Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Population Growth and Development
Uploaded by
Naphtali KoomsonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Population Growth and Development
Uploaded by
Naphtali KoomsonCopyright:
Available Formats
POPULATION GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
POPULATION: Population refers to the total number of people living in a
specific geographical area at a specific time.
POPULATION CENSUS: A population census refers to a process of
systematically collecting, evaluating, analyzing, publishing and disseminating
information on all persons in a country at a specific time. A population census is
usually carried out every 10 years.
IMPORTANCE OF POPULATION CENSUS
➢ It provides data on the population.
➢ It is used for planning purposes.
➢ It helps to attract investors.
➢ It is used to plan on importation of goods and services.
➢ Used to calculate the standard of living
CHARACTERISTICS OF GHANA AGE DISTRIBUTION
The characteristics of Ghana’s age distribution based on the 2021 Population and Housing Census
include the following;
1. There is a high dependency ratio as a result of the needs of the population under 17 years have to be
provided by the much smaller older population
2. Ghana’s population age structure is transitioning from one dominated by children (0-14 years) to one
dominated by young people (15-35years).
3. There are more young people in urban than rural areas.
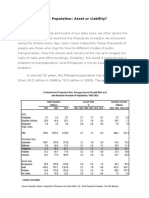
POPULATION STRUCTURE 2021 PHC
SEX TOTAL NUMBER PERCENT
15,182,459 49.3
MALE
15,610,149 50.7
FEMALE
TOTAL 30,792,608 100
POPULATION
POPULATION GROWTH
Population growth refers to the rate at which a country’s population increases within a stated time.
Ghana’s population grew by 25% between 2000 and 2021.
Rapid Population Growth simply refers to the high and fast rate at which the population within a
stated time in a particular area. Rapid population growth is greatly influenced by the high birth rate,
immigration and low death rate.
CAUSES OF HIGH (RAPID) POPULATION GROWTH
1. The high fertility rate among females in Ghana is a major cause of high population growth in Ghana.
2. The prestige in the tradition of large family size. The traditional cultures see many children as
prestigious, wealthy and secure.
3. The practice of marrying more than one wife is a factor. (polygamy)
4. Most couples in Ghana do not use any form of contraception to control birth.
This is due to both religious and traditional beliefs.
5. Early marriage among girls in Ghana is a contributory fact. Many girls are
forced into early marriages.
6. High incidence of teenage pregnancy.
7. Low death rate as a result of the improved health care system.
Urbanization is the process by which cities or towns grow which is mostly
influenced by rural-urban migration.
EFFECTS OF RAPID POPULATION GROWTH
POSITIVE EFFECTS
1. The high birth rate provides a large and cheap labour force in the future.
2. The high population provides a growing market for manufactured predicts/
NEGATIVE EFFECTS
1. Rapid population growth brings about a high depending ratio hence a burden on one's finances.
2. It also leads to poor maternal and child health. The child and the mother may have health problems.
3. Rapid population growth leads to a shortage of food in the future
4. It leads to the development of slums in towns and cities
5. Rapid population growth leads to increased pressure on social amenities and facilities such as
hospitals, schools, etc.
6. Crimewave increases, especially in the slummy areas.
HOW TO CONTROL RAPID POPULATION GROWTH
1. Girl-child education must be encouraged among all Ghanaians. Equal
opportunities must be given to both boys and girls.
2. The use of contraception must be encouraged among couples. The government
can reduce the cost to entice people to use them.
3. The government should control illegal immigration.
4. There should be public education regularly to assist people to see the need to
reduce their family sizes and the negative effects of a large family on the
family, individuals, community, and the nation.
5. Life in rural areas must be improved through the provision of social amenities
and job opportunities.
RURAL-URBAN MIGRATION
It is the movement of people from rural areas (villages) to urban areas (towns
and cities) for livelihood. Rural-urban drift is influenced by push and pull
factors. The push factors are conditions in the villages driving the people away
from the villages to the towns and cities. On the other hand, pull factors are
conditions prevailing in the cities that attract people to seek a livelihood in the
town and cities.
CAUSES OF RURAL-URBAN MIGRATION
1. Lack of social amenities that make life comfortable pushes/drive the people
into the cities.
2. There is a lack of job opportunities in the rural areas hence the youth move to
the cities to look for greener pastures
3. People leave rural areas to run away from cruel and outmoded cultural practices such as FGM.
4. People also migrate to be able to further their education to a higher level
5. Others also move to engage in trading because of bigger markets in towns and cities.
6. Low income in rural areas. Farmers in rural areas often do not get good prices for their farm produce.
EFFECTS OF RURAL-URBAN MIGRATION
1. Rural-urban migration leads to pressure on existing social amenities such as schools, and toilets in
the towns and cities
2. It brings about the disintegration of the family as a unit
3. Additionally, it leads to poor parental control in the villages since fathers leave
the villages to seek jobs in towns.
4. Unemployment increases in urban centres because of overpopulation in the
cities.
5. It also leads to the development of slums mostly in towns and cities.
SOCIAL PROBLEMS ASSOCIATED WITH RURAL-URBAN DRIFT
1. The high rate of unemployment
2. Broken homes
3. Streetism
4. Increase in a crime wave
5. High poverty
6. Environmental pollution
7. Prostitution
8. Pressure on social amenities
9. The high rate of substances or narcotics such as marijuana
10. Increase in teenage pregnancy (early motherhood)
11. Development of slums
HOW TO REDUCE RURAL-URBAN MIGRATION
1. Agriculture must be modernized through the introduction and use of
modern tools, equipment, and machines such as tractors, and combine
harvesters.
2. Social amenities such as schools, hospitals, and electricity among others
must be provided in rural areas.
3. Agro-based industries such as processing factories should be established in rural areas to provide
employment opportunities to the youth.
4. A cultural practice that infringes or violate people’s right and freedoms
must be established. E.g., Trokosi, cruel widowhood rites
5. Ready market and good pricing must be provided for farm produce.
6. High educational institutions such as secondary schools or polytechnics
should be situated close to rural areas or villages in the country.
You might also like
- Patient Health Questionnaire 9 - Depression (PHQ-9)Document1 pagePatient Health Questionnaire 9 - Depression (PHQ-9)MemMed Administrator100% (2)
- Module 4 - Population Growth Economic Development - Causes - Consequences and Controversies - PPTDocument56 pagesModule 4 - Population Growth Economic Development - Causes - Consequences and Controversies - PPTAlyssa Alejandro100% (4)
- IMMI Grant NotificationDocument3 pagesIMMI Grant NotificationJose Maria atorrasagasti oyarzabalNo ratings yet
- Lec13-Causes and Effects of Population Growth in IndiaDocument4 pagesLec13-Causes and Effects of Population Growth in IndiaarjunNo ratings yet
- Guevarra Vs Eala Case DigestDocument2 pagesGuevarra Vs Eala Case Digestemman2g.2baccay100% (3)
- Consequences of Population GrowthDocument2 pagesConsequences of Population GrowthJoel AndrewsNo ratings yet
- Branches of International LawDocument12 pagesBranches of International LawAdelina AbromavičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Population Growth Factor of Economic DevelopmentDocument28 pagesPopulation Growth Factor of Economic DevelopmentAryan NarayanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Population ExplosionDocument11 pagesProject Report On Population ExplosionFarnaz Bharwani60% (5)
- Supreme Court PIL Challenging Exception to Marital RapeDocument15 pagesSupreme Court PIL Challenging Exception to Marital RapeSahida Parveen100% (1)
- Soc Sci Final RequirementsDocument16 pagesSoc Sci Final RequirementsRachelle Aruyal EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Soc Sci Final RequirementsDocument16 pagesSoc Sci Final RequirementsTrisha Frias AruyalNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument16 pagesDemographyDARLYN TABEROSNo ratings yet
- Population Explosion and ControlDocument22 pagesPopulation Explosion and Controlpratiktripathy55No ratings yet
- The Country: Population Growth Rat - Is The Rate at Which The Number of Individuals in A Population Increases in ADocument4 pagesThe Country: Population Growth Rat - Is The Rate at Which The Number of Individuals in A Population Increases in ANeil RoseroNo ratings yet
- Community Health-1Document52 pagesCommunity Health-1MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Poverty & Income Distrb.Document39 pagesTopic 2 - Poverty & Income Distrb.Khairul AfiqNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Family Planning - PopulationDocument5 pagesAssignment - Family Planning - PopulationDARLYN AJAKNo ratings yet
- Population ConceptsDocument11 pagesPopulation ConceptsItisshatakshiNo ratings yet
- Rural-Urban Migration: Lecturer: Mr. T Moyo Department of Sociology Midlands State UniversityDocument20 pagesRural-Urban Migration: Lecturer: Mr. T Moyo Department of Sociology Midlands State UniversityREJOICE STEPHANIE DZVUKUMANJANo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument8 pagesREVIEWERSagad KeithNo ratings yet
- Biology Project Class 12Document14 pagesBiology Project Class 12bhaveshtupe06No ratings yet
- 2 Population GrowthDocument25 pages2 Population GrowthShane VeiraNo ratings yet
- Global Demography 11Document5 pagesGlobal Demography 11Regis, Julia Elyssa B.No ratings yet
- Problems Arising From Overpopulation and Their Impact on Reproductive Health-1Document24 pagesProblems Arising From Overpopulation and Their Impact on Reproductive Health-1Heba AhmedNo ratings yet
- World Population: Global Population and Mobility (Handouts)Document7 pagesWorld Population: Global Population and Mobility (Handouts)Carl Lanuzga100% (1)
- Geo - Ethiopia and The Horn - 7Document55 pagesGeo - Ethiopia and The Horn - 7yehualashet TadesseNo ratings yet
- Demographic TrendsDocument43 pagesDemographic TrendsPrince AlexNo ratings yet
- Population IssuesDocument17 pagesPopulation IssuesDennis RañonNo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 Issues On Population Demographic Trends and Implications of Population GrowthDocument14 pagesGROUP 1 Issues On Population Demographic Trends and Implications of Population GrowthJonnel GadinganNo ratings yet
- Pink and Blue Environment Future Modern PresentationDocument29 pagesPink and Blue Environment Future Modern PresentationcutieemayenggNo ratings yet
- Assigment 6573-WPS OfficeDocument23 pagesAssigment 6573-WPS OfficeTehmina HanifNo ratings yet
- 4c Population StudiesDocument50 pages4c Population StudiesSabbath the sign of GodNo ratings yet
- DInamika PendudukDocument53 pagesDInamika Pendudukyueza zuha yezekhielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PopulationDocument7 pagesChapter 4 PopulationAffu EnterpriseNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast The Population Dynamic of HICs and LICsDocument9 pagesCompare and Contrast The Population Dynamic of HICs and LICsMegharashi RimjhimNo ratings yet
- Nationality: Vietnamese Ethnic Groups: Vietnamese, Hmong, Tay, Muong, Nung, Hoa, Rade, JaraiDocument6 pagesNationality: Vietnamese Ethnic Groups: Vietnamese, Hmong, Tay, Muong, Nung, Hoa, Rade, JaraiHaila MacabangunNo ratings yet
- WINTER SEMESTER 2021-22 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES DIGITAL ASSIGNMENT FIVEDocument10 pagesWINTER SEMESTER 2021-22 ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES DIGITAL ASSIGNMENT FIVEDevarakonda SrinivasNo ratings yet
- Where World Population Has GrownDocument13 pagesWhere World Population Has GrownSyasya ZdsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentDocument50 pagesChapter 6 - Population Growth and Economic DevelopmentKenzel lawasNo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument14 pagesGlobal DemographyCel Caren MakidatoNo ratings yet
- Population Problem in IndiaDocument4 pagesPopulation Problem in IndiaNavotna ShuklaNo ratings yet
- AcknowledgementDocument39 pagesAcknowledgementhvnirpharakeNo ratings yet
- 4 PopulationDocument39 pages4 PopulationJoseph MusosoNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and DemographyDocument2 pagesEpidemiology and Demographysamuel mbuguaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Pop GrowthDocument5 pagesAnswers To Pop GrowthKatrina PaquizNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document6 pagesUnit 6KAYEMBANo ratings yet
- TCW IM Demoraphy and Migration Pages 63 69Document7 pagesTCW IM Demoraphy and Migration Pages 63 69rhika jimenezNo ratings yet
- Prospects and Problems of Urban DevelopmentDocument5 pagesProspects and Problems of Urban Developmentmannie edetNo ratings yet
- Population (Umar Khan) - 2Document2 pagesPopulation (Umar Khan) - 2Mnx zNo ratings yet
- Malaysia Country ReportDocument35 pagesMalaysia Country ReportMAGED MOHMMED AHMED QASEMNo ratings yet
- College of Teacher Education Second Semester, A.Y. 2020-2021 Population ProblemsDocument3 pagesCollege of Teacher Education Second Semester, A.Y. 2020-2021 Population ProblemsMIRANDA ALVINNo ratings yet
- Week 1-3 Lessons Family Planning Terminologies: Plans/Glossary - AspxDocument8 pagesWeek 1-3 Lessons Family Planning Terminologies: Plans/Glossary - AspxMa. Angelica GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Arrival of Young Talent The Send-Down Movement and Rural Education in ChinaDocument38 pagesArrival of Young Talent The Send-Down Movement and Rural Education in ChinaGeorge PaulNo ratings yet
- Global DemographyDocument17 pagesGlobal DemographyRose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Trends in UrbanisationDocument22 pagesTrends in UrbanisationSajna MujeebNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of A Youthful Population UgandaDocument3 pagesA Case Study of A Youthful Population Ugandafaryal khanNo ratings yet
- Managing Human PopulationDocument46 pagesManaging Human PopulationAlarm ManNo ratings yet
- Causes of Rapid Population Growth in the PhilippinesDocument3 pagesCauses of Rapid Population Growth in the PhilippinesJulius Gabriel CallejoNo ratings yet
- Urbanization Poverty Natural ResourcessDocument32 pagesUrbanization Poverty Natural ResourcessUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- What Is Urbanization?Document8 pagesWhat Is Urbanization?FaryalNo ratings yet
- IBINABO JACK CHAPTER ONE & TWODocument35 pagesIBINABO JACK CHAPTER ONE & TWOPrincewill Happiness jacobNo ratings yet
- Population Growth Factor of Economic DevelopmentDocument34 pagesPopulation Growth Factor of Economic DevelopmentDeshikNo ratings yet
- How Important Is Social Developmet For Economic GrowthDocument16 pagesHow Important Is Social Developmet For Economic GrowthEhsanul Haque ShiponNo ratings yet
- S C J P S: Telefax No.: (074) 442-3071 E-Mail Address: Ub@ubaguio - Edu Website: WWW - Ubaguio.eduDocument4 pagesS C J P S: Telefax No.: (074) 442-3071 E-Mail Address: Ub@ubaguio - Edu Website: WWW - Ubaguio.eduUniversal CollabNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.Document2 pagesExercise 1.Satyajeet PawarNo ratings yet
- Women and Children MCQDocument46 pagesWomen and Children MCQRahul Pillai100% (1)
- CourseraDocument2 pagesCourseraasmita mhamunkar100% (2)
- Internship Report NgoDocument14 pagesInternship Report Ngosamarth chauhanNo ratings yet
- LS 110-1Document53 pagesLS 110-1EljabriNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document5 pagesChap 1Ketchup MyouiNo ratings yet
- Woman Education in Pakistan: Challenges and ImportanceDocument2 pagesWoman Education in Pakistan: Challenges and ImportanceTalha TalalNo ratings yet
- Bullying Quiz From Teaching ToleranceDocument2 pagesBullying Quiz From Teaching Toleranceapi-268360678No ratings yet
- Personal Opinion/Comment: Re: Death Penalty As Capital Punishment and Its AbolitionDocument1 pagePersonal Opinion/Comment: Re: Death Penalty As Capital Punishment and Its AbolitionAguilar John FrancisNo ratings yet
- (U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictDocument5 pages(U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictFauquier NowNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Delinquency and the Indian Legal SystemDocument12 pagesJuvenile Delinquency and the Indian Legal SystemIshitaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam Ca1Document2 pagesPrelim Exam Ca1John Paul FernandezNo ratings yet
- Essay Hermanos RestrepoDocument1 pageEssay Hermanos RestrepoMauri GuañunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Business and Its Internal ConstituenciesDocument29 pagesUnit 4 Business and Its Internal ConstituenciesSurender Singh100% (2)
- School Directory: North West DelhiDocument33 pagesSchool Directory: North West DelhiAnkit TayalNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect EssayDocument9 pagesCause and Effect EssayWilda Fitriana ZuhriNo ratings yet
- California AB 1104 (2017) AnalysisDocument5 pagesCalifornia AB 1104 (2017) AnalysisThePoliticalHatNo ratings yet
- History of Us To Understand What Motivates Women To Be SuccessfulDocument2 pagesHistory of Us To Understand What Motivates Women To Be SuccessfulBryan Rivas ChavezNo ratings yet
- S.S. Jain Subodh Law College, JaipurDocument13 pagesS.S. Jain Subodh Law College, JaipurashupathakaNo ratings yet
- Factors Impacting Alcohol Engagement among Senior High StudentsDocument2 pagesFactors Impacting Alcohol Engagement among Senior High StudentsWilmer John AlbaricoNo ratings yet
- CorruptionDocument2 pagesCorruptionFloriane NatocNo ratings yet
- Cincinnati FY24 Leveraged Support - RecommendedDocument2 pagesCincinnati FY24 Leveraged Support - RecommendedWVXU NewsNo ratings yet
- Cyberbullying and Its Negative EffectsDocument1 pageCyberbullying and Its Negative EffectsAljean Nathalia OteroNo ratings yet
- National Security and Campus SafetyDocument5 pagesNational Security and Campus SafetyLourie BaslotNo ratings yet