Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Up 2
Uploaded by
Hannah CenaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Up 2
Uploaded by
Hannah CenaCopyright:
Available Formats
III.
Assignment
1. What is the purpose of dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, or ddNTPs?
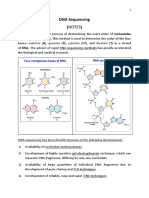
Dideoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, or ddNTPs are used in DNA sequencing. Its
purpose is to act as chain terminators to create a set of DNA fragments of different lengths.The
ddNTPs lack a 3' hydroxyl group, which is essential for the formation of a phosphodiester bond
between adjacent nucleotides during DNA synthesis. This missing hydroxyl group prevents
further DNA synthesis once a ddNTP is incorporated into the growing DNA chain.
The Sanger sequencing technique involves the addition of ddNTPs with dNTPs and a
DNA polymerase in a reaction mixture to generate a set of partially elongated DNA strands.
Incorporating a ddNTP into a growing DNA chain terminates the extension reaction and
produces a DNA fragment of a defined length. These fragments can be generated by using
different concentrations of dNTPs and ddNTPs, thereby creating a ladder of DNA fragments with
varying lengths that enable the underlying DNA sequence to be deduced. The ladder is
subjected to electrophoresis for evaluation, with the sequence being read by detecting the
fluorescent labels bonded to different ddNTPs.
2. What is the difference between the first steps of DNA sequencing to PCR in terms of
the number of primers being used?
In DNA sequencing, a single primer is typically used to initiate DNA synthesis. This
primer is complementary to a specific region of the DNA template, and DNA polymerase
extends from this primer to replicate the DNA strand. On the other hand, in PCR, two primers
are used. These primers are designed to specifically bind to the DNA sequences flanking the
target region to be amplified.
You might also like
- Interview Guide Questionnaire For ParticipantsDocument4 pagesInterview Guide Questionnaire For ParticipantsHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Tole S.B. Asst. Prof. K.T.Patil College of Pharmacy, OsmanabadDocument22 pagesMrs. Tole S.B. Asst. Prof. K.T.Patil College of Pharmacy, OsmanabadShobha Tole100% (2)
- Bio101 2 DnaSequencingDocument6 pagesBio101 2 DnaSequencingdmjuncalNo ratings yet
- Lec-9 DNA SequencingDocument31 pagesLec-9 DNA SequencingRabiul IslamNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing PosterDocument1 pageDNA Sequencing PosterTapasNo ratings yet
- Dna Sequencing MethodsDocument29 pagesDna Sequencing MethodsWilson Anandaraj92% (13)
- Presented By, Raihanathus Sahdhiyya A, I M.Sc. MicrobiologyDocument14 pagesPresented By, Raihanathus Sahdhiyya A, I M.Sc. MicrobiologyKhoid DiamNo ratings yet
- Sanger SequencingDocument14 pagesSanger Sequencingummu sahdhiyya3No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 2023 - DNA SequencingDocument67 pagesLecture 3 - 2023 - DNA SequencingChen ZhonghaoNo ratings yet
- Genomics 2Document15 pagesGenomics 21SI19BT002 AVINASH K ANo ratings yet
- Biotech Group 5Document6 pagesBiotech Group 5CarminexxxNo ratings yet
- Biochem Group ProjDocument21 pagesBiochem Group ProjYves Christian PineNo ratings yet
- Genome Sequencing: Sanger Sequencing: The Chain Termination MethodDocument5 pagesGenome Sequencing: Sanger Sequencing: The Chain Termination MethodansahNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument36 pagesBiotechnologyFarwa JawadNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsKelly ZhuNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids NOTESDocument8 pagesNucleic Acids NOTESelaineNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument21 pagesDNA SequencingAsfoor gake1No ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing SlidesDocument64 pagesDNA Sequencing SlideskittyngameNo ratings yet
- 7.1 DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument6 pages7.1 DNA Structure and ReplicationAbdelrahman HarrathNo ratings yet
- Chimeric DNA Byproducts in Strand Displacement AmpDocument16 pagesChimeric DNA Byproducts in Strand Displacement AmpGRAÇAS PERFUMARIANo ratings yet
- Sanger Sequencing and The Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument4 pagesSanger Sequencing and The Polymerase Chain ReactionNicolas JayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: DNA Manipulation: Site/sequence)Document4 pagesChapter 12: DNA Manipulation: Site/sequence)Kerry JiangNo ratings yet
- Section 1Document15 pagesSection 1MOSTAFA HAMDYNo ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument34 pagesDNA Sequencingmnouma1612No ratings yet
- Lecture 9-DNA SequencingDocument22 pagesLecture 9-DNA SequencingTehreem JahangiriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document19 pagesLecture 2MuhammadFakhriAimi100% (1)
- in 2-3 Sentences, Explain The Overall Goal of A PCR ReactionDocument6 pagesin 2-3 Sentences, Explain The Overall Goal of A PCR ReactionNurul Ilma SeptianiNo ratings yet
- LigationDocument5 pagesLigationHanumant SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : Principle of The PCRDocument5 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : Principle of The PCRSalvador MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : General MethodsDocument11 pagesThe Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) : General MethodsLetícia NascimentoNo ratings yet
- 2.7 NewDocument64 pages2.7 NewReeya WhabiNo ratings yet
- 3 Unit1Document9 pages3 Unit1Rajeev SinghNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic - Biotechnology - Forensic Biology and - Biological SystematicsDocument5 pagesDiagnostic - Biotechnology - Forensic Biology and - Biological SystematicsAngelle Loise EstanteNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids SummaryDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids SummaryIvan MiglioriniNo ratings yet
- Concise Notes Summary Genetic Engineering PCRDocument26 pagesConcise Notes Summary Genetic Engineering PCRVoice AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Akshat Goel Xii - C R.NoDocument17 pagesSubmitted By: Akshat Goel Xii - C R.NoAkshat GoelNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesDNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing & ApplicationDocument15 pagesDNA Sequencing & Applicationshamidr99No ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Document67 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Derick SemNo ratings yet
- What Is DNA SequencingDocument8 pagesWhat Is DNA SequencingjosephineNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencin2Document2 pagesDNA Sequencin2praneeth06No ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument8 pagesDNA SequencingAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Methods Molecular Cardiology:n: The Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument7 pagesMethods Molecular Cardiology:n: The Polymerase Chain ReactionmarcelsNo ratings yet
- Genetics Engineering PPT Grp#09Document52 pagesGenetics Engineering PPT Grp#09Alina RajputNo ratings yet
- Sanger Sequencing and Next-Generation Gene Sequencing: Basic Principles and Applications in PathologyDocument5 pagesSanger Sequencing and Next-Generation Gene Sequencing: Basic Principles and Applications in Pathologyprathap somuNo ratings yet
- 10 - Basic Recombinant DNA TechniquesDocument77 pages10 - Basic Recombinant DNA TechniquesNguyenHongThamNo ratings yet
- Assignment Biology Fadzil Bin Ismail - K14Document3 pagesAssignment Biology Fadzil Bin Ismail - K14FADZIL BIN ISMAIL BI22110364No ratings yet
- DNA SequencingDocument23 pagesDNA SequencingAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- Dna Analysis - 1.2Document21 pagesDna Analysis - 1.2Aparna PrahladNo ratings yet
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (Notes) : Group (-OH Group Attached To 3'-End of DNA), It Needs A Primer, To Which It CanDocument9 pagesPolymerase Chain Reaction (Notes) : Group (-OH Group Attached To 3'-End of DNA), It Needs A Primer, To Which It CanRakesh GedalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11 Nucleic AcidDocument31 pagesChapter-11 Nucleic AcidMD Limon IslamNo ratings yet
- Prinsip PCRDocument4 pagesPrinsip PCRZaid al GifariNo ratings yet
- Sequencing NotesDocument14 pagesSequencing NotesRASHINo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids - Topic 7 HLDocument28 pagesNucleic Acids - Topic 7 HLGracieNo ratings yet
- DNA Sequencing: Dibya Ranjan Dalei Adm no-9PBG/16 Dept. of PBG, Ca, BBSR, OuatDocument23 pagesDNA Sequencing: Dibya Ranjan Dalei Adm no-9PBG/16 Dept. of PBG, Ca, BBSR, OuatEm NomanNo ratings yet
- Explain How Nucleotides Joined Into Two Chains Form The Strands of A DNA MoleculeDocument2 pagesExplain How Nucleotides Joined Into Two Chains Form The Strands of A DNA MoleculeMelanie Joy ArellanoNo ratings yet
- PCRDocument3 pagesPCRarian.boostani2002No ratings yet
- Chia-Pet (Chromatin Interaction Analysis by Paired-End Tag Sequencing)Document13 pagesChia-Pet (Chromatin Interaction Analysis by Paired-End Tag Sequencing)Naresh Prasad SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Number TwoDocument6 pagesNumber TwoNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- DNA HybridizationDocument1 pageDNA HybridizationNauman_pk2No ratings yet
- DNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyFrom EverandDNA in Supramolecular Chemistry and NanotechnologyEugen StulzNo ratings yet
- Free-Body Diagram: The Object Remains at Rest. (Net Force O N)Document4 pagesFree-Body Diagram: The Object Remains at Rest. (Net Force O N)Hannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument2 pagesProjectile MotionHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Modules 1-5: FOR Dichotomo Uskey& OralDocument33 pagesModules 1-5: FOR Dichotomo Uskey& OralHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Module-2 CnidarianDocument10 pagesModule-2 CnidarianHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Cena - Comm Final ExerciseDocument3 pagesCena - Comm Final ExerciseHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Folk Dances in The Philippines Traditional Folk Dances in The PhilippinesDocument1 pageTraditional Folk Dances in The Philippines Traditional Folk Dances in The PhilippinesHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Δ XYZ: x=29m, y=15m, ∠Z=122°: Law Of Cosines WorksheetDocument3 pagesΔ XYZ: x=29m, y=15m, ∠Z=122°: Law Of Cosines WorksheetHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document7 pagesModule 2Hannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Prac Res FinalizationDocument51 pagesPrac Res FinalizationHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis ExperimentDocument5 pagesOsmosis ExperimentHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Multiplying Rational Algebraic Expression What I KnowDocument23 pagesLesson 1: Multiplying Rational Algebraic Expression What I KnowHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Complex Acid-Base Systems PDFDocument35 pagesComplex Acid-Base Systems PDFHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Age Structure Diagrams: A Way of Predicting Population ChangesDocument16 pagesAge Structure Diagrams: A Way of Predicting Population ChangesHannah CenaNo ratings yet