Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reported Speech 23 Hoje
Reported Speech 23 Hoje
Uploaded by
nelinho da marcia ernesto0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesApontamento ou ficha de leitura
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentApontamento ou ficha de leitura
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesReported Speech 23 Hoje
Reported Speech 23 Hoje
Uploaded by
nelinho da marcia ernestoApontamento ou ficha de leitura
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
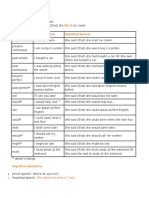
We use said when we are simply reporting someone’s words.
We use said when it is clear or not
important who the person was speaking to:
I saw Helen yesterday. She said that wasn’t going out with Liam any more. (= we know that she
said this to ‘me’).
ACTUAL WORDS REPORTED
SPEECH
present simple past simple
‘I need a drink.’ He said (that) he needed a drink.
Present continuous past continuous
‘‘I’m feeling ill’’ She said that (that) she was
feeling ill.
past simple /present perfect past perfect (had + past participle)
‘I enjoyed the party.’ He said (that) he had enjoyed the
party.
will would
‘I’ll phone later.’ She said (that) she would phone later.
can could
‘I can’t come.’ She said (that) she couldn’t come.
1. "Don't play with matches," his mother said.
1. His mother told him not to play with matches.
2. "I've forgotten to bring my lunch with me," he said.
2. He said that he'd forgotten to bring his lunch with him.
3. "Will you be home soon?" she asked her husband.
3. She asked her husband if he would be home soon.
4. "Go to bed!" father said to the children.
4. Father told the children to go to bed.
Will
Will is used to show desire, preference, choice or consent:
I will accept your offer. Will you please be quiet?
To show the future:
It will be a great party. I will probably go out tonight.
To express capability:
The ship will take three hundred guests. This bottle will hold two liters of wine.
To express determination or insistence:
I will pass my driving test. I will do as you say.
Should (advice)
. ‘Should’ and ‘ought to’ are less strong and used to give advice or propose a possible course of action.
Examples: You should go and speak to your boss.
We should drive careful the car.
Should (suggestions)
Should is often used to give an opinion, to make a suggestion, express a preference or an idea.
I should walk to work.
You should stay at home if you are feeling tired.
He should be more open to ideas.
Should – to ask for an opinion.
Should we tell him about our idea?
What should we do now?
Present
First is the present tense, which indicates actions or conditions occurring now. Present tense is often
used to state general information as well as thoughts and opinions.
Ex. Water freezes at 32 degrees Fahrenheit.
Ex. They are angry about the decision.
Past
Next is the past tense, which indicates actions or conditions that have occurred already and do not
extend into the present.
Ex. Madalena felt better after her test.
Ex. Nelson invaded Poland on September 1, 1939.
Future
The last one of the simple tenses is the future that indicates actions that have yet to begin. To form the
future tense, you will use will or shall plus the base or the present principal part of the verb.
Ex. I will graduate the year after next.
Ex. The exhibition will come to Houston in October.
Exercise
Identify the tense of the underlined verb in each sentence.
1. She will attend a conference in Washington. 6. A squirrel drops its nuts when it gets frightened.
2. Barbara and Mary refused to sign the petition. 7. A good story will have action and drama.
3. The dancers rehearse every day. 8. We spotted a bird with red wings and tail.
4. Storytelling existed before written history. 9. The animals’ unpleasant shrieks warn other
5. Blue jays have many unusual habits. animals of danger.
10. We will practice our math skills this year.
Never give up
EDUCATION IS KIES OF THE DEVELOPMENT
You might also like
- Reported Speech TheoryDocument4 pagesReported Speech TheoryAna PCidNo ratings yet
- Pipe Steel Pipe CatalogueDocument16 pagesPipe Steel Pipe Cataloguezishanf_1No ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Chapter 2 Practice TestDocument20 pagesAP Chemistry Chapter 2 Practice TestbonnniiiNo ratings yet
- NSSCO - Mathematics Paper 2 6131-2 - First Proof 08.04.2022Document20 pagesNSSCO - Mathematics Paper 2 6131-2 - First Proof 08.04.2022Auwanga Enkali100% (1)
- Unit 5 Lesson 2: Reported Speech: Statements/ SentencesDocument7 pagesUnit 5 Lesson 2: Reported Speech: Statements/ SentencesJesus PonceNo ratings yet
- Hakin9 Magazine 020EneroFebrero 2009Document84 pagesHakin9 Magazine 020EneroFebrero 2009aman_arora100% (4)
- Nhóm 10 - Reported SpeechDocument98 pagesNhóm 10 - Reported SpeechTrọng Nhân TrươngNo ratings yet
- Water Supply and Sewerage DesignDocument48 pagesWater Supply and Sewerage DesignJeremy Molayem100% (5)
- Presentation BFPDocument18 pagesPresentation BFPEuben PatronNo ratings yet
- Future in The PastDocument10 pagesFuture in The PastEmi SaliuNo ratings yet
- Unofficial TranscriptDocument3 pagesUnofficial Transcriptapi-516350014No ratings yet
- Simple Past, Past Perfect, Past ContinuousDocument23 pagesSimple Past, Past Perfect, Past ContinuousAli Mohamad RezzaNo ratings yet
- Arnett-Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis IIDocument17 pagesArnett-Facial Keys To Orthodontic Diagnosis IIFiorella Loli Pinto100% (1)
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAndreea PaulaNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech Grammar and Reporting VerbsDocument3 pagesReported Speech Grammar and Reporting VerbsMaría HerederoNo ratings yet
- 171654bf3612bd00da7 86164239indirect SpeechDocument2 pages171654bf3612bd00da7 86164239indirect Speechea_ae_1No ratings yet
- Reported Speech Charts, Said-Told, Reported ImperativesDocument18 pagesReported Speech Charts, Said-Told, Reported ImperativesFrancisco J HernándezNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument22 pagesReported SpeechevilNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Document23 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Katerina KornevaNo ratings yet
- EnglishGU RefDocument12 pagesEnglishGU RefJuan joseNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech ErrolDocument13 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech ErrolLizette SocratesNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument5 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechbingernchoNo ratings yet
- Sessions 12 and 13Document16 pagesSessions 12 and 13Francisco Milton SiueiaNo ratings yet
- Modul 14Document8 pagesModul 14ChaerunnisaNo ratings yet
- 1858 - 72495 - Reported SpeechDocument18 pages1858 - 72495 - Reported SpeechFikri HaikalNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech - ExplanationDocument2 pagesReported Speech - ExplanationFilip JeremicNo ratings yet
- EstiloindirectoDocument19 pagesEstiloindirectoTatiana García SolanoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech (Indirect Speech)Document22 pagesReported Speech (Indirect Speech)Dinkar AsthanaNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect: Have BeenDocument10 pagesPresent Perfect: Have BeenBusuiocMariaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument8 pagesReported SpeechHienNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument11 pagesEnglishrastamanl9No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument8 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechAik CantikNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech: Here's How It WorksDocument8 pagesReported Speech: Here's How It WorksMarina PeshovskaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesReported SpeechKilo MihaiNo ratings yet
- English V Guide 6 Weeks, 10, 11, 12Document11 pagesEnglish V Guide 6 Weeks, 10, 11, 12gomezjulianaNo ratings yet
- Grammar BreefingDocument6 pagesGrammar BreefingIrene AllegraNo ratings yet
- 1 Reported Speech PDFDocument17 pages1 Reported Speech PDFdinu69inNo ratings yet
- But, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in TheDocument9 pagesBut, If The Reporting Verb Is in The Past Tense, Then Usually We Change The Tenses in TheRenatoNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument34 pagesReported SpeechIvana RadulovicNo ratings yet
- Direct, Indirect, Reported SpeechDocument24 pagesDirect, Indirect, Reported SpeechKHALIDOO6No ratings yet
- DestroyedDocument14 pagesDestroyedДильназ КожахметоваNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechYefer romañaNo ratings yet
- Sympathy ExpressionDocument7 pagesSympathy ExpressionNindhita Dyah SNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument20 pagesReported SpeechYamir Apaza RadoNo ratings yet
- Passive With Reporting VerbsDocument7 pagesPassive With Reporting VerbsmarcosgarciacarreraNo ratings yet
- Tense Direct Speech Reported SpeechDocument9 pagesTense Direct Speech Reported SpeechGeo KemoNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech For FCEDocument4 pagesReported Speech For FCEMarinaNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument6 pagesReported SpeechLaura GPNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechAndrei HanNo ratings yet
- Grammar Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesGrammar Reported SpeechMaría Esperanza Velázquez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect SpeechHasib QureshiNo ratings yet
- Indirect SpeechDocument3 pagesIndirect SpeechMariana AndoneNo ratings yet
- Continuous Tense ExplanationDocument5 pagesContinuous Tense Explanationcna.english.courseNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech in EnglishDocument2 pagesIndirect Speech in EnglishOlga KukhtinaNo ratings yet
- Me - Past Continuous and Past SimpleDocument5 pagesMe - Past Continuous and Past SimplekjakaNo ratings yet
- Indirect Speech, Also Known As Reported Speech or Indirect Discourse, Is A Means ofDocument6 pagesIndirect Speech, Also Known As Reported Speech or Indirect Discourse, Is A Means ofMikael RanteNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument3 pagesReported SpeechMacarena Berdugo MenaNo ratings yet
- ENGL 1301 Editing Examples With CorrectionsDocument5 pagesENGL 1301 Editing Examples With Correctionsabiodun ogunwomojuNo ratings yet
- Reported Speech All Kinds Grammar Drills Grammar Guides 109024Document97 pagesReported Speech All Kinds Grammar Drills Grammar Guides 109024Ioana IuraNo ratings yet
- 2 Grammar and ExercisesDocument29 pages2 Grammar and ExercisesesraerkocakNo ratings yet
- Pre UnitDocument21 pagesPre UnitMICAELA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Direct and IndirectDocument6 pagesDirect and IndirectAyesha AfzalNo ratings yet
- REPORTED SPEECH - Los Verbos de Información en Inglés-.OKDocument16 pagesREPORTED SPEECH - Los Verbos de Información en Inglés-.OKPilar Martinez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous TenseDocument5 pagesPast Continuous TensePathricia KasumNo ratings yet
- Re-Thinking Sustainable DeveloDocument27 pagesRe-Thinking Sustainable DeveloFarhan AlvianaNo ratings yet
- Homeowners Guide To Stormwater BMP Maintenance: What You Need To Know To Take Care of Your PropertyDocument24 pagesHomeowners Guide To Stormwater BMP Maintenance: What You Need To Know To Take Care of Your PropertyClaire KidwellNo ratings yet
- Broadbent Sugar Centrifugal BrochureDocument0 pagesBroadbent Sugar Centrifugal BrochureHossam Mohamed KandilNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI TIẾNG ANH 8 NĂM 2020-2021Document1 pageĐỀ THI TIẾNG ANH 8 NĂM 2020-2021Mạnh HùngNo ratings yet
- Can Giraffes Dance?: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCan Giraffes Dance?: Learning ObjectivesPaula RamirezNo ratings yet
- Hydropower NoteDocument446 pagesHydropower NoteUmesh RegmiNo ratings yet
- TVL Ict 110 Academic AwardsDocument12 pagesTVL Ict 110 Academic AwardsnerenNo ratings yet
- Nochetto Adaptive FEMDocument138 pagesNochetto Adaptive FEMonebyzerooutlookNo ratings yet
- Course BUILDERS QUANTITIES AND ESTIMATING IDocument3 pagesCourse BUILDERS QUANTITIES AND ESTIMATING Ihafiz hilmiNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: Digital Brush DC Servo DriverDocument12 pagesUser's Manual: Digital Brush DC Servo DriverDương Nguyễn ĐắcNo ratings yet
- FM CH 2Document18 pagesFM CH 2sosina eseyewNo ratings yet
- Fema306 PDFDocument270 pagesFema306 PDFSuhas MangaloreNo ratings yet
- Data Warehousing & Mining: Unit - IvDocument32 pagesData Warehousing & Mining: Unit - IvSunil Kr PandeyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Enhanced K To 12 Curriculum GuideDocument29 pagesMathematics: Enhanced K To 12 Curriculum GuideAgnes G. Arguilles TaladtadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics ModuleDocument120 pagesIntroduction To Statistics ModuleAnesu MajaruNo ratings yet
- MGMT E-1000 Syllabus Fall 2015 Sept 29Document6 pagesMGMT E-1000 Syllabus Fall 2015 Sept 29LourdesNo ratings yet
- CV Asif Amin 2018Document6 pagesCV Asif Amin 2018Ahmed RazaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris XDocument15 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris XJodoh SoobinNo ratings yet
- 6 Categories of Information SystemDocument10 pages6 Categories of Information SystemCharmaine MagtangobNo ratings yet
- Venus Hotelware Horeca247Document99 pagesVenus Hotelware Horeca247vmtechnologyvkmNo ratings yet
- Microteaching Lesson CoreDocument4 pagesMicroteaching Lesson Coreapi-316731131No ratings yet
- Heymann2019 - A Personal History of Sensory ScienceDocument22 pagesHeymann2019 - A Personal History of Sensory Sciencemireya perla esquivel sanabriaNo ratings yet