrameworksDocument15 pagesThe Role of Theory in Research: Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworkssaad aliNo ratings yet
- Neha Bhosle - Sociology Optional Notes - Paper 1 PDFDocument371 pagesNeha Bhosle - Sociology Optional Notes - Paper 1 PDFya ghg100% (1)
- Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchDocument22 pagesQuantitative and Qualitative ResearchMansoor ZainNo ratings yet
- Unit 1:: Emergence of The Social SciencesDocument39 pagesUnit 1:: Emergence of The Social Sciencesrain estrelNo ratings yet
- Mgsu MaDocument11 pagesMgsu Majagjeet singhNo ratings yet
- Pol. Science and International RelationsDocument6 pagesPol. Science and International Relationsm3gp13 yo20% (10)
- MGT 410 Organziational Behavior: - Expectations - Syllabus - Overview - Chapter 1Document15 pagesMGT 410 Organziational Behavior: - Expectations - Syllabus - Overview - Chapter 1ANUJ SAINNo ratings yet
- NOA Sociology 01Document39 pagesNOA Sociology 01Nazrat AnemNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Types and Examples of Research in Different AreasDocument23 pagesLesson 5 Types and Examples of Research in Different AreasKyle DomingoNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ReviewerDocument21 pagesUcsp ReviewerJAYZEL VIBARNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - 2022 - Theory - Durkheim - StrainDocument44 pagesWeek 1 - 2022 - Theory - Durkheim - StrainTara ツNo ratings yet
- Social Science Class: University of Cebu Pri - Main Shs SchoolDocument18 pagesSocial Science Class: University of Cebu Pri - Main Shs SchoolDee Cyree RusiaNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Reasearch - Dr. Siti ParianiDocument26 pagesQualitative Reasearch - Dr. Siti ParianiChandra PNo ratings yet
- CIDAM - WIW MAP DissDocument4 pagesCIDAM - WIW MAP DissKIRIL Eyti100% (1)
- Social Theory, Perspective, & Method2Document44 pagesSocial Theory, Perspective, & Method2Jonah StroupNo ratings yet
- Ie 1Document7 pagesIe 1soheila savarNo ratings yet
- Ucsp CM Grade 11 PDFDocument14 pagesUcsp CM Grade 11 PDFSheila Marie DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Culture, Value, NormsDocument44 pagesWeek 1 Culture, Value, Normsion jinNo ratings yet
- T.1 Epistemology of Social Sciences and Values in Educational ProcessDocument15 pagesT.1 Epistemology of Social Sciences and Values in Educational ProcessLucía Olmo de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Material Covered in Quiz 1 (Kısa Sınav 1) : - Lessons 01, 02, 03, 04 - Structure of The TestDocument5 pagesMaterial Covered in Quiz 1 (Kısa Sınav 1) : - Lessons 01, 02, 03, 04 - Structure of The TestgulsumNo ratings yet
- Research Methods in Criminal Justice and Criminology: An Interdisciplinary ApproachFrom EverandResearch Methods in Criminal Justice and Criminology: An Interdisciplinary ApproachNo ratings yet
- List SiswaDocument49 pagesList SiswaNovita HayatiNo ratings yet
- TN History 11th Class Updated Volume 2 PDFDocument179 pagesTN History 11th Class Updated Volume 2 PDFAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Opening Reason To Transcendence - A Philosofical Grounding of ArchitectureDocument104 pagesOpening Reason To Transcendence - A Philosofical Grounding of ArchitectureVictor TironiNo ratings yet
- Inona No Tena Mahasambatra Ny Fianakaviana?Document2 pagesInona No Tena Mahasambatra Ny Fianakaviana?Rivo RoberalimananaNo ratings yet
- Indian Psychology by MadhuDocument3 pagesIndian Psychology by MadhuSmita DasNo ratings yet
- OSSM HandbookDocument227 pagesOSSM Handbooktorozco2100% (2)
- Critical Analysis ' The World Is Too Much With Us.Document4 pagesCritical Analysis ' The World Is Too Much With Us.MsM Yaqoob100% (1)
- A System of Sand DivinationDocument5 pagesA System of Sand DivinationKali KlmNo ratings yet
- PLAN40 LessonDocument25 pagesPLAN40 LessonJovelyn A. Maliza100% (2)
- Muslim Saints of South IndiaDocument267 pagesMuslim Saints of South IndiaMohammed Abdul Hafeez, B.Com., Hyderabad, IndiaNo ratings yet
- Fr. Justin ThesisDocument132 pagesFr. Justin ThesisQasha Justin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Medieval PhilosophyDocument39 pagesMedieval PhilosophyJorhen PanisNo ratings yet
- Pulwama Attack (Final Draft) PDFDocument17 pagesPulwama Attack (Final Draft) PDFAshutosh Kumar100% (1)
- Waiting On God's TimingDocument2 pagesWaiting On God's TimingAnastasiafynnNo ratings yet
- The Waqf and The Public Sphere Miriam HoexterDocument20 pagesThe Waqf and The Public Sphere Miriam HoexterMathias Jalfim MaraschinNo ratings yet
- Kal Am PattuDocument4 pagesKal Am PattusingingdrumNo ratings yet
- IAS Gurukul Test Series & Daily Answer Writing Schedule h2Document3 pagesIAS Gurukul Test Series & Daily Answer Writing Schedule h2Nandan BansalNo ratings yet
- Birth Chart Stuff PDFDocument19 pagesBirth Chart Stuff PDFanaNo ratings yet
- Vidarshana Bawana Kramaya Buddhist MeditationDocument231 pagesVidarshana Bawana Kramaya Buddhist Meditationසසුන් කෙත අස්වැද්දුම93% (27)
- Let Go and Let God...Document28 pagesLet Go and Let God...jemalexisclementeNo ratings yet
- Ethics Final ReviewerDocument6 pagesEthics Final ReviewerDyne OdyanaraNo ratings yet
- Names & Titles of Jesus in Alphabetical OrderDocument2 pagesNames & Titles of Jesus in Alphabetical Orderncmodular67% (3)
- Shortened Maianne Dacy Jewish Influence On Early Christian LiturgyDocument6 pagesShortened Maianne Dacy Jewish Influence On Early Christian LiturgyTomDokNo ratings yet
- Biography of Fazlul Huq PDFDocument3 pagesBiography of Fazlul Huq PDFsamia haqNo ratings yet
- The Stages of Spiritual Growth Jul 26 2019Document12 pagesThe Stages of Spiritual Growth Jul 26 2019Janyson Ferreira100% (1)
- Cause and Effect EssayDocument2 pagesCause and Effect EssayPan YoonNo ratings yet
- List of Political Ideologies: AnarchismDocument106 pagesList of Political Ideologies: AnarchismBenjamin KonjicijaNo ratings yet
- Lord You Are Good LyricsDocument1 pageLord You Are Good Lyricskenman7777No ratings yet
- Swarna Akarshana Bhairava MantraDocument5 pagesSwarna Akarshana Bhairava Mantranavinnaithani100% (1)
- TCW Midterms ReviewerDocument6 pagesTCW Midterms ReviewerZhyra ManaloNo ratings yet