Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment#4 - MEC 0326.1-2
Uploaded by
MarkJude MorlaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment#4 - MEC 0326.1-2
Uploaded by
MarkJude MorlaCopyright:
Available Formats
Mark Jude Morla
BSME 3-2
Mechanical Engineering Lab 1
Assignment 4
Mechanical Tachometer -A mechanical tachometer is a device used to measure the rotational speed of a
rotating shaft or machine part. It typically consists of a spinning flywheel or rotating disk and a series of gears
and linkages that translate the rotational motion to a display indicating the speed in RPM.
How it works?
1. Ensure that the centrifugal tachometer is suitable for the type of rotating shaft or machine part you
want to measure. Centrifugal tachometers are typically used for measuring the RPM of engines,
motors, and other rotating equipment, but they may not be suitable for very high or very low RPM
applications.
2. Mount the tachometer onto the rotating shaft or machine part. This can typically be done using a
clamp or a screw-on attachment. Make sure that the tachometer is securely mounted and that it does
not interfere with the operation of the equipment.
3. Check that the tachometer is properly calibrated for the RPM range you want to measure. Some
centrifugal tachometers have adjustable calibration settings that allow you to fine-tune the
measurement accuracy.
4. Start the equipment and bring it up to the desired RPM range. This may require adjusting the throttle
or other controls, depending on the equipment.
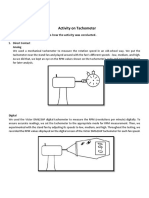
5. Hold the centrifugal tachometer close to the rotating shaft or machine part. The tachometer will use
the centrifugal force generated by the spinning to measure the RPM. It's important to hold the
tachometer steady and at a consistent distance from the rotating part to ensure accurate readings.
6. Read the RPM value from the tachometer display. Some centrifugal tachometers will have a digital
display, while others will use a mechanical dial or gauge to indicate the RPM.
You might also like
- GM Automatic Overdrive Transmission Builder's and Swapper's GuideFrom EverandGM Automatic Overdrive Transmission Builder's and Swapper's GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Vibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisFrom EverandVibration Basics and Machine Reliability Simplified : A Practical Guide to Vibration AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Atf Fault Codes PDFDocument120 pagesAtf Fault Codes PDFFatih YÜKSEL100% (3)
- Cheng Gong CG956G Service ManualDocument76 pagesCheng Gong CG956G Service ManualDanilo Marin90% (10)
- Operator’S Guide to Rotating Equipment: An Introduction to Rotating Equipment Construction, Operating Principles, Troubleshooting, and Best PracticesFrom EverandOperator’S Guide to Rotating Equipment: An Introduction to Rotating Equipment Construction, Operating Principles, Troubleshooting, and Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- SANAS Tachometer CalibrationDocument7 pagesSANAS Tachometer Calibrationpankrasius herbudi100% (1)
- TR 45-01 Criteria For Laboratories Accredited To Calibrate Tachometer and Measure Rotational SpeeedDocument7 pagesTR 45-01 Criteria For Laboratories Accredited To Calibrate Tachometer and Measure Rotational SpeeedNANDO7695100% (1)
- Break-Out Machines Level 1Document34 pagesBreak-Out Machines Level 1llereador100% (3)
- JP 580电测系统说明书(全英文3.0) 2060331 PDFDocument48 pagesJP 580电测系统说明书(全英文3.0) 2060331 PDFivan cardenas quito50% (2)
- RAS Rot2ProgDocument12 pagesRAS Rot2ProgAlen JefryNo ratings yet
- Major Process Equipment Maintenance and RepairFrom EverandMajor Process Equipment Maintenance and RepairRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Control System For Controllable Pitch Marine Propellers: Operation ManualDocument36 pagesControl System For Controllable Pitch Marine Propellers: Operation ManualGonzalez JeanNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering Design: Project ReportDocument7 pagesComplex Engineering Design: Project ReportXyed Haider BukhariNo ratings yet
- Timer of Tree Phase MotorDocument10 pagesTimer of Tree Phase MotorHaryad HewaNo ratings yet
- Sanas TR 45-03Document8 pagesSanas TR 45-03joko purwantoNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual of the Speed Controller ESG1003 Series ESG1003 系列转速控制器使用说明书Document60 pagesOperating Manual of the Speed Controller ESG1003 Series ESG1003 系列转速控制器使用说明书luis fangNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 121210210811 Phpapp02Document57 pagesChapter1 121210210811 Phpapp02sharkeraNo ratings yet
- TachometerDocument17 pagesTachometerAmrita MitraNo ratings yet
- Proposal Report For CentrifugeDocument3 pagesProposal Report For CentrifugeDinesh KatochNo ratings yet
- Tachometers: Balmaceda, Chris Francisco, MilfrenDocument15 pagesTachometers: Balmaceda, Chris Francisco, Milfrenjude100% (1)
- TRW Steering Box Service ManualDocument0 pagesTRW Steering Box Service ManualJuanLopez64Ch100% (1)
- AHRI Guideline G IP 2016Document11 pagesAHRI Guideline G IP 2016Muhammad IqbaalNo ratings yet
- Speed Measuring DevicesDocument6 pagesSpeed Measuring DevicesralphNo ratings yet
- Report - VHDL TachometerDocument28 pagesReport - VHDL TachometerShaunak De100% (2)
- Using Orbits For Condition MonitoringDocument4 pagesUsing Orbits For Condition MonitoringMuhtiarNo ratings yet
- Install Troubshoot ManDocument19 pagesInstall Troubshoot ManMohamed MabroukNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance HandbookDocument868 pagesOperation and Maintenance HandbooksadruelNo ratings yet
- Outcome Based Lab Task Report: To Identify The Suitable Motor To Control Hard Disk DriveDocument14 pagesOutcome Based Lab Task Report: To Identify The Suitable Motor To Control Hard Disk DriveSUSEENDRAN VNo ratings yet
- Renr8482-07-01-All-Power Train-SystemDocument108 pagesRenr8482-07-01-All-Power Train-Systemwilly12345120% (1)
- Servo Motor and Servo MechanismDocument11 pagesServo Motor and Servo MechanismkloirywbdNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Motor ControlDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Electric Motor Contrololanvillegas2003No ratings yet
- Term Paper On Explain About The Balancing of MachinesDocument16 pagesTerm Paper On Explain About The Balancing of MachinesAshish VaniyaNo ratings yet
- TachoDocument3 pagesTachoAbhisek PurohitNo ratings yet
- Pumpsmart: Configuration & Operation GuideDocument177 pagesPumpsmart: Configuration & Operation GuideIgor ChavarríaNo ratings yet
- TechtipstachometersDocument1 pageTechtipstachometersSweta SipraNo ratings yet
- Servo MotorsDocument8 pagesServo MotorsFairos ZakariahNo ratings yet
- SGT Torque Converter Governor: Supplement To Manual 04048Document24 pagesSGT Torque Converter Governor: Supplement To Manual 04048pcatruongNo ratings yet
- S30i - S31i - S32i Handbook B63947 En01 - v1Document432 pagesS30i - S31i - S32i Handbook B63947 En01 - v1nandopiol100% (1)
- S30i S31i S32i Handbook B63947 En01 v2Document472 pagesS30i S31i S32i Handbook B63947 En01 v2Cristobal PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document34 pagesChapter 1Abdelrahman KassmNo ratings yet
- Vibration Workshop OptDocument84 pagesVibration Workshop OptOlusegun Olugbade100% (2)
- Trans Fast Learn Adapts - Document ID - 1688788-1Document2 pagesTrans Fast Learn Adapts - Document ID - 1688788-1Kristiandi PradiptaNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Installation of Vibration Monitoring Equipment For Gas TurbinesDocument51 pagesEvaluating Installation of Vibration Monitoring Equipment For Gas TurbinesReshmi VinuNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Servo Motor: January 2018Document4 pagesAssignment On Servo Motor: January 2018Simagn BekeleNo ratings yet
- Biodex RTM 400Document44 pagesBiodex RTM 400Wilbur CurtisNo ratings yet
- Procedure On Setting Base Ignition Timing IMSDocument1 pageProcedure On Setting Base Ignition Timing IMSJestoniNo ratings yet
- Installation Operation Maintenance Instruction: Mechanical Diaphragm Metering PumpDocument24 pagesInstallation Operation Maintenance Instruction: Mechanical Diaphragm Metering PumpPablo Martin Ruiz VirruetaNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Dynamic Balancing MachineDocument9 pagesDesign and Development of Dynamic Balancing MachineSibasish SahuNo ratings yet
- IEICOS DTTM Torsion Testing Machine Operation ManualDocument6 pagesIEICOS DTTM Torsion Testing Machine Operation ManualsunilNo ratings yet
- Job Card Kel.4 - Tppu IIDocument3 pagesJob Card Kel.4 - Tppu IIYulina Maria ButarbutarTPPU IINo ratings yet
- Centrifuge Power PointDocument13 pagesCentrifuge Power PointNuril Liana YasinNo ratings yet
- Ontrac Major Technical FeaturesDocument3 pagesOntrac Major Technical FeaturesAnnie De WildeNo ratings yet
- Servo MotorDocument31 pagesServo Motoradiamiru25% (4)
- Time RiteDocument27 pagesTime RitenematoadNo ratings yet
- Servo MotorDocument8 pagesServo MotorzaidNo ratings yet
- Research Project GyrocompassDocument4 pagesResearch Project GyrocompassNaisy Gaoiran100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Lecture 2Document39 pagesThermodynamics Lecture 2MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lecture 6Document32 pagesThermodynamics Lecture 6MarkJude Morla100% (1)
- Assignment#3 - MEC 0326.1-2Document1 pageAssignment#3 - MEC 0326.1-2MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Activity#tachometer - MEC 0326.1-2Document4 pagesActivity#tachometer - MEC 0326.1-2MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Activity#2 - MEC 0326.1-2Document1 pageActivity#2 - MEC 0326.1-2MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Morla Mec-0313-2 HW2Document3 pagesMorla Mec-0313-2 HW2MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Morla Mec-0313-2 HW1Document3 pagesMorla Mec-0313-2 HW1MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Morla Mec-0313-2 HW3Document3 pagesMorla Mec-0313-2 HW3MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Lazaro Mec 0313 2 Hw5Document2 pagesLazaro Mec 0313 2 Hw5MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet
- Lazaro Cet-0216-11 HW1Document2 pagesLazaro Cet-0216-11 HW1MarkJude MorlaNo ratings yet