100% found this document useful (1 vote)
424 views4 pagesSol Worksheet Chapter 12
The document is a physics worksheet about electric charges. It contains two sections:
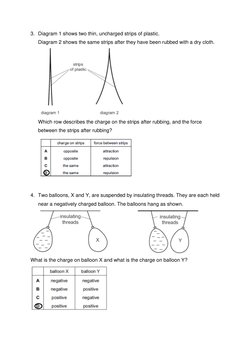
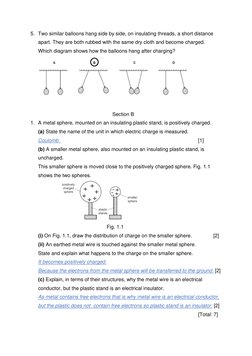
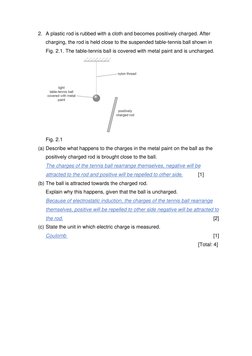
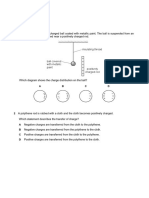
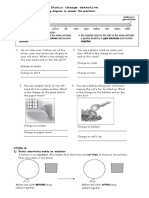
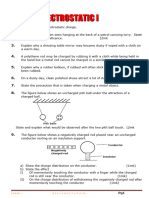
Section A contains multiple choice questions about charging objects with static electricity. Section B contains short answer questions about charging conducting and insulating objects.
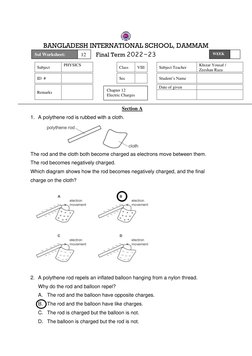
The key points are: 1) A polythene rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed with cloth due to electron transfer. 2) Oppositely charged objects repel, while like charges attract. 3) Charging conducting objects by induction can lead to opposite surface charges forming.
Uploaded by
M. ShafiqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
424 views4 pagesSol Worksheet Chapter 12
The document is a physics worksheet about electric charges. It contains two sections:
Section A contains multiple choice questions about charging objects with static electricity. Section B contains short answer questions about charging conducting and insulating objects.
The key points are: 1) A polythene rod becomes negatively charged when rubbed with cloth due to electron transfer. 2) Oppositely charged objects repel, while like charges attract. 3) Charging conducting objects by induction can lead to opposite surface charges forming.
Uploaded by
M. ShafiqCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Physics Final Term Worksheet
- Advanced Electrostatics Questions