Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Epistaxis
Epistaxis
Uploaded by
عهود الشهريOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Epistaxis
Epistaxis
Uploaded by
عهود الشهريCopyright:
Available Formats
Epistaxis
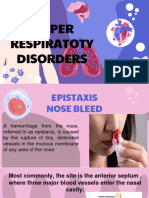
.Epistaxis (a nosebleed) occurs most frequently in children before adolescence
Bleeding of the nasal mucosa occurs most often from the anterior portion of the
septum. Most cases are benign, but in children with bleeding disorders or other
.hematologic concerns, epistaxis should be further investigated and treated
The child with recurrent epistaxis or epistaxis that is difficult to control should be
.further evaluated for underlying bleeding or platelet concerns
Nursing Assessment
Explore the child's history of initiating factors such as local inflammation, mucosal
.drying, or local trauma (usually nose picking). Inspect the nasal cavity for blood
Nursing Management
The presence of blood often frightens children and their parents. The nurse and
parents should remain calm. The child should sit up and lean forward (lying down
may allow aspiration of the blood). Apply continuous pressure to the anterior portion
of the nose by pinching it closed. Encourage the child to breathe through the mouth
during this treatment portion. Ice or a cold cloth applied to the bridge of the nose may
also be helpful. The bleeding usually stops within 10 to 15 minutes. Apply petroleum
jelly or water-soluble gel to the nasal mucosa with a cotton-tipped applicator to
.moisten the mucosa and prevent a recurrence
You might also like
- Epistaxis (Nose Bleed), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandEpistaxis (Nose Bleed), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Nasal PolypsDocument43 pagesNasal PolypsManasa anonymous100% (2)
- Pediatrics Nclex Review PointersDocument14 pagesPediatrics Nclex Review PointersCathryn Dominique Tan100% (1)
- Nursing Care of A Child With Respiratory DisorderDocument85 pagesNursing Care of A Child With Respiratory DisorderChris CharzNo ratings yet
- Congenital Anomalies in Newborn (Critical)Document46 pagesCongenital Anomalies in Newborn (Critical)Shereen Mohamed Soliman HammoudaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Epistaxis in ChildrenDocument39 pagesPresentation On Epistaxis in ChildrenAdditi SatyalNo ratings yet
- EPISTAXIS LectureDocument30 pagesEPISTAXIS LectureDhienWhieNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Infection in ChildrenDocument70 pagesAcute Respiratory Infection in Childrenmayadwintas100% (1)
- 6 EpistaxisDocument19 pages6 EpistaxissuciNo ratings yet
- Choanal Atresia, Epistaxis & AspirationDocument12 pagesChoanal Atresia, Epistaxis & Aspirationsubinj_350% (2)
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase StudyAnnisa Trihandayani100% (2)
- Untitled 1Document17 pagesUntitled 1Jennifer Catahimican Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- EpistaxisDocument9 pagesEpistaxisAswathy RCNo ratings yet
- What To Do:: Different Kinds of NosebleedsDocument3 pagesWhat To Do:: Different Kinds of NosebleedsJr MateoNo ratings yet
- Nur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseDocument9 pagesNur 218 Peds Exam 1 Study Guide Role of The Pediatric NurseNurseme13No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemHani El-asferNo ratings yet
- Pubdoc 4 14280 150Document6 pagesPubdoc 4 14280 150jadarcNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia TrachomatisDocument2 pagesCleft Lip: Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (May Cause Ulceration and Destruction) and Chlamydia TrachomatisteabagmanNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Therapeutic ManagementDocument1 pageEpistaxis: Therapeutic ManagementJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Ms. Shital BhutkarDocument37 pagesEpistaxis: Ms. Shital BhutkarSuhas Ingale0% (1)
- Nosebleed PDFDocument4 pagesNosebleed PDFgsundar8173No ratings yet
- EpistaxisDocument27 pagesEpistaxisghofran001997No ratings yet
- Nose BleedingDocument1 pageNose BleedingAjayDeewanNo ratings yet
- EPISTAXIS-bleeding From The Nose (Most Common) Etiology (Cause)Document34 pagesEPISTAXIS-bleeding From The Nose (Most Common) Etiology (Cause)Julliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Eyes Ear Throat (New)Document19 pagesEyes Ear Throat (New)coosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Birth InjuriesDocument13 pagesBirth InjuriesMARIA JAVED BSN-FA20-022No ratings yet
- EpistaxixDocument18 pagesEpistaxixvirendra singhNo ratings yet
- EpistaksisDocument3 pagesEpistaksisyudishannaNo ratings yet
- Managing NosebleedsDocument7 pagesManaging NosebleedsHasbiallah YusufNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis Scott BrownDocument3 pagesEpistaxis Scott BrownDaisy Haryono0% (1)
- Nasal Injury and Foreign BodiesDocument18 pagesNasal Injury and Foreign BodiesmasyfuqNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis: Pavlo Razumnyi, MD, International SOS PhysicianDocument25 pagesEpistaxis: Pavlo Razumnyi, MD, International SOS PhysicianPasha UmnyiNo ratings yet
- Physical and Developmental Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument10 pagesPhysical and Developmental Disorders of The Gastrointestinal SystemJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- Basog - ReportTonsillitis and EpistaxisDocument4 pagesBasog - ReportTonsillitis and EpistaxisclaribelleNo ratings yet
- Opening Statement: Have You Ever Had Blood Coming Out of Your Nose? or Seen Some People Have It? I Think Almost All of Us DoDocument2 pagesOpening Statement: Have You Ever Had Blood Coming Out of Your Nose? or Seen Some People Have It? I Think Almost All of Us DoChantika ChacaNo ratings yet
- To Be ConDocument53 pagesTo Be ConLiza AingelicaNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis Managemen T: Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Medical Faculty Udayana UniversityDocument26 pagesEpistaxis Managemen T: Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Medical Faculty Udayana UniversityTadeus Max PinatihNo ratings yet
- Epistaxis Nasal Fracture Laryngeal Obstruction Gomez PedongDocument9 pagesEpistaxis Nasal Fracture Laryngeal Obstruction Gomez PedongPowell TabogocNo ratings yet
- EpistaxisDocument39 pagesEpistaxisAbubakar JallohNo ratings yet
- Nosebleed and PoisoningDocument28 pagesNosebleed and PoisoningRenz100% (2)
- Nosebleed Handout PDFDocument1 pageNosebleed Handout PDFnoel_buenconsejoNo ratings yet
- Specific Injuries, Burn, Shock and Sudden IllnessDocument82 pagesSpecific Injuries, Burn, Shock and Sudden Illnessmotidesalegn25No ratings yet
- Jamstel Ivan Christofer Bayoneto I - AristotleDocument4 pagesJamstel Ivan Christofer Bayoneto I - AristotleJamstel BayonetoNo ratings yet
- Deviated Nose..... Ear Nose and ThroatDocument83 pagesDeviated Nose..... Ear Nose and ThroatBinita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- NCM 113 Upper Respiratory DiseaseDocument68 pagesNCM 113 Upper Respiratory DiseaseJerah Aceron SatorreNo ratings yet
- Causes, Workup and Management of Epistaxis: AssignmentDocument4 pagesCauses, Workup and Management of Epistaxis: AssignmentFarhan AfzalNo ratings yet
- Assaignment Title: Causes, Work Up & Management of Epistaxis Discipline: MBBSDocument11 pagesAssaignment Title: Causes, Work Up & Management of Epistaxis Discipline: MBBSJahanzaib SaeedNo ratings yet
- Nasal Obstruction: Nitha K 2nd Year MSC NursingDocument65 pagesNasal Obstruction: Nitha K 2nd Year MSC NursingNITHA KNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus PresentationDocument49 pagesHydrocephalus PresentationSourina BeraNo ratings yet
- The Nosebhs InggrisDocument6 pagesThe Nosebhs InggrisFajra FajiraNo ratings yet
- 1 PB PDFDocument5 pages1 PB PDFpopoyingNo ratings yet
- Frisco Family Ent Epistaxis Nosebleed Precautions 365Document2 pagesFrisco Family Ent Epistaxis Nosebleed Precautions 365Jay ImperioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaDocument7 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: Acute Otitis MediaAbigael Patricia GutierrezNo ratings yet
- CursDocument11 pagesCursIrina ŞerpeanuNo ratings yet
- Journal Sianosis BayiDocument5 pagesJournal Sianosis BayiMadelaineNo ratings yet
- 01 EpistaxisDocument23 pages01 Epistaxiswissam salimNo ratings yet
- Expose On EntDocument20 pagesExpose On EntDUCHELNo ratings yet
- Diseases in Children Word FileDocument12 pagesDiseases in Children Word FileLezrae Chescka Javier IlumbaNo ratings yet
- Growth and Adjustment Problems of NewbornDocument17 pagesGrowth and Adjustment Problems of NewbornchristeneratoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nasopharynx & AdenoidsDocument3 pagesAnatomy of Nasopharynx & AdenoidsAmy KochNo ratings yet