100% found this document useful (2 votes)
651 views39 pagesInterlock and Logic
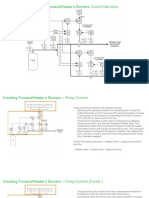
The document discusses guidelines for defining which safety-critical actions should be performed by an interlock safety (IS) system versus a distributed control system (DCS) due to the higher cost of IS hardware. It states that trips in the IS are generally based on 2-out-of-3 voting and the IS must protect personnel, critical equipment, and processes that could result in significant production losses if tripped. The DCS handles less critical actions like starting/stopping motors and switching operating modes. It then provides examples of specific interlock logics for various plant equipment.
Uploaded by
Harish KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
651 views39 pagesInterlock and Logic
The document discusses guidelines for defining which safety-critical actions should be performed by an interlock safety (IS) system versus a distributed control system (DCS) due to the higher cost of IS hardware. It states that trips in the IS are generally based on 2-out-of-3 voting and the IS must protect personnel, critical equipment, and processes that could result in significant production losses if tripped. The DCS handles less critical actions like starting/stopping motors and switching operating modes. It then provides examples of specific interlock logics for various plant equipment.
Uploaded by
Harish KumarCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Interlock & Logic Diagram Introduction
- Pump Diagrams
- Trip Procedures
- Steam Condensate Pump
- Lube Oil System
- Polishing Pump
- Compressor Systems
- Interlock Diagrams