Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vol 6 Ascorbic Acid
Uploaded by
regdddOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vol 6 Ascorbic Acid
Uploaded by
regdddCopyright:
Available Formats
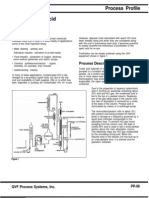
Eighty percent of the world's supply of ascorbic acid is produced in China.
[20]
Ascorbic acid is prepared in industry from glucose in a method based on the
historical Reichstein process. In the first of a five-step process, glucose is
catalytically hydrogenated to sorbitol, which is then oxidized by the microorganism
Acetobacter suboxydans to sorbose. Only one of the six hydroxy groups is oxidized
by this enzymatic reaction. From this point, two routes are available. Treatment of
the product with acetone in the presence of an acid catalyst converts four of the
remaining hydroxyl groups to acetals. The unprotected hydroxyl group is oxidized to
the carboxylic acid by reaction with the catalytic oxidant TEMPO (regenerated by
sodium hypochlorite � bleaching solution). Historically, industrial preparation via
the Reichstein process used potassium permanganate as the bleaching solution. Acid-
catalyzed hydrolysis of this product performs the dual function of removing the two
acetal groups and ring-closing lactonization. This step yields ascorbic acid. Each
of the five steps has a yield larger than 90%.[21]
You might also like
- Creating A Trading Plan EminiMindDocument37 pagesCreating A Trading Plan EminiMindregddd50% (2)
- CH3-CH-OH CoohDocument105 pagesCH3-CH-OH CoohAniket GawdeNo ratings yet
- Lipid Biosynthesis: Medical BiochemistryDocument22 pagesLipid Biosynthesis: Medical BiochemistryGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Tca CycleDocument29 pagesTca CycleShovana DeyNo ratings yet
- Krebs CycleDocument26 pagesKrebs CycleTanChiaZhiNo ratings yet
- L004 - Ritik Jain - MSDocument6 pagesL004 - Ritik Jain - MSritikNo ratings yet
- Organic Acid AssignmentDocument8 pagesOrganic Acid AssignmentHamza MalikNo ratings yet
- AlkylationDocument9 pagesAlkylationabhishek sharma100% (1)
- TCA Cycle PPT LecDocument52 pagesTCA Cycle PPT LecjaveriaNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid MetabolismDocument28 pagesFatty Acid MetabolismPrakash KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Arease: Nov. 8, 1966 W. Wogt Et Al 3,284,495 Process For The Continuous Manufacture, Purification andDocument3 pagesArease: Nov. 8, 1966 W. Wogt Et Al 3,284,495 Process For The Continuous Manufacture, Purification andRachmad HermawanNo ratings yet
- Lipid BiosynthesisDocument187 pagesLipid BiosynthesisThanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Tca CycleDocument29 pagesTca Cyclefatimamuzammil406No ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument10 pagesBeta OxidationAiane Gramatica100% (1)
- A01 269Document11 pagesA01 269icingrockNo ratings yet
- 0304 S1 Abs PDFDocument7 pages0304 S1 Abs PDFFajar RumantoNo ratings yet
- Genbio Group 5 Kreb CycleDocument27 pagesGenbio Group 5 Kreb CycleSophia PacatangNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument34 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty AcidsZelda LoverNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism-Sk SirDocument6 pagesLipid Metabolism-Sk SirSubrata KunduNo ratings yet
- Star Control - Acetic Acid ProductionDocument3 pagesStar Control - Acetic Acid ProductionHisyamAl-MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of VanillinDocument2 pagesSynthesis of VanillinaizatNo ratings yet
- The Krebs CycleDocument21 pagesThe Krebs CycleMusonda MulengaNo ratings yet
- Lec - 9 - Citric AcidDocument12 pagesLec - 9 - Citric AcidTarequl Islam NishadNo ratings yet
- Topical and Prospective Processes of Acetoxylation: Grzegorz Lewandowski, Marcin Bartkowiak, Eugeniusz MilchertDocument6 pagesTopical and Prospective Processes of Acetoxylation: Grzegorz Lewandowski, Marcin Bartkowiak, Eugeniusz MilchertAnonymous b9fcR5No ratings yet
- United States Patent 0: '3, l50, l74 ICCDocument2 pagesUnited States Patent 0: '3, l50, l74 ICCMuhammadAmdadulHoqueNo ratings yet
- BCH242-BCH252 2021 Lipid MetabDocument37 pagesBCH242-BCH252 2021 Lipid MetabEmmanuella OffiongNo ratings yet
- Caprolactam Process DescriptionDocument8 pagesCaprolactam Process DescriptionJohannah Jane Abuel100% (2)
- 835 Thermal - Ketonization.mechanism - And.scopecc88Document10 pages835 Thermal - Ketonization.mechanism - And.scopecc88Jaipratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument21 pagesCitric Acid CycleKunda JosephNo ratings yet
- Design Report 1Document12 pagesDesign Report 123vikenNo ratings yet
- Glycerol Acetylation 1Document224 pagesGlycerol Acetylation 1Matheus ZimermannNo ratings yet
- Monoricinolein DensityDocument8 pagesMonoricinolein DensityGanesh Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Liquid-Liquid Phase Equilibria For Reactive Extraction of Lactic Acid With Organophosphorus SolventsDocument6 pagesInvestigation of Liquid-Liquid Phase Equilibria For Reactive Extraction of Lactic Acid With Organophosphorus Solventskudsiya firdousNo ratings yet
- Produccion de Acido Acetico A Partir de La Oxidacion de EtilenoDocument6 pagesProduccion de Acido Acetico A Partir de La Oxidacion de EtilenoBrayan CortésNo ratings yet
- The Citric Acid Cycle, Harper - Illustrated Biochemistry 26th Ed, 20031Document6 pagesThe Citric Acid Cycle, Harper - Illustrated Biochemistry 26th Ed, 20031milietofathaNo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty AcidDocument27 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty Acidnegurii hearteuNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid ProductionDocument4 pagesAcetic Acid Productionfatin_mujahidahNo ratings yet
- pp06 2Document2 pagespp06 2electroquimicaNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Saturated Fatty Acid 111Document10 pagesBiosynthesis of Saturated Fatty Acid 111ThvNo ratings yet
- TCA CYCLE - STEPS REGULATIION AND SIGNIFICANCE - Further Reference - Dr. Nguyen Van Toan (PHD)Document53 pagesTCA CYCLE - STEPS REGULATIION AND SIGNIFICANCE - Further Reference - Dr. Nguyen Van Toan (PHD)tieumymy2606No ratings yet
- Acetic AcidDocument11 pagesAcetic AcidkalyanyaminiNo ratings yet
- Krebs Cycle Part BDocument15 pagesKrebs Cycle Part BjawwadNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument15 pagesCitric Acid CycleShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Patent Asam Asetat 2015Document22 pagesPatent Asam Asetat 2015Nyimas Ulfatry100% (1)
- Chemistry 125 Laboratory 11Document5 pagesChemistry 125 Laboratory 11SmaeUBNo ratings yet
- Production of Acrylic AcidDocument20 pagesProduction of Acrylic AcidAkshay Srivastava100% (1)
- Acetic Acid ProductionDocument6 pagesAcetic Acid Productionmmoradi55No ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument25 pagesBeta OxidationManoj SigdelNo ratings yet
- Oxalicacidmanufacturing 201231154014Document18 pagesOxalicacidmanufacturing 201231154014Mg H100% (1)
- Acrylic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520 ProductionDocument8 pagesAcrylic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520 Productionapi-3714811No ratings yet
- Bio AromaticsDocument18 pagesBio AromaticsÁngeles HerreraNo ratings yet
- Production of Acrylic Acid Form Propylene: University Institute of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument41 pagesProduction of Acrylic Acid Form Propylene: University Institute of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringGaurav Spencer67% (3)
- Sorbitan Esters PlantDocument9 pagesSorbitan Esters PlantHolman SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Acido AceticoDocument13 pagesAcido Aceticoting_tatNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Body ProductionDocument4 pagesRegulation of Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Body ProductionJireh Mae CorderoNo ratings yet
- Manufacture: 1. Oxalic Acid From Sodium FormateDocument10 pagesManufacture: 1. Oxalic Acid From Sodium Formate23viken100% (1)
- PEAPEDocument4 pagesPEAPESara TalathiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document29 pagesUnit 3ASHISH K.K.No ratings yet
- Asymmetric Catalysis on Industrial Scale: Challenges, Approaches and SolutionsFrom EverandAsymmetric Catalysis on Industrial Scale: Challenges, Approaches and SolutionsHans Ulrich BlaserNo ratings yet
- Trading StructuresDocument3 pagesTrading StructuresregdddNo ratings yet
- Vol 991 EconDocument2 pagesVol 991 EconregdddNo ratings yet
- RSI CalcDocument2 pagesRSI CalcregdddNo ratings yet
- Mike MentzerDocument57 pagesMike Mentzerregddd100% (3)