Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eng Reviewer 3rdq
Uploaded by
Michaela Loraine BarbastroOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eng Reviewer 3rdq
Uploaded by
Michaela Loraine BarbastroCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
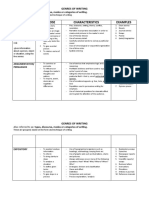
THE STAGES OF WRITING
P-rewriting WRITING (DRAFTING)
O-utlining The writer uses the organized information and
turn it to a series of paragraphs for the essay
W-riting
E-diting
EDITING STAGE
R-ewriting (PROOFREADING)
The writer reads their draft and looks for errors
(COPS)
PREWRITING (PLANNING)
-Capitalization
The writer gathers information for their essay.
-Organization
-Brainstorming
-Punctuation
-Concept mapping
-Spelling
-Researching
REWRITING STAGE
OUTLINING (ORGANIZING)
(PUBLISHING)
The writer sorts their ideas to see if their
The writer changes the draft after considering the
thoughts are organized
errors, and finally writes again the essay
-Introduction
-Body
-Conclusion
COHERENCE AND COHENSION
To achieve organization of ideas, we should have
coherent sentences and paragraphs
:The coherence of an essay depends on order of
ideas and use of cohesive devices to link the
sentences
COHESIVE DEVICES (TRANSITION WORDS)
Use to connect sentences, it helps establish the
relationship among ideas
2. TOULMIN METHOD (for HOOK
argumentative essay)
Techniques in writing the introduction
Logical Method of
1. ANECDOTE
Reasoning
Share a related story
BY: Stephen e. toulmin 2. DEFINITION
Define an important term
3. QUOTATION
Use a saying
Parts of toulmin:
4. QUESTIONS
A. INTRODUCTION Use series of questions
5. ANALOGY
1. CLAIM
Relate connected ideas
B. BODY 6. TRIVIA
Use interesting ideas
1. DATA 7. STATISTICS
Use interesting ideas
2. WARRANT
3. BACKING BODY
C. CONCLUSION DATA (CITATION)
1. COUNTER CLAIM Evidence supporting your claim
2. REBUTTAL WARRANT (REASON)
Explanation of the data
BACKING (OPTIONAL)
Elaboration of the warrant
INTRODUCTION
CONCLUSION
Claim
COUNTER CLAIM (COUNTER)
Value position
Disagreement to the claim
-Agree
REBUTTAL
-Disagree
Disagreement to the counter, reiteration of claim
3. TYPES OF TEXTS PLAIN FOLKS (ORDINARY
PEOPLE)
P - PERSUASIVE
It implies that regular people can be relatable
I - INFORMATIVE
#i can relate to this!
A – ARGUMENTATIVE TESTIMONIAL (CELEBRITIES)
It uses a famous person to influence the audience
PERSUASIVE #i trust celebrities and experts!
- To convince LOADED LANGUAGE
(OFFERS/PROMISES)
- To persuade
It highlights positive words
INFORMATIVE
#those words are powerful!
- To give information
- To educate EMOTIONAL APPEAL (STRONG
FEELINGS)
ARGUMENTATIVE
Uses words that evoke strong feelings
- To express opinion #so much feels
- - to argue
ETHICAL APPEAL (MORAL
STANDARD)
4. PROPAGANDA TECHNIQUES It taps into people’s values
WHAT? #The way to do good, for good
- The act of convincing someone to do something NAME CALLING (COMPARISON)
HOW? It is a contrast style of persuation that creates
negative impact to other brand
- In order to convince people, persuasive
techniques are used #Brand X VS Brand Y
BANDWAGON (MAJORITY) TRANSFER (CONNECTIONS)
It is used to influence people by telling them that It links a positive attribute to the product to create
they should be part of the majority a favourable effects to the audience
#Everyone else is doing it! #connections
5. CRITIQUE REVIEW 6. LITERARY CRITICISM
It is a method used to interpret any given
Is a serious examination and judgement, giving
work of literature
critical commentary on the quality of a text
- Objective How does literary criticism work?
- Unbiased - Literary Lens (Approach)
- Review - Literature
- Literary criticism
What can we critique?
STRUCTURALISM (Claude
STORIES Levi-Strauss)
Novels, fairy tales, myths, fables, anime, manga It focuses on form of language to understand the
text. Form over content
NON-FICTION
-grammar
Essays, anecdotes, biographies, documentaries
-vocabulary
POETRY
-language
Epic, ballad, songs, sonnets, elegy, comedy, tragedy
FORMALISM (John Crowe
MOVIES
Ransom)
Films, short clips, videos
“New Criticism.” Only focuses on its elements and
literary devices are analyse
STEPS -Direct critique
D.A.I.A MORALISM (Plato)
Teaches values, morals, ethics, and virtues to its
audience.
DESCRIBE
#LessonLearned
- Present the background
MARXISM (Karl Marx)
ANALYZE
Exhibits how social and economic aspects
- Examine the parts for the meaning
contribute to the struggle in power considering the
INTERPRET social classes
- State the important points #PoorvsRich
ASSESS FEMINISM (Simone De
Beauvoir)
- Judge or criticize
Focuses on how the female characters are treated
in the given literature
HISTORICAL (Michaela
Foucault)
“Biographical.” The background of the author as a
factor in text creation
#Author’s Background
READER-RESPONSE ( Martin
Heidegger)
Own viewpoint in response to the author
#personalcriticism
You might also like
- 2016 Long Range Plans-G. 3-4Document2 pages2016 Long Range Plans-G. 3-4trixalexaNo ratings yet
- Properties of A Well Writen TextDocument21 pagesProperties of A Well Writen TextnvargasNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical ModesDocument14 pagesRhetorical ModesTopPrizeAlbumNo ratings yet
- Rws Lesson Week 1.1: "Definition of Discourse" DISCOURSE-derived From "Discurses" inDocument13 pagesRws Lesson Week 1.1: "Definition of Discourse" DISCOURSE-derived From "Discurses" indivinegrace.cruz.mnlNo ratings yet
- GRADE 8 UNIT PLAN 3rd QDocument10 pagesGRADE 8 UNIT PLAN 3rd QKrystlene Anne GallardoNo ratings yet
- Eng ReviewerDocument4 pagesEng ReviewerYasha DumplyngNo ratings yet
- Bloom S TaxonomyDocument6 pagesBloom S TaxonomyBeatriz GaleraNo ratings yet
- English 20 & 30 Skills & Curriculum - 1Document3 pagesEnglish 20 & 30 Skills & Curriculum - 1api-439626674No ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1VANESSA KEITH CARONNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Charlie Ferrer EstradaNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking Innovative Thinking Empathy Resilience Teamwork CommunicationDocument5 pagesCritical Thinking Innovative Thinking Empathy Resilience Teamwork CommunicationmauNo ratings yet
- Reading and WritingDocument4 pagesReading and WritingJelian MontenegroNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W2Kathlyn PerezNo ratings yet
- Yr 5 Whole Curriculum MapDocument5 pagesYr 5 Whole Curriculum Mapangela_harper6112No ratings yet
- Timedwriteessayforunit5 IndependentreadingDocument2 pagesTimedwriteessayforunit5 Independentreadingapi-254762267No ratings yet
- ENGLISH REVIEWER 3rdDocument3 pagesENGLISH REVIEWER 3rdclairowrightsNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1mikee vicmudoNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument3 pagesENGLISHKinsin ChowNo ratings yet
- Jab Post Qeof Dag ArgumentDocument3 pagesJab Post Qeof Dag Argumentapi-375829917No ratings yet
- Genres of WritingDocument2 pagesGenres of WritingJada JohnNo ratings yet
- Week 3 English 8 and 10 Very FinalDocument6 pagesWeek 3 English 8 and 10 Very FinalCristy Gasco SumpayNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1PieNo ratings yet
- My Curriculum MatrixDocument17 pagesMy Curriculum MatrixBuctuan JaneNo ratings yet
- 1ST SEM Midterms RNWDocument4 pages1ST SEM Midterms RNWUnknown WandererNo ratings yet
- Eng QTDocument3 pagesEng QTAnne Clarrise KilmeNo ratings yet
- DLL English 6 q1 w1 OkDocument10 pagesDLL English 6 q1 w1 OkSELYN MONTAJESNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Sonny Mar LomaNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Jeanne MioleNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Melanie DucalangNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1kriella hyacinthNo ratings yet
- Progressive Drama CriteriaDocument7 pagesProgressive Drama Criteriaapi-264819644No ratings yet
- Analyzing NonfictionDocument65 pagesAnalyzing NonfictionRickenbach_Law100% (1)
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W2Document8 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W2SHELLA MARIE MANAHANNo ratings yet
- Writing Reports at Level 3Document27 pagesWriting Reports at Level 3Lily FakhreddineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in RawsDocument11 pagesReviewer in RawsAngela EronicoNo ratings yet
- Objecti Ves-Facts Subjecti Ve - Opinion S: Sensory DetailsDocument2 pagesObjecti Ves-Facts Subjecti Ve - Opinion S: Sensory DetailsDebil DimunyuNo ratings yet
- Narrative Task Sheet 2023Document4 pagesNarrative Task Sheet 2023Jared PantsiosNo ratings yet
- Assessment ScheduleDocument2 pagesAssessment ScheduleDanielle ColeNo ratings yet
- English HandoutDocument3 pagesEnglish HandoutJobed EspantoNo ratings yet
- 2023 Section 2 Essay Feedback - AudenDocument2 pages2023 Section 2 Essay Feedback - AudenAlbert DengNo ratings yet
- Module 16Document18 pagesModule 16PEARL JOY QUEBRARNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitledMa. Leiah Ericka De ChavezNo ratings yet
- Remixed LessonDocument4 pagesRemixed LessonChris WebbNo ratings yet
- LR Post Qeof Dag ArgumentDocument3 pagesLR Post Qeof Dag Argumentapi-3758299170% (1)
- Eng8 Wk4.1Document8 pagesEng8 Wk4.1Jepoy D VloggerNo ratings yet
- DLL - MTB 1 - Q3 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - MTB 1 - Q3 - W1Jemima joy antonioNo ratings yet
- Muet Scheme of Work 2011Document2 pagesMuet Scheme of Work 2011faizaraz100% (1)
- DifferentationDocument22 pagesDifferentationmarinel de claroNo ratings yet
- Eng8 Wk4.2Document8 pagesEng8 Wk4.2Jepoy D VloggerNo ratings yet
- Eng8 Wk6Document4 pagesEng8 Wk6Jepoy D VloggerNo ratings yet
- Eapp 3Document4 pagesEapp 3daniNo ratings yet
- October 17 - 21, 2022Document4 pagesOctober 17 - 21, 2022Anthony Gio L. AndayaNo ratings yet
- Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson LogDocument7 pagesMonday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: GRADES 1 To 12 Daily Lesson Logmark dotonNo ratings yet
- DLL English-6 Q1 W1Document7 pagesDLL English-6 Q1 W1Hesed MendozaNo ratings yet
- DLL July 18-22Document14 pagesDLL July 18-22JhuvzCLunaNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document7 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1JAYCEE GONZALESNo ratings yet
- DLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - English 6 - Q1 - W1Lopez Rhen DaleNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment Template 2Document3 pagesPre-Assessment Template 2api-405145876No ratings yet
- AP Language Rhetorical Analysis Setup ResourceDocument9 pagesAP Language Rhetorical Analysis Setup ResourceLakshmy menonNo ratings yet
- A Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasFrom EverandA Portfolio of Reflections: Reflection Sheets for Curriculum AreasNo ratings yet
- Let'S Try This Activity 2: #Respectisamust: Malabayabas, Juliana M. 11-Convivial Homeroom ModuleDocument1 pageLet'S Try This Activity 2: #Respectisamust: Malabayabas, Juliana M. 11-Convivial Homeroom Modulelalaluuu minNo ratings yet
- What Are The Important Stipulations in Magna Carta For Teachers and The Code of Ethics For Professional Teachers?Document1 pageWhat Are The Important Stipulations in Magna Carta For Teachers and The Code of Ethics For Professional Teachers?Junnel CasanovaNo ratings yet
- Mission Vision and ValuesDocument12 pagesMission Vision and ValuesGso ParañaqueNo ratings yet
- Exam 2019 Questions and AnswersDocument19 pagesExam 2019 Questions and AnswersĐạt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 2016 Financial Industry Cybersecurity Report: SecurityscorecardDocument22 pages2016 Financial Industry Cybersecurity Report: SecurityscorecardHiba AfanehNo ratings yet
- 15 Points Seafarers Should Consider For Successful MLCDocument4 pages15 Points Seafarers Should Consider For Successful MLCTimoty James Paulin100% (1)
- Hi-Tea Menu PackageDocument32 pagesHi-Tea Menu PackageRupesh GuravNo ratings yet
- War Memoirs 1917 - 1919 PDFDocument322 pagesWar Memoirs 1917 - 1919 PDFMauro Nahuel100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Global Marketing Plus 2014 Mymarketinglab With Pearson Etext Package 8 e Warren J Keegan Mark C Green Full DownloadDocument24 pagesSolution Manual For Global Marketing Plus 2014 Mymarketinglab With Pearson Etext Package 8 e Warren J Keegan Mark C Green Full Downloadcarlyterrysnycxdekbz100% (42)
- The Effects of Smartphone Addiction To The Mental Health Among Nursing StudentsDocument59 pagesThe Effects of Smartphone Addiction To The Mental Health Among Nursing StudentsJustine CagatanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Freedom by MacSwiney, Terence J. (Terence Joseph), 1879-1920Document72 pagesPrinciples of Freedom by MacSwiney, Terence J. (Terence Joseph), 1879-1920Gutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- AP US History Cram Chart 2021Document1 pageAP US History Cram Chart 2021Aubrey BalesNo ratings yet
- WritDocument4 pagesWritKathryn20% (1)
- Flying Tiger CopenhagenDocument3 pagesFlying Tiger CopenhagenWan ShahrilNo ratings yet
- SANIDAD v. AGUASDocument2 pagesSANIDAD v. AGUASMarinette OndaNo ratings yet
- Module 7 CVP Analysis SolutionsDocument12 pagesModule 7 CVP Analysis SolutionsChiran AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Corporate Opportunity Doctrine: An Impediment To Corporate InnovationDocument37 pagesCorporate Opportunity Doctrine: An Impediment To Corporate InnovationOluseun AdesanyaNo ratings yet
- Starbuck's Case - CRM - Jonas KocherDocument3 pagesStarbuck's Case - CRM - Jonas Kocherleni thNo ratings yet
- Character Analysis of PearlDocument5 pagesCharacter Analysis of PearlMadysen100% (3)
- YM Website - User Manual: BookingDocument19 pagesYM Website - User Manual: Bookingwinda hervianaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Overview of Satellite Systems PDFDocument21 pages01 - Overview of Satellite Systems PDFAhmed RiyadNo ratings yet
- Word Formation - Olp2016 (Made by Na)Document2 pagesWord Formation - Olp2016 (Made by Na)NaNo ratings yet
- Submission of List of All Recognized School Co-Curricular and Extra-Curricular Clubs and OrganizationsDocument5 pagesSubmission of List of All Recognized School Co-Curricular and Extra-Curricular Clubs and OrganizationsCHAPEL JUN PACIENTENo ratings yet
- Law of Evidence 2021course OutlineDocument11 pagesLaw of Evidence 2021course OutlineJiaNo ratings yet
- Vikram Sarabhai Library: New Arrivals (Books)Document10 pagesVikram Sarabhai Library: New Arrivals (Books)ds ram sktNo ratings yet
- M.Ed Entrance Sample Model Question Paper Ans ErsDocument19 pagesM.Ed Entrance Sample Model Question Paper Ans Erssubhas9804009247No ratings yet
- Mortgage ProjectDocument8 pagesMortgage Projectrmbj94_scribd100% (1)
- Examining The Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory of Motivation of BabyDocument9 pagesExamining The Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory of Motivation of Babyseventh skyeNo ratings yet
- Mahalakshimpuram WestDocument3 pagesMahalakshimpuram Westrt prepNo ratings yet
- Alfonso v. Land Bank of The Phils. - MendozaDocument1 pageAlfonso v. Land Bank of The Phils. - MendozaDonna Mendoza100% (1)