0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views4 pagesIntangible Assets
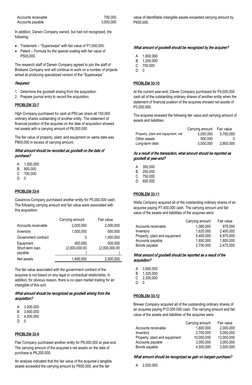
1. Judicature Company purchased an entity for $7.5 million. The fair value of assets acquired was $4.6 million and liabilities assumed were $1.9 million. Compute the amount of goodwill under 3 methods.
2. Java Company purchased an entity for $6 million. Determine goodwill using residual method and record the acquisition.
3. Mayer Company purchased an entity for $8 million. Determine goodwill and record the acquisition.
Uploaded by
Dianna DayawonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views4 pagesIntangible Assets
1. Judicature Company purchased an entity for $7.5 million. The fair value of assets acquired was $4.6 million and liabilities assumed were $1.9 million. Compute the amount of goodwill under 3 methods.
2. Java Company purchased an entity for $6 million. Determine goodwill using residual method and record the acquisition.
3. Mayer Company purchased an entity for $8 million. Determine goodwill and record the acquisition.
Uploaded by
Dianna DayawonCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
- Problem 33-1 to 33-36