0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views4 pagesJoint Probability Examples and Solutions
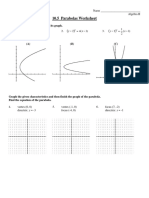
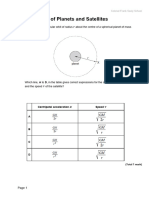
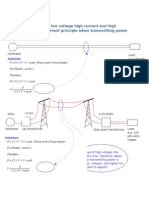
The document provides 10 examples of calculating joint probabilities from data presented in tables or scenarios. The examples calculate probabilities such as:
- The joint probability of passed students in mathematics and economics being 38%
- The joint probability of students scoring above 80% on both SAT tests being 30%
- The joint probability of rolling a 5 twice in a row on a fair six-sided die being 2.8%
- The joint probability of drawing a black 10 card from a standard deck of playing cards being 3.9%
Uploaded by
Its BalochCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views4 pagesJoint Probability Examples and Solutions
The document provides 10 examples of calculating joint probabilities from data presented in tables or scenarios. The examples calculate probabilities such as:
- The joint probability of passed students in mathematics and economics being 38%
- The joint probability of students scoring above 80% on both SAT tests being 30%
- The joint probability of rolling a 5 twice in a row on a fair six-sided die being 2.8%
- The joint probability of drawing a black 10 card from a standard deck of playing cards being 3.9%
Uploaded by
Its BalochCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd