Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2Q0WJLP3NO60K
Uploaded by
Syeda SadiaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2Q0WJLP3NO60K
Uploaded by
Syeda SadiaCopyright:
Available Formats
8 E
Quick Quiz
On your answer sheet, write in or circle the correct letter for each question.
8Ea C The mass of products is the same as
1 Combustion is a scientific word for: the mass of reactants.
A exploding B burning D The change in mass depends on what
the reactants and products are.
C evaporating D getting hotter
4 When 4.8 g of magnesium reacts with 3.2 g
2 A fuel is: of oxygen, how much magnesium oxide is
A a substance formed from living formed?
organisms that lived a long time ago A 1.6 g B 4.9 g
B a substance that explodes C 7.0 g D 8.0 g
C a substance that contains
hydrocarbons 8Ec
1 The three sides of a fire triangle are:
D a substance that transfers energy
usefully, usually by heating. A fire, water, heat B heat, water, fuel
3 When hydrogen reacts with oxygen, the C heat, oxygen, fuel D fire, oxygen, fuel
product is:
2 What does this hazard symbol warn of?
A water B oxide
C carbon dioxide D hydrogen
4 The products of combustion of a
hydrocarbon are:
A hydrogen + oxygen A The substance is explosive.
B carbon dioxide + water B The substance burns easily.
C carbon dioxide + hydrogen C The substance supplies oxygen to fires.
D carbon + water D The substance puts out fires.
3 What happens in an exothermic reaction?
8Eb
1 Oxidation is always: A Energy is released that increases the
temperature of the surroundings.
A a reaction in which a substance
combines with oxygen. B Energy is taken in from the
surroundings, reducing the
B a reaction in which a substance burns temperature.
in oxygen.
C The reacting substances always
C a reaction in which a substance burns explode.
in air.
D You need to heat a substance or
D an explosive reaction. substances to get a reaction to occur.
2 When zinc burns in oxygen it forms: 4 The best way to put out a small electrical
A water B zinc hydroxide fire is:
C zinc carbonate D zinc oxide A spray it with water to cool it down.
3 During a chemical reaction, reactants form B spray with foam to exclude air and cool
products. Compare the mass of reactants it down.
with the mass of products formed. C cover with a wet cloth to exclude air
A The mass of reactants is greater than and cool it down.
the mass of products. D spray with a powder extinguisher to
B The mass of products is greater than exclude air.
the mass of reactants.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2014. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 1 Page 1 of 2
8 E
Quick Quiz
8Ed 8Ee
1 Name two pollutants that may be formed 1 What does global warming mean?
when fossil fuels are burnt in a vehicle A The warming effect of the Sun on the
engine. Earth.
A carbon dioxide and sulfur B The natural warming effect caused by
B sulfur dioxide and water greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
C nitrogen oxides and sulfur C The additional warming effect caused
by increasing amounts of carbon
D nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide dioxide in the air.
2 Why are carbon monoxide and soot D The way the climate is changing as a
particles found in the exhaust gases of result of more carbon dioxide in the air.
vehicles?
2 Which of these factors caused the Earth’s
A These substances are in the fuel used surface temperature to vary thousands of
in the vehicle. years ago?
B The fuel reacts completely with oxygen A release of carbon dioxide by burning
in the air. fossil fuels
C The fuel does not react fully with B variation in the energy emitted by the
oxygen in the air. Sun
D These substances are formed from C variation in the number of vehicles on
impurities in the fuel. Earth
3 How do sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides D variation in ice ages
help cause acid rain?
3 Which description explains how carbon
A These acidic gases dissolve in water dioxide helps to cause the greenhouse
droplets in clouds. effect?
B These alkaline gases react with water A It blocks energy from the Sun from
droplets in clouds. reaching the Earth’s surface.
C They make rain happen more easily. B It absorbs energy emitted from the
Earth’s surface and re-emits it out into
D The gases react together forming space.
sulfonitroxidic acid in clouds.
C It absorbs energy emitted from the
4 How does a catalytic converter help to Earth’s surface so that it doesn’t get
reduce pollution from burning fossil fuels? any warmer.
A It filters out soot particles from the D It absorbs energy emitted from the
gases formed. Earth’s surface and re-emits it back to
B It changes pollutant gases into less the surface.
harmful gases. 4 Which of these methods would not help to
C It absorbs sulfur dioxide so that it isn’t reduce the amount of carbon dioxide
released into the air. released each year?
D It reacts with the pollutants to form a A Changing from fossil fuel power
solid, which has to be scraped out of stations to nuclear power stations.
the converter at regular intervals. B Fitting catalytic converters to all
vehicles.
C Setting government targets for carbon
dioxide production and fines for
industries that exceed their target.
D Travelling by bus or train rather than by
car.
© Pearson Education Ltd 2014. Copying permitted for
purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 2 Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Oxidation: Summary SheetsDocument2 pagesCombustion and Oxidation: Summary Sheetsanna russuNo ratings yet
- 8e Mark SchemeDocument6 pages8e Mark SchemeLamis AhmedNo ratings yet
- Burning Fuels: I CanDocument5 pagesBurning Fuels: I CanAddy The human100% (1)
- 8id-1 Floating & Sinking: Wood 0.7 Iron 8 Polystyrene 0.01 Ice 0.92 Aluminium 2.7Document2 pages8id-1 Floating & Sinking: Wood 0.7 Iron 8 Polystyrene 0.01 Ice 0.92 Aluminium 2.7Zak Remtulla100% (1)
- 8f Summary SheetsDocument3 pages8f Summary SheetsBeedu AvengersNo ratings yet
- KS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test MC AnswersDocument8 pagesKS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test MC AnswersPaul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 1 Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesQuick Quiz: 1 Page 1 of 2rania0% (2)
- Year 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesYear 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemerickyNo ratings yet
- Answer Answer 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20Document4 pagesAnswer Answer 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 5 15 6 16 7 17 8 18 9 19 10 20Liana Jalil100% (1)
- 8C Summary SheetDocument2 pages8C Summary Sheet박찬우100% (2)
- 9A QuizDocument31 pages9A Quizcaleb100% (1)
- 8 EmarkDocument1 page8 Emarkleelakdd108No ratings yet
- 8 CtestDocument4 pages8 Ctestleelakdd108No ratings yet
- 9F Summary SheetsDocument2 pages9F Summary SheetsZain AliNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Carbohydrate Protein Vitamins Minerals Fibre Constipation) WaterDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Carbohydrate Protein Vitamins Minerals Fibre Constipation) WaterHelenNo ratings yet
- 9b Quick QuizDocument3 pages9b Quick QuizNafiul Munsur Year 7No ratings yet
- Plant Growth ProcessesDocument11 pagesPlant Growth ProcessesAhmed HamedNo ratings yet
- 9DC Plants Photosynthesis and Plants For Food Multiple Choice TestDocument2 pages9DC Plants Photosynthesis and Plants For Food Multiple Choice Testapi-3698146100% (1)
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument4 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassSandyDavidNo ratings yet
- 8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsDocument3 pages8ca - Aerobic Respiration: Word SheetsOanaEmmNo ratings yet
- 8e Combustion Scheme of LearningDocument4 pages8e Combustion Scheme of LearningJude HassanNo ratings yet
- 8a End of Unit Test Higher CompressDocument6 pages8a End of Unit Test Higher CompressPatricia BouldstridgeNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForDocument3 pagesQuick Quiz: © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForBesty Maranatha100% (1)
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDerick Du Plessis100% (1)
- Quick Quiz: Copymaster File 9Document2 pagesQuick Quiz: Copymaster File 9ReenuNo ratings yet
- Force Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1Document2 pagesForce Field Questions: Name Ghadeer Hussain Al-Khayat Class Date 1ghadeer alkhayatNo ratings yet
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008shazia imamNo ratings yet
- 7G Particles Test 2004Document2 pages7G Particles Test 2004api-36981460% (1)
- 9 EquizDocument2 pages9 EquizEzra Loganathan Muniandi100% (1)
- Activity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Document86 pagesActivity Pack &student Book Answers - 8Eliana FalahatNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Science WorkbookDocument56 pagesYear 8 Science WorkbookA.K MonNo ratings yet
- Exploring Science 8 Sample PagesDocument8 pagesExploring Science 8 Sample PagesFozia Ghulam Mustafa Fozia Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet
- 8g Materials and Their PropertiesDocument30 pages8g Materials and Their PropertiesTheo Thomas100% (1)
- Summary Sheets: SolutionsDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Solutions박찬우No ratings yet
- End of Topic Test 8B SDocument7 pagesEnd of Topic Test 8B SAbdulla AlkaabiNo ratings yet
- ESWS - Teacher Guide 2014Document32 pagesESWS - Teacher Guide 2014Vikrant ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 9A Activity Pack Worksheets PDFDocument44 pages9A Activity Pack Worksheets PDFJESUS EDUARDO CARBONO NIEBLESNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionazharNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument4 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassSawani100% (1)
- Science 9dDocument4 pagesScience 9dno100100% (1)
- Fertilisation Seed DispDocument1 pageFertilisation Seed Dispazhar100% (1)
- 7a Summary SheetDocument2 pages7a Summary SheetNoor Ulain NabeelaNo ratings yet
- 8itest PDFDocument4 pages8itest PDFleelakdd10833% (3)
- Lesson 3 - 8eb-3 PhlogistonDocument1 pageLesson 3 - 8eb-3 PhlogistonameemaNo ratings yet
- Es Int 9e QQ AspDocument3 pagesEs Int 9e QQ AspRifaa WidasmaraNo ratings yet
- Elements and Compounds Revision QuestionsDocument3 pagesElements and Compounds Revision QuestionsEngy AlasutyNo ratings yet
- 8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersDocument1 page8F Quick Check Quiz AnswersClaire LNo ratings yet
- 8a End of Unit Test StandardDocument8 pages8a End of Unit Test StandardAaron Joseph100% (1)
- Mark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsDocument1 pageMark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsSumathi Ganasen100% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips - End of Unit Test Physicslocker Exploring Science8h End of Unit Test 8 H NameDocument4 pagesDokumen - Tips - End of Unit Test Physicslocker Exploring Science8h End of Unit Test 8 H Nameumi100% (1)
- 7E Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each Question. 7eaDocument3 pages7E Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each Question. 7eakhaleddaoudNo ratings yet
- Solutions Practice TestDocument4 pagesSolutions Practice TestHappy HemsNo ratings yet
- Year 8 science assessment on rocks and weatheringDocument6 pagesYear 8 science assessment on rocks and weatheringprincesstraillNo ratings yet
- KS3 Chem 7G Practice Questions about Solids, liquids and gasesDocument14 pagesKS3 Chem 7G Practice Questions about Solids, liquids and gasesRumeysaNo ratings yet
- 9c End of Unit TestDocument5 pages9c End of Unit TestEliza Budarz0% (1)
- 7J - CAT Test Yourself and Answers Unit TestDocument6 pages7J - CAT Test Yourself and Answers Unit TestDuma DumaiNo ratings yet
- 8e CombustionDocument36 pages8e CombustionMohamed HALAWA92% (12)
- IGCSE Energetics ExerciseDocument37 pagesIGCSE Energetics ExerciseWilliam TsuiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics (Multiple Choice) QPDocument14 pagesChemical Energetics (Multiple Choice) QPRagesh DuduNo ratings yet
- CamscannerDocument54 pagesCamscannerSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Brandenz1229 - Physics Final Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesBrandenz1229 - Physics Final Cheat SheetSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Past Paper Questions 2002-2010Document15 pagesCapacitor Past Paper Questions 2002-2010Anamika AhmedNo ratings yet
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument21 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetDinu PereraNo ratings yet
- 17DX53QL3ZQV5Document2 pages17DX53QL3ZQV5Syeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- MATHSDocument21 pagesMATHSSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- English Language ExamDocument10 pagesEnglish Language ExamSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document21 pagesQuestion 1Syeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- P1 - Chapter Review 7Document8 pagesP1 - Chapter Review 7Syeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesAnswer The Following QuestionsSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh StudiesDocument7 pagesBangladesh StudiesSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
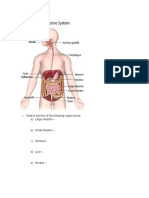
- What Is Function of The Following Organs Below A) Large IntestineDocument2 pagesWhat Is Function of The Following Organs Below A) Large IntestineSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- 11Document2 pages11Syeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Answer The Following Questions: 1. Name The 7 Life Processes? AnsDocument2 pagesAnswer The Following Questions: 1. Name The 7 Life Processes? AnsSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Jan 2022 Chem Unit 3 QPDocument20 pagesJan 2022 Chem Unit 3 QPSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Jan 2022 Chem Unit 2 QPDocument28 pagesJan 2022 Chem Unit 2 QPSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Jan 2022 M1 MSDocument15 pagesJan 2022 M1 MSSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Jan 2020 C12 QPDocument48 pagesJan 2020 C12 QPSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Jan 2022 Chem Unit 3 MsDocument26 pagesJan 2022 Chem Unit 3 MsSyeda SadiaNo ratings yet
- Resume: OBJECTIVE To Gain A Contract Position Within The Oil & Gas Industry As A PipelineDocument4 pagesResume: OBJECTIVE To Gain A Contract Position Within The Oil & Gas Industry As A PipelinegwarrackNo ratings yet
- SAEP-88 Appendix J: Materials Selection Table (MST) Template (1 of 2Document2 pagesSAEP-88 Appendix J: Materials Selection Table (MST) Template (1 of 2Afzal AsifNo ratings yet
- PeroxideTriangleDiagrams TAPPIDocument8 pagesPeroxideTriangleDiagrams TAPPIEugênia PheganNo ratings yet
- Solutions NCERTDocument16 pagesSolutions NCERTPrecisive OneNo ratings yet
- Down Memory Lane 2Document27 pagesDown Memory Lane 2abguy0% (1)
- PENEX PROCESS TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEWDocument34 pagesPENEX PROCESS TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEWSALAM ALINo ratings yet
- Gate QuestionsDocument30 pagesGate QuestionsVicky SharmaNo ratings yet
- Petrochemical Processes 1 Alain Chauvel Handbook PDFDocument420 pagesPetrochemical Processes 1 Alain Chauvel Handbook PDFZander_83% (12)
- Gas dehydration process diagramDocument1 pageGas dehydration process diagramIbnu Ari WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument26 pagesChemical ReactionsEvernim OmpacanNo ratings yet
- Section 7-Flame Arrestertesting and Certification: 7.1 GeneralDocument2 pagesSection 7-Flame Arrestertesting and Certification: 7.1 GeneralROUSHAN KESHRINo ratings yet
- Liquefied Natural Gas: Trust The Industry's Longest-Serving Turnkey ContractorDocument12 pagesLiquefied Natural Gas: Trust The Industry's Longest-Serving Turnkey Contractorvignesh100% (1)
- Moga Ji 862015 BJ As T 16778Document12 pagesMoga Ji 862015 BJ As T 16778Francisco OppsNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document14 pagesCH 01jessicasjsNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Chapter 2Document3 pages1st Year Chemistry Chapter 2Zeeshan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Distillation Without Hot Utilities Development of NovelDocument37 pagesDistillation Without Hot Utilities Development of NovelForcus onNo ratings yet
- Aakash Kaliraman Seminar Presentation-1Document18 pagesAakash Kaliraman Seminar Presentation-1Ajay PGI/15/CV/006No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties and Applications of Common RefrigerantsDocument57 pagesThermodynamic Properties and Applications of Common RefrigerantsAniket MandalNo ratings yet
- Energy WoodDocument2 pagesEnergy WoodMag FhearadhaighNo ratings yet
- Brochure Pillard LONOxFLAM R G2 Windbox VersionDocument2 pagesBrochure Pillard LONOxFLAM R G2 Windbox Versionsathish subramaniyanNo ratings yet
- Why Use Reticulated or Piped Gas Systems in Apartment ComplexesDocument5 pagesWhy Use Reticulated or Piped Gas Systems in Apartment ComplexesvictorNo ratings yet
- Heater Design CalculationDocument19 pagesHeater Design CalculationRafizi SalihuddinNo ratings yet
- S6 Test 5Document7 pagesS6 Test 5XD XDNo ratings yet
- F-01 Fire - Watch - Fire - WatchDocument61 pagesF-01 Fire - Watch - Fire - Watchravindra dolaiNo ratings yet
- Catalytic Reforming and Isomerization Tutorial SheetDocument2 pagesCatalytic Reforming and Isomerization Tutorial SheetRohit Sahu100% (1)
- NOCL Cuddalore Refinery Meeting Tamil Nadu Fuel DemandDocument3 pagesNOCL Cuddalore Refinery Meeting Tamil Nadu Fuel DemandBiswa1983No ratings yet
- Petroleum Development Geology 010 - IntroductionDocument22 pagesPetroleum Development Geology 010 - IntroductionGiovanni KarsopawiroNo ratings yet
- Removing Chloroprene from 1,2-Dichloroethane by Heat TreatmentDocument7 pagesRemoving Chloroprene from 1,2-Dichloroethane by Heat TreatmentsundharNo ratings yet
- Absorption Equilibria Gas-Liquid Contact StagesDocument16 pagesAbsorption Equilibria Gas-Liquid Contact StagesAmyNo ratings yet
- Sattler PDFDocument232 pagesSattler PDFRodrigo Mazzarella100% (1)